Meridian List
Information provided by: MINDinst in association with ChatGPT and Yin Yang House.
Yin Yang House offers a lot of information about Traditional Chinese Medicine and the different practices there of. All images in this search engine that depicts acupoints are borrowed from them. They do a really good job in conveying information about TCM. The text content and the search engne itself is generated by ChatGPT and MINdinst.
About Meridian List
Date of launch: 17.01.2024
This list contains all the acupoints in the following list of meridians:
- lung meridian
- large intestine meridian
- stomach meridian
- spleen meridian
- heart meridian
- small intestine meridian
- liver meridian
- gallbladder meridian
- kidney meridian
- urinary bladder meridian
- conception vessel meridian
- governing vessel meridian
- pericardium meridian
- tripple burner meridian
You may use this search engine as an encyclopedia of acupoints.
All the information given here is derived from ChatGPT, the images are mainly gathered from Yin Yang House and elsewhere on the internet including my own image designs and the search engine is administered and designed by admin.
Alarm points (Xi-points)
These acupoints have quite special roles. If you stimulate one of them you activate every acupoint for that specific meridian.
The Alarm points are as follows:
- Shui Quan | Water Spring | Kidney 5 | KI-5
- Jin Men | Metal Gate | Urinary Bladder 63 | UB-63
- Yang Lao | Nursing the Aged | Small Intestine 6 | SI-6
- Yin Xi | Yin Cleft | Heart 6 | HT-6
- Wai Qiu | Outer Hill | Gallbladder 36 | GB-36
- Hui Zong | Convergence and Gathering | Triple Heater 7 | TH-7
- Xi Men | Xi Cleft Gate | Pericardium 4 | PC-4
- Zhong Du | Central Metropolis | Liver 6 | LR-6
- Di Ji | Earth's Crux | Spleen 8 | SP-8
- Liang Qiu | Beam Hill | Stomach 34 | ST-34
- Wen Liu | Warm Dwelling | Large Intestine 7 | Li-7
- Lie Que | Broken Sequence | Lung 7 | LU-7
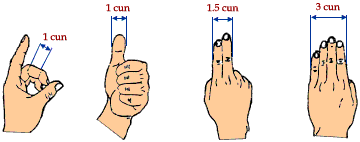
What is Cun?
Cun is the measurement system used to locate the different acupoints.
It is usually the patients cun that is usual in measuring, which is one thumb-width.
See more ways of measuring cun in the image below:
How to stimulate Aupoints and how long?
Acupoints are believed to be power buttons on our body that can be stimulated to guide the flow of qi. There are several techniques that can be used to stimulate acupoints, and practitioners are free to use their imagination to find what works best for them.
- Acupuncture with thin needles: Insert the needle directly into the acupoint to activate it.
- Moxibustion: Use a moxa stick or moxa wool to apply heat to the acupoint. Hover a glowing end of a stick over the acupoint while fluctuating closeness in tact with your breathing until the area is red. Circling clockwise tonifies the energy, while circling counter-clockwise disperses the energy. Use direct moxa with moxa wool by placing a small pebble of moxa wool on the intended acupoint, light it and let it burn.
- Finger tips: Stick out your thumb and close the other fingers to allow the energy radiated from them to combine to tilt out the thumb tip. You can also use a wand (like paulo sant, copper, or similar) or a crystal pointer.
- Massage: Massage the acupoint to activate it.
- Breathing: Direct your attention and focus on the spot to breathe more deeply into it. Every cell actually breathes, and if you watch your skin through a microscope, you can observe this.
- Intention and visualization: Use your imagination to create a needle or other tool and program it to vaporize after a set time. Place it in the acupoint(s) of your desire and meditate until the set timing of the thought-needle has passed.
- Qi Gong: Use movements to activate meridians and acupoints. For example, hover your arm up and down your other arm in tact with relaxed breathing to stimulate parts of the lung, large intestine, heart, small intestine, triple burner, and pericardial meridians.
- Yoga: Use asanas to stimulate the meridians flowing where you stretch.
- Sound vibrations: Use a tuning fork or headset to apply sound vibrations to the acupoint area. Visualize the vibrations activating the acupoint.
- Color vibrations: Use the vibrations of certain colors to stimulate the acupoints.
It's also important to note that the best acupuncturist is the one who uses only one needle per session in one acupoint. It's not necessary to activate many points at once but only a few and treat only a few illnesses per session.
Working with Qi and energy medicine in general may be challenging, especially if you are expecting a result. Qi likes to do what it does without restraint though it allows us to adjust the flow of it. This meaning that if you treat for example a headache, just stimulate the point for the set duration, breathe deep, relax and then continue your day as if nothing has happened. If you are treating something that goes deeper, like psoriasis, just set a plan of treatment and follow through, once again with out expectation. Just be happy and thankfull for the fact that you are alive.
The suggested duration of treatment is as follows:
This is the treatment plan taught at the Nei Jing School.
The treatment itself should last between 5-15 minutes if your are using acupressure. 10-20 minutes with a needle. Untill the point is red with Moxibustion.
Once you have found a treatment, you or a person that treats you do the treatment 3 days straight at first and then once every week untill you do not feel or notice the illness anymore. One could try to do the math for how long one should commit to treatment like this: 1 month pr. year the illness has existed in your body. Thsi meaning that if you have had a bad back for 15 years then you should try treatment for 15 months.
Otherwise, if you follow your own plan that is quite allright. The above is only to provide a sort of frame of reference in regards to treatment, but you do not have to follow those guidelines. Remember that Qi likes to do what it does without restraint.
Related Content:
Content comingVisit Our Store!
You are welcome to visit ZenCart, your online destination for a diverse range of alternative medicine tools and products. Our carefully curated selection is designed to support your holistic journey towards optimal health and well-being.
At ZenCart, we are committed to providing the highest quality products, from acupuncture needles to moxa equiptment, yoga gear and EMF protection.
Embrace the power of alternative medicine and explore the world of natural healing with ZenCart. Discover a healthier, happier you as you embark on a journey towards balance and harmony.
Lung Meridian
This meridian is commonly under the Element Metal.
Zhong Fu | Central Treasury | Lung 1 | LU-1
This is an important acupuncture point located on the chest. It is located on the front of the chest, in the first intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the anterior midline, at the level of the first rib. LU-1 is a primary point for treating respiratory conditions, as it is located near the lungs and helps to regulate the flow of Qi (life energy) in the body. It is used to treat lung-related conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, cough, and chest congestion. This point is also used to treat emotional and mental conditions such as anxiety, sadness, and grief, as it is believed to help regulate the flow of Qi in the chest and relieve tension. In addition, LU-1 is also used to treat conditions related to the upper back, shoulder, and neck, such as stiffness and pain. It is believed that stimulating this point can help to relieve tension and improve circulation in the area. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-1 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.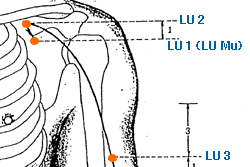
Yun Men | Cloud Gate | Lung 2 | LU-2
This is an important acupuncture point located on the chest. It is located on the front of the chest, in the second intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the anterior midline, at the level of the upper border of the clavicle. LU-2 is a primary point for treating respiratory conditions, as it is located near the lungs and helps to regulate the flow of Qi (life energy) in the body. It is used to treat lung-related conditions such as cough, chest congestion, asthma, and bronchitis. Stimulating this point is believed to help regulate the lung's function, relieve congestion, and promote the circulation of Qi and blood. In addition, LU-2 is also used to treat conditions related to the neck and upper back, such as neck pain, stiffness, and tension. It is believed that stimulating this point can help to relieve tension and improve circulation in the area. LU-2 is also used to regulate emotions and improve mental health. It is believed that stimulating this point can help to calm the mind, relieve anxiety and stress, and promote emotional balance. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-2 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Tian Fu | Celestial Storehouse | Lung 3 | LU-3
This is an important acupuncture point located on the arm. It is located on the medial aspect of the upper arm, on the radial side of the biceps brachii muscle, 3 cun below the axillary fold. LU-3 is a primary point for treating respiratory conditions, as it is believed to help regulate the function of the lungs and relieve lung-related symptoms. It is used to treat cough, asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions. Stimulating this point is thought to help open up the chest and promote the circulation of Qi and blood, thus alleviating respiratory congestion and improving breathing. In addition to respiratory conditions, LU-3 is also used to treat other conditions such as chest pain, shoulder and arm pain, and stiffness. It is believed to help promote the circulation of Qi and blood in the upper body, thus relieving tension and pain. LU-3 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, depression, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-3 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.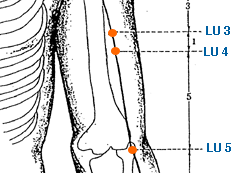
Xia Bai | Guarding White | Lung 4 | LU-4
This is an important acupuncture point located on the arm. It is located When both arms are hanging freely, this point is precisely on both sides of the Lung. 4 cun distal to axillary fold, lateral border of bicep on the upper arm, on the lateral border of muscle biceps brachii, 4 cun inferior to the anterior axillary fold. LU-4 is a primary point for treating respiratory conditions, as it is believed to help regulate the function of the lungs and relieve lung-related symptoms. It is used to treat cough, asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions. Stimulating this point is thought to help open up the chest and promote the circulation of Qi and blood, thus alleviating respiratory congestion and improving breathing. In addition to respiratory conditions, LU-4 is also used to treat other conditions such as arm and elbow pain, wrist pain, and stiffness. It is believed to help promote the circulation of Qi and blood in the upper body, thus relieving tension and pain. LU-4 is also used to stimulate the immune system and strengthen the body's defenses. It is used to treat conditions such as colds, flu, and other respiratory infections, as well as to boost overall immune function. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-4 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Chi Ze | Cubit Marsh | Lung 5 | LU-5
This is an important acupuncture point located on the arm. It is located The point is in the depression of the elbow fossa at the ulnar aspect. In the cubital crease, radial side of biceps brachii tendon. At the elbow, in the cubital crease, in the depression lateral to biceps brachii tendon. LU-5 is a primary point for treating respiratory conditions, as it is believed to help regulate the function of the lungs and relieve lung-related symptoms. It is used to treat cough, asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions. Stimulating this point is thought to help open up the chest and promote the circulation of Qi and blood, thus alleviating respiratory congestion and improving breathing. In addition to respiratory conditions, LU-5 is also used to treat other conditions such as elbow and arm pain, wrist pain, and stiffness. It is believed to help promote the circulation of Qi and blood in the upper body, thus relieving tension and pain. LU-5 is also used to regulate the Wei Qi, or the protective energy that circulates around the body's surface and acts as a barrier against external pathogens. It is used to treat conditions such as the common cold, flu, and other respiratory infections, as well as to boost overall immune function. LU-5 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, depression, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-5 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Kong Zui | Collection Hole | Lung 6 | LU-6
This is an important acupuncture point located on the arm. It is located on the radial side of the forearm, approximately 7 cun above the wrist crease. LU-6 is a primary point for treating respiratory conditions, as it is believed to help regulate the function of the lungs and relieve lung-related symptoms. It is used to treat cough, asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions. Stimulating this point is thought to help open up the chest and promote the circulation of Qi and blood, thus alleviating respiratory congestion and improving breathing. In addition to respiratory conditions, LU-6 is also used to treat other conditions such as wrist pain, elbow pain, and stiffness. It is believed to help promote the circulation of Qi and blood in the upper body, thus relieving tension and pain. LU-6 is also used to regulate the Wei Qi, or the protective energy that circulates around the body's surface and acts as a barrier against external pathogens. It is used to treat conditions such as the common cold, flu, and other respiratory infections, as well as to boost overall immune function. LU-6 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, depression, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In addition, LU-6 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the lung meridian and is used to help support and strengthen the lungs. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-6 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.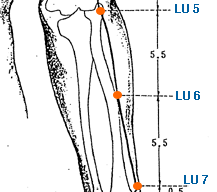
Lie Que | Broken Sequence | Lung 7 | LU-7
This is an important acupuncture point located on the arm. It is located on the radial aspect of the forearm, about 1.5 cun above the wrist crease. LU-7 is a primary point for treating respiratory conditions, as it is believed to help regulate the function of the lungs and relieve lung-related symptoms. It is used to treat cough, asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions. Stimulating this point is thought to help open up the chest and promote the circulation of Qi and blood, thus alleviating respiratory congestion and improving breathing. In addition to respiratory conditions, LU-7 is also used to treat other conditions such as neck and shoulder pain, headache, and fever. It is believed to help promote the circulation of Qi and blood in the upper body, thus relieving tension and pain. LU-7 is also used to regulate the Wei Qi, or the protective energy that circulates around the body's surface and acts as a barrier against external pathogens. It is used to treat conditions such as the common cold, flu, and other respiratory infections, as well as to boost overall immune function. LU-7 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, depression, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In addition, LU-7 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the lung meridian and is used to help support and strengthen the lungs. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-7 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Lung Meridian.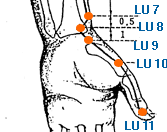
Jing Qu | Channel Ditch | Lung 8 | LU-8
This is an important acupuncture point located on the arm. It is located on the radial aspect of the wrist, in the depression between the styloid process of the radius and the radial artery. LU-8 is a primary point for treating respiratory conditions, as it is believed to help regulate the function of the lungs and relieve lung-related symptoms. It is used to treat cough, asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions. Stimulating this point is thought to help open up the chest and promote the circulation of Qi and blood, thus alleviating respiratory congestion and improving breathing. In addition to respiratory conditions, LU-8 is also used to treat other conditions such as wrist pain, elbow pain, and stiffness. It is believed to help promote the circulation of Qi and blood in the upper body, thus relieving tension and pain. LU-8 is also used to regulate the Wei Qi, or the protective energy that circulates around the body's surface and acts as a barrier against external pathogens. It is used to treat conditions such as the common cold, flu, and other respiratory infections, as well as to boost overall immune function. LU-8 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, depression, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In addition, LU-8 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the lung meridian and is used to help support and strengthen the lungs. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-8 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Tai Yuan | Great Abyss | Lung 9 | LU-9
This is an important acupuncture point located on the arm. It is located on the radial aspect of the wrist, in the depression between the styloid process of the radius and the ulna. LU-9 is a primary point for treating respiratory conditions, as it is believed to help regulate the function of the lungs and relieve lung-related symptoms. It is used to treat cough, asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions. Stimulating this point is thought to help open up the chest and promote the circulation of Qi and blood, thus alleviating respiratory congestion and improving breathing. In addition to respiratory conditions, LU-9 is also used to treat other conditions such as wrist pain, elbow pain, and stiffness. It is believed to help promote the circulation of Qi and blood in the upper body, thus relieving tension and pain. LU-9 is also used to regulate the Wei Qi, or the protective energy that circulates around the body's surface and acts as a barrier against external pathogens. It is used to treat conditions such as the common cold, flu, and other respiratory infections, as well as to boost overall immune function. LU-9 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, depression, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In addition, LU-9 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the lung meridian and is used to help support and strengthen the lungs. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-9 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Yu Ji | Fish Borde | Lung 10 | LU-10
This is an important acupuncture point located on the arm. It is located on the palmar surface of the hand, in the depression between the second and third metacarpal bones, just proximal to the metacarpophalangeal joint. LU-10 is a primary point for treating respiratory conditions, as it is believed to help regulate the function of the lungs and relieve lung-related symptoms. It is used to treat cough, asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions. Stimulating this point is thought to help open up the chest and promote the circulation of Qi and blood, thus alleviating respiratory congestion and improving breathing. In addition to respiratory conditions, LU-10 is also used to treat other conditions such as wrist pain, elbow pain, and stiffness. It is believed to help promote the circulation of Qi and blood in the upper body, thus relieving tension and pain. LU-10 is also used to regulate the Wei Qi, or the protective energy that circulates around the body's surface and acts as a barrier against external pathogens. It is used to treat conditions such as the common cold, flu, and other respiratory infections, as well as to boost overall immune function. LU-10 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, depression, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In addition, LU-10 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the lung meridian and is used to help support and strengthen the lungs. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-10 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Shao Shang | Lesser Shang | Lung 11 | LU-11
This is an important acupuncture point located on the thumb. It is located at the tip of the thumb, just below the nail. LU-11 is primarily used to treat sore throat and other throat-related conditions. It is believed to have a cooling and soothing effect on the throat, and can be used to alleviate inflammation and swelling of the throat. This point is often used in combination with other acupuncture points to treat respiratory conditions such as colds, coughs, and bronchitis. In addition to its effects on the throat and respiratory system, LU-11 is also used to treat other conditions such as toothache, facial pain, and earache. It is believed to have a local analgesic effect, and can help to relieve pain and discomfort in the affected area. LU-11 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, nervousness, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In traditional Chinese medicine, the lung meridian is associated with the metal element, which is believed to be responsible for regulating the immune system and promoting overall health and vitality. LU-11 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the lung meridian, and can be used to help support and strengthen the lungs. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LU-11 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.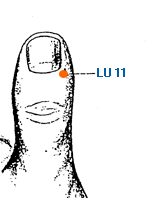
Large Intestine Meridian
This meridian is commonly under the Element Metal.
Shang Yang | Metal Yang | Large Intestine 1 | Li-1
This is an important acupuncture point located on the index finger. It is located at the radial side of the index finger, close to the corner of the nail, on the junction of the red and white skin. LI-1 is primarily used to treat conditions of the large intestine, such as constipation, diarrhea, and other digestive disorders. It is believed to have a regulating effect on the large intestine, and can be used to promote bowel movement and alleviate symptoms of abdominal pain and bloating. In addition to its effects on the large intestine, LI-1 is also used to treat other conditions such as toothache, facial pain, and headache. It is believed to have a local analgesic effect, and can help to relieve pain and discomfort in the affected area. LI-1 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, nervousness, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In traditional Chinese medicine, the large intestine meridian is associated with the metal element, which is believed to be responsible for regulating the immune system and promoting overall health and vitality. LI-1 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the large intestine meridian, and can be used to help support and strengthen the digestive system. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-1 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.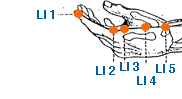
Er Jian | Second Space | Large Intestine 2 | Li-2
This is an important acupuncture point located on the index finger. It is located on the radial side of the index finger, in the depression distal to the metacarpophalangeal joint. LI-2 is primarily used to treat conditions of the large intestine, such as constipation, diarrhea, and other digestive disorders. It is believed to have a regulating effect on the large intestine, and can be used to promote bowel movement and alleviate symptoms of abdominal pain and bloating. In addition to its effects on the large intestine, LI-2 is also used to treat other conditions such as toothache, facial pain, and headache. It is believed to have a local analgesic effect, and can help to relieve pain and discomfort in the affected area. LI-2 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, nervousness, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In traditional Chinese medicine, the large intestine meridian is associated with the metal element, which is believed to be responsible for regulating the immune system and promoting overall health and vitality. LI-2 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the large intestine meridian, and can be used to help support and strengthen the digestive system. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-2 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
San Jian | Third Space | Large Intestine 3 | Li-3
This is an important acupuncture point located on the index finger. It is located on the radial side of the index finger, proximal to the head of the 2nd metacarpal bone. LI-2 is primarily used to treat conditions of the large intestine, such as constipation, diarrhea, and other digestive disorders. It is believed to have a regulating effect on the large intestine, and can be used to promote bowel movement and alleviate symptoms of abdominal pain and bloating. In addition to its effects on the large intestine, LI-2 is also used to treat other conditions such as toothache, facial pain, and headache. It is believed to have a local analgesic effect, and can help to relieve pain and discomfort in the affected area. LI-2 is also believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and emotions. It is used to treat anxiety, nervousness, and other emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In traditional Chinese medicine, the large intestine meridian is associated with the metal element, which is believed to be responsible for regulating the immune system and promoting overall health and vitality. LI-2 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the large intestine meridian, and can be used to help support and strengthen the digestive system. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-2 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
He Gu | Tigers Gape | Large Intestine 4 | Li-4
This is one of the most well-known and commonly used acupuncture points. It is located on the dorsum of the hand, in the web between the thumb and the index finger. LI-4 is used to treat a wide variety of conditions, including pain, inflammation, and digestive disorders. It is believed to have a regulating effect on the large intestine, and can be used to promote bowel movement and alleviate symptoms of abdominal pain and bloating. In addition to its effects on the large intestine, LI-4 is also used to treat other conditions such as headache, toothache, and sinus congestion. It is believed to have a local analgesic effect, and can help to relieve pain and discomfort in the affected area. LI-4 is also believed to have a balancing and regulating effect on the body's energy, or qi. It is used to treat conditions such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-4 is also believed to have a tonifying effect on the body's defensive qi, which is responsible for regulating the immune system and promoting overall health and vitality. It is used to treat conditions such as colds, flu, and other respiratory infections. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-4 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Yang Xi | Yang Ravine | Large Intestine 5 | Li-5
This is an important acupuncture point located on the forearm. It is located on the radial side of the wrist, in the depression between the tendons of the extensor pollicis longus and brevis muscles. LI-5 is primarily used to treat conditions of the large intestine, such as constipation, diarrhea, and other digestive disorders. It is believed to have a regulating effect on the large intestine, and can be used to promote bowel movement and alleviate symptoms of abdominal pain and bloating. In addition to its effects on the large intestine, LI-5 is also used to treat other conditions such as wrist pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and tennis elbow. It is believed to have a local analgesic effect, and can help to relieve pain and discomfort in the affected area. LI-5 is also believed to have a regulating effect on the body's energy, or qi. It is used to treat conditions such as headache, dizziness, and emotional imbalances, and is believed to help promote relaxation and a sense of calm. In traditional Chinese medicine, the large intestine meridian is associated with the metal element, which is believed to be responsible for regulating the immune system and promoting overall health and vitality. LI-5 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the large intestine meridian, and can be used to help support and strengthen the digestive system. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-5 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Pian Li | Veering Passageway | Large Intestine 6 | Li-6
This is an acupuncture point located on the forearm. It is found on the radial aspect of the forearm, about 3 cm above the wrist crease, between the tendons of the brachioradialis and the abductor pollicis longus muscles. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-6 is considered to be an important point for the treatment of various disorders of the large intestine, which is the primary organ associated with the Large Intestine meridian. It is believed to be an effective point for addressing issues such as constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and other digestive problems. In addition to its effects on the digestive system, LI-6 is also believed to have a regulatory effect on the body's energy or Qi. It is used in the treatment of conditions such as headaches, migraines, and shoulder pain, as well as for promoting general relaxation and stress reduction. LI-6 is also considered to be a point that can be used to support the immune system. It is believed to have an effect on the Wei Qi, which is a type of protective energy that circulates throughout the body and helps to defend against external pathogens. By strengthening the Wei Qi, LI-6 can help to boost the immune system and promote overall health. Overall, LI-6 is an important acupuncture point for addressing a wide range of health conditions related to the digestive system, immune system, and musculoskeletal system. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-6 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition, and will provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.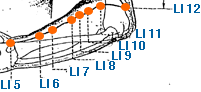
Wen Liu | Warm Dwelling | Large Intestine 7 | Li-7
This is an acupuncture point located on the wrist. It is found on the radial aspect of the wrist, between the tendons of the brachioradialis and the abductor pollicis longus muscles, approximately 2 cm proximal to the wrist crease. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-7 is considered to be an important point for the treatment of various disorders related to the large intestine, which is the primary organ associated with the Large Intestine meridian. It is believed to be an effective point for addressing issues such as constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. In addition to its effects on the digestive system, LI-7 is also believed to have a regulatory effect on the body's energy or Qi. It is used in the treatment of conditions such as headaches, neck and shoulder pain, and pain in the arm or hand. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and is used for the treatment of anxiety, depression, and insomnia. LI-7 is also considered to be a point that can be used to support the immune system. It is believed to have an effect on the Wei Qi, which is a type of protective energy that circulates throughout the body and helps to defend against external pathogens. By strengthening the Wei Qi, LI-7 can help to boost the immune system and promote overall health. Overall, LI-7 is an important acupuncture point for addressing a wide range of health conditions related to the digestive system, musculoskeletal system, and mental and emotional health. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-7 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition and provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Large Intestine Meridian.
Xia Lian | Lower Angle | Large Intestine 8 | Li-8
This is an acupuncture point located on the wrist. It is found 4 cun distal to LI-11, on the radial side of the posterior antebrachial region, 4 cun distal cubital crease, on the line connecting LI 5 at the wrist and LI 11 at the lateral cubital crease. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-8 is believed to have a regulatory effect on the Large Intestine meridian, which is the primary organ associated with this point. It is commonly used to address a wide range of conditions related to the digestive system, including constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. LI-8 is also considered to have a tonifying effect on the Qi of the body, and is often used to treat conditions such as fatigue, weakness, and general debility. Additionally, it is believed to have a beneficial effect on the skin and can be used to treat skin conditions such as eczema, acne, and other forms of dermatitis. In acupuncture theory, LI-8 is also considered to be a point that can help to clear heat from the body, which makes it useful for treating conditions such as fever, sore throat, and other inflammatory conditions. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can be used to treat anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia. Overall, LI-8 is an important acupuncture point for treating a wide range of conditions related to the digestive system, skin, immune system, and mental health. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-8 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition and provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Shang Lian | Upper Angle | Large Intestine 9 | Li-9
This is an acupuncture point located on the forearm. It is found On the radial side of the posterior antebrachial region, 3 cun distal cubital crease, on the line connecting LI 5 at the wrist and LI 11 at the lateral cubital crease. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-9 is believed to have a regulatory effect on the Large Intestine meridian, which is the primary organ associated with this point. It is commonly used to address a wide range of conditions related to the digestive system, including constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. LI-9 is also considered to have a tonifying effect on the Qi of the body, and is often used to treat conditions such as fatigue, weakness, and general debility. Additionally, it is believed to have a beneficial effect on the skin and can be used to treat skin conditions such as eczema, acne, and other forms of dermatitis. In acupuncture theory, LI-9 is also considered to be a point that can help to clear heat from the body, which makes it useful for treating conditions such as fever, sore throat, and other inflammatory conditions. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can be used to treat anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia. Overall, LI-9 is an important acupuncture point for treating a wide range of conditions related to the digestive system, skin, immune system, and mental health. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-9 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition and provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Shou San Li | Arm Three Miles | Large Intestine 10 | Li-10
This is an acupuncture point located on the forearm. It is found on the lateral side of the arm, approximately 2 cm distal to the elbow crease, and lies between the brachioradialis and the extensor carpi radialis longus muscles. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-10 is believed to have a regulatory effect on the Large Intestine meridian, which is the primary organ associated with this point. It is commonly used to address a wide range of conditions related to the digestive system, including constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. LI-10 is also believed to have a tonifying effect on the Qi of the body, and is often used to treat conditions such as fatigue, weakness, and general debility. Additionally, it is considered to have a beneficial effect on the tendons and muscles of the body, and can be used to treat conditions such as muscle spasms, stiffness, and pain. In acupuncture theory, LI-10 is also considered to be a point that can help to clear heat from the body, which makes it useful for treating conditions such as fever, sore throat, and other inflammatory conditions. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can be used to treat anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia. Overall, LI-10 is an important acupuncture point for treating a wide range of conditions related to the digestive system, muscle and joint health, immune system, and mental health. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-10 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition and provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Qu Chi | Pool at the Bend | Large Intestine 11 | Li-11
This is an acupuncture point located on the elbow. It is found on the outer end of the elbow crease, in the depression on the lateral side of the elbow where the arm bends when the elbow is flexed. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-11 is believed to have a regulatory effect on the Large Intestine meridian, which is the primary organ associated with this point. It is commonly used to address a wide range of conditions related to the digestive system, including constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. LI-11 is also believed to have a beneficial effect on the immune system, and is often used to treat conditions such as colds, flu, and other respiratory infections. It is also believed to have a tonifying effect on the Qi of the body, and can be used to treat conditions such as fatigue, weakness, and general debility. In acupuncture theory, LI-11 is also considered to be a point that can help to clear heat from the body, which makes it useful for treating conditions such as fever, sore throat, and other inflammatory conditions. It is also believed to have a beneficial effect on the skin, and can be used to treat conditions such as acne, eczema, and other skin irritations. Overall, LI-11 is an important acupuncture point for treating a wide range of conditions related to the digestive system, immune system, and skin health. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-11 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition and provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Zhou Liao | Elbow Bone Hole | Large Intestine 12 | Li-12
This is an acupuncture point located On the lateral side of the cubital crease, 1 cun superior to LI 11, at the junction of the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus with the epicondyle. Locate LI 12 with the elbow flexed. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-12 is believed to have a regulatory effect on the Large Intestine meridian, which is the primary organ associated with this point. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as pain and stiffness in the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow, as well as numbness and weakness in the arm. LI-12 is also believed to have a beneficial effect on the energy channels in the body, and can be used to treat conditions such as fatigue, weakness, and general debility. It is believed to promote the circulation of Qi and blood in the upper body, and can help to relieve tension and stress. In acupuncture theory, LI-12 is also considered to be a point that can help to clear heat from the body, which makes it useful for treating conditions such as fever, sore throat, and other inflammatory conditions. It is also believed to have a beneficial effect on the skin, and can be used to treat conditions such as acne, eczema, and other skin irritations. Overall, LI-12 is an important acupuncture point for treating a wide range of conditions related to the upper body, including pain and stiffness, numbness and weakness, and tension and stress. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-12 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition and provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.
Shou Wuli | Arm Five Miles | Large Intestine 13 | Li-13
This is an acupuncture point located 3 cun proximal to LI-11 on the lateral brachial region, 3 cun superior to LI 11, on the line connecting LI 11 at the cubital crease and LI15 inferior to the acromion. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-13 is believed to have a regulatory effect on the Large Intestine meridian, which is the primary organ associated with this point. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the upper arm, elbow, and forearm, as well as conditions such as tennis elbow and frozen shoulder. LI-13 is also believed to have a beneficial effect on the energy channels in the body, and can be used to treat conditions such as fatigue, weakness, and general debility. It is believed to promote the circulation of Qi and blood in the upper body, and can help to relieve tension and stress. In acupuncture theory, LI-13 is also considered to be a point that can help to clear heat from the body, which makes it useful for treating conditions such as fever, sore throat, and other inflammatory conditions. It is also believed to have a beneficial effect on the skin, and can be used to treat conditions such as acne, eczema, and other skin irritations. Overall, LI-13 is an important acupuncture point for treating a wide range of conditions related to the upper body, including pain, numbness, and weakness, as well as tension and stress. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LI-13 or any other acupoint for treatment. The acupuncturist will be able to determine whether this point is appropriate for a particular individual's condition and provide guidance on proper stimulation techniques and frequency of treatment.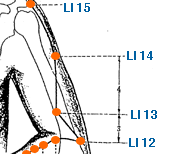
Bi Nao | Upper Arm | Large Intestine 14 | Li-14
This is an acupoint located in the upper arm. Specifically, it is located On the lateral brachial region, on the anterior margin of the insertion of the deltoid muscle, on the line connecting LI 11 at the cubital crease and LI15 inferior to the acromion. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-14 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi (energy) and blood in the arm, as well as to relieve pain and promote the health of the upper body. It is often used to treat conditions such as shoulder pain and stiffness, upper arm pain, elbow pain, and muscle atrophy. In addition, LI-14 is believed to be effective in treating respiratory disorders such as asthma, cough, and bronchitis, as well as disorders of the digestive system such as constipation and diarrhea. It is also believed to be helpful for women's health issues, such as menstrual irregularities and breast problems. As with all acupuncture points, it's important to consult a licensed acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment of any health conditions.
Jian Yu | Shoulder Bone | Large Intestine 15 | Li-15
This is an acupoint located on the upper arm. It is found in the depression between the anterior border of the acromion and the greater tubercle of the humerus. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-15 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi and blood in the shoulder and arm, and to help relieve pain and stiffness in the area. It is commonly used to treat shoulder pain and limited range of motion, as well as conditions such as frozen shoulder, rotator cuff injuries, and arthritis affecting the shoulder joint. LI-15 is also thought to be useful for treating respiratory and chest problems, such as cough, asthma, and shortness of breath. It may also help to alleviate stress and anxiety, as well as promote relaxation and overall well-being. As with all acupuncture points, it's important to consult a licensed acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment of any health conditions. They can determine if LI-15 is an appropriate treatment option for an individual's specific needs.
Ju Gu | Great Bone | Large Intestine 16 | Li-16
This is an acupoint located On the superior aspect of the scapular region, in the depression posterior to the acromial extremity of the clavicle and anterior to the scapular spine. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-16 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi and blood in the shoulder and upper arm, and to help relieve pain and stiffness in the area. It is commonly used to treat shoulder pain, frozen shoulder, rotator cuff injuries, and other conditions affecting the shoulder joint. LI-16 is also thought to be useful for treating respiratory and chest problems, such as cough, asthma, and shortness of breath, as well as digestive issues, including stomach pain, bloating, and constipation. It may also help to alleviate stress and anxiety and promote relaxation and overall well-being. As with all acupuncture points, it's important to consult a licensed acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment of any health conditions. They can determine if LI-16 is an appropriate treatment option for an individual's specific needs.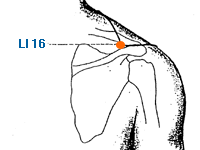
Tian Rong | Celestial Tripod | Large Intestine 17 | Li-17
This is an acupoint located on the side of the neck, just below the earlobe. Specifically, it is located in a depression that forms when the mouth is opened. In traditional Chinese medicine, LI-17 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi and blood in the neck and head region, and to help alleviate pain and stiffness in the area. It is commonly used to treat neck and shoulder pain, as well as headaches, migraines, and other conditions affecting the head and face. LI-17 is also thought to be useful for treating throat and voice problems, such as sore throat, hoarseness, and difficulty speaking. It may also help to alleviate stress and anxiety and promote relaxation and overall well-being. As with all acupuncture points, it's important to consult a licensed acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment of any health conditions. They can determine if LI-17 is an appropriate treatment option for an individual's specific needs.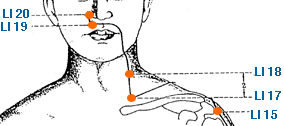
Fu Tu | Protuberance Assistant | Large Intestine 18 | Li-18
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the neck, on the sternocleidomastoid muscle, 3 cun lateral to the laryngeal prominence. This point is believed to help regulate the function of the throat and neck, and stimulate the flow of Qi and blood in the area. It is also used to treat a variety of conditions related to the head and neck. LI-18 is commonly used to alleviate sore throat, hoarseness, and other voice and throat problems. It may also help to treat neck pain and stiffness, as well as headaches and migraines. Some practitioners also use LI-18 to treat cough, asthma, and other respiratory conditions. In addition, LI-18 may be useful for treating anxiety and stress-related conditions, as it is thought to have a calming effect on the mind and body. However, as with all acupuncture points, it's important to consult a licensed acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment of any health conditions. They can determine if LI-18 is an appropriate treatment option for an individual's specific needs.
Jian Li | Grain Bone Hole | Large Intestine 19 | Li-19
This is located directly below the lateral margin of the nostril at the level of GV 26. LI-19 is mainly used to treat disorders of the head and neck, such as sore throat, toothache, and neck pain. It is also believed to help with shoulder pain and stiffness, as well as facial paralysis and spasms. In addition, LI-19 can be used to alleviate symptoms associated with colds and flu, such as fever, chills, and coughing. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Ying Xiang | Welcome Fragrance | Large Intestine 20 | Li-20
This is an acupuncture point located on the face, specifically on the lateral side of the nostril. More specifically, LI-20 is located at the level of the midpoint of the lateral border of the nostril, in a small depression. This point is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat a variety of conditions related to the head and face. It is particularly effective in treating sinus problems, such as sinusitis, congestion, and allergies, as it helps to open up the nasal passages and clear phlegm. LI-20 is also believed to be helpful in treating other conditions such as facial pain, headaches, and toothaches. In addition to its therapeutic uses, LI-20 is also commonly used in cosmetic acupuncture to improve the appearance of the face. It is believed to be effective in reducing wrinkles and improving the overall texture and tone of the skin. As with any acupuncture treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner before undergoing treatment with LI-20.
Kidney Meridian
This meridian is commonly under the Element Water.
Yong Quan | Gushing Spring | Kidney 1 | KI-1
This is an acupoint located on the big toe, just below the nail bed on the lateral side of the big toe. It is also known as Da Dun in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and is the first point of the Liver meridian. In TCM, LR-1 is believed to regulate the functions of the liver and improve the circulation of Qi and blood in the body. It is commonly used to treat conditions related to the liver, such as jaundice, hepatitis, and liver qi stagnation. It is also believed to have a regulating effect on the female reproductive system and can be used to treat menstrual disorders, PMS, and infertility. Additionally, LR-1 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the body, helping to improve energy levels and promote overall health and vitality. It can also be used to treat conditions related to the lower body, such as lower back pain, sciatica, and knee pain.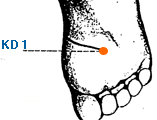
Ran Gu | Blazing Valley | Kidney 2 | KI-2
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) located on the sole of the foot. Specifically, it is located in a depression on the sole of the foot, anterior and inferior to the medial malleolus, at the junction of the red and white skin. In TCM, KI-2 is believed to be the starting point of the Kidney meridian, which is responsible for the regulation of the Kidney system. KI-2 is traditionally used to tonify the Kidney and to regulate the water metabolism in the body. Some of the conditions that KI-2 is believed to treat include: KI-2 is often used in combination with other acupoints to treat these conditions. It is important to note that while KI-2 has been used traditionally to treat these conditions, it is not a substitute for medical treatment and should be used as a complementary therapy under the guidance of a licensed healthcare provider.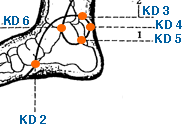
Tai Xi | Great Ravine | Kidney 3 | KI-3
This is an acupuncture point in traditional Chinese medicine located on the medial aspect of the foot, in the depression between the medial malleolus and the Achilles tendon. Specifically, it is located in the middle of the space between the tip of the medial malleolus and the attachment of the Achilles tendon. KI-3, known as Tai Xi, is an important point in treating many disorders, especially those related to the Kidney. According to TCM theory, the Kidney is responsible for many vital functions in the body, including growth and development, reproduction, bone health, and regulation of body fluids. Therefore, KI-3 is used to tonify and regulate the Kidney Qi, Yin, and Yang. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as low back pain, knee pain, heel pain, tinnitus, dizziness, and insomnia. It is also believed to be effective in treating conditions like hypertension, asthma, and diabetes. In addition to its therapeutic benefits, KI-3 is also used for diagnostic purposes in TCM. By palpating and observing the condition of KI-3, a practitioner can gain insight into the overall state of a patient's Kidney system, helping to guide treatment.
Da Zhong | Large Goblet | Kidney 4 | KI-4
This is an acupuncture point that is located on the medial aspect of the foot. Specifically, it is located in a depression between the medial malleolus and the Achilles tendon, level with the tip of the medial malleolus. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, KI-4 is believed to tonify the Kidney qi, nourish Yin and Yang, and regulate the Ren and Chong channels. It is used to treat various disorders related to the Kidney system, such as urinary tract disorders, sexual dysfunction, lower back pain, knee pain, heel pain, and tinnitus. KI-4 is also used to treat some emotional disorders such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Acupuncturists may use KI-4 in combination with other points to achieve the desired therapeutic effects. It is generally not used during pregnancy, as it is believed to be an acupoint that can stimulate uterine contractions. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine if KI-4 is appropriate for individual health concerns.
Shui Quan | Water Spring | Kidney 5 | KI-5
This is an acupuncture point located on the medial side of the foot, in the depression between the medial malleolus and the Achilles tendon. It is located midway between KI-3 and KI-7. KI-5 is often used to treat conditions related to the urinary system, such as frequent urination, enuresis, and incontinence. It is also believed to be effective in treating disorders of the reproductive system, such as impotence, irregular menstruation, and leukorrhea. In addition, KI-5 is believed to help relieve ankle pain, headaches, insomnia, and dizziness. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and spirit, and may be used to treat anxiety, restlessness, and other emotional imbalances. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Kidney Meridian.
Zhao Hai | Shining Sea | Kidney 6 | KI-6
This is located on the inside of the ankle, in the depression between the medial malleolus (inner ankle bone) and the Achilles tendon. This acupoint is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat conditions related to the kidneys, such as urinary incontinence, frequent urination, night sweats, and tinnitus. It is also believed to be effective in treating menstrual disorders, infertility, and impotence. In addition, KI-6 can help to relieve ankle pain, leg cramps, and lower back pain. Stimulating KI-6 can be done through acupressure, acupuncture, or moxibustion, and it is often used in conjunction with other acupoints to promote overall wellness and balance in the body. As with any form of alternative therapy, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner before attempting to use KI-6 or any other acupoint for medical purposes.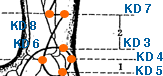
Fu Liu | Recovered Leg | Kidney 7 | KI-7
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine located on the medial aspect of the lower leg, in a depression that is approximately two cun above the tip of the medial malleolus, and posterior to the border of the tibia bone. This point is known as Fu Liu in Chinese, which means recovered leg. KI-7 is traditionally used to treat various conditions related to the Kidney meridian, including lower back pain, tinnitus, deafness, sore throat, toothache, dizziness, and night sweats. It is also said to benefit the Kidney system by nourishing yin, regulating water metabolism, and calming the mind. In addition, it is sometimes used to treat conditions such as edema, insomnia, and menstrual disorders. As with all acupoints, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare provider before using KI-7 for any specific condition.
Jiao Gu | Corner Bone | Kidney 8 | KI-8
Known as Jiao Gu or the Corner Bone point, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the medial aspect of the lower leg. Specifically, it is located in the depression between the tip of the medial malleolus (the bony bump on the inside of the ankle) and the Achilles tendon. KI-8 is said to be an influential point for the bones, as well as an important point for treating disorders related to the kidneys, which are associated with the water element in Chinese medicine. It is often used to treat disorders such as lower back pain, knee pain, bone disorders, tinnitus, night sweats, and urinary problems, among others. In addition, it is believed to help regulate the body's water metabolism, making it useful in treating conditions such as edema, urinary tract infections, and other conditions related to the kidneys and bladder. As with all acupoints, it is important to seek guidance from a qualified practitioner before using KI-8 or any other acupoint for therapeutic purposes.
Zhu Bin | Guest House | Kidney 9 | KI-9
Known as Zhu Bin, is an acupuncture point on the Kidney meridian. It is located in the depression anterior and inferior to the medial malleolus. In traditional Chinese medicine, KI-9 is believed to nourish the Kidney yin and tonify the Kidney yang, which helps to regulate the water passages and promote urination. KI-9 is commonly used to treat various conditions related to the Kidney meridian, such as urinary problems, genital disorders, and lower back pain. It may also be used to alleviate symptoms of fatigue, palpitations, and insomnia. Additionally, KI-9 is often used in acupuncture to induce labor and facilitate childbirth. However, it is important to note that acupuncture should only be performed by a licensed practitioner and that medical advice should always be sought for any health concerns.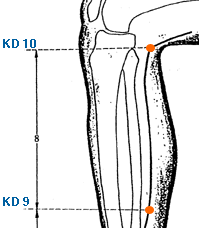
Yin Gu | Yin Valley | Kidney 10 | KI-10
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the medial aspect of the knee joint, approximately 2 cun superior to the superior border of the patella, on the bulge of the medial condyle of the tibia. KI-10 is believed to be a powerful point for treating knee problems, including knee pain, stiffness, and weakness. It is also commonly used to treat genitourinary disorders such as urinary incontinence, nocturnal emissions, and other reproductive issues. In addition, KI-10 is thought to be beneficial for digestive issues, including diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. In traditional Chinese medicine, KI-10 is believed to tonify the Kidney and nourish the Yin, and is often used in conjunction with other acupoints in the Kidney meridian to treat a variety of conditions. As with all acupoints, KI-10 should only be used by a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified practitioner.
Heng Gu | Pubic Bone | Kidney 11 | KI-11
This is an acupuncture point in the Kidney meridian. It is known as the Heng Gu point, and is located on the abdomen. Specifically, it is located on the lower abdomen, 2 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) below the center of the umbilicus. KI-11 is believed to be useful for treating a variety of conditions, including lower abdominal pain, genital-urinary disorders, impotence, menstrual irregularities, hernia, and other conditions affecting the lower abdomen and groin area. It is also believed to be helpful in tonifying the Kidney qi, promoting fertility, and treating emotional disorders such as anxiety and depression. However, as with all acupuncture points, the use of KI-11 should be determined by a qualified practitioner based on individual diagnosis and treatment needs.
Da He | Great Manifestation | Kidney 12 | KI-12
Known as Da He or Great Manifestation, is located on the abdomen. Specifically, it is located on the lower abdomen, 3 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) below the center of the umbilicus and 0.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, KI-12 is believed to regulate the Kidney and Liver, tonify the Blood, resolve dampness, and benefit the lower back and knees. It is commonly used to treat disorders such as lower back pain, knee pain, weakness and numbness of the lower limbs, and dampness in the lower body. It may also be used to treat disorders related to menstrual irregularities, such as irregular or heavy periods, dysmenorrhea, and amenorrhea. KI-12 can be stimulated by various techniques, including acupuncture, acupressure, and moxibustion. Moxibustion, in particular, is believed to be especially effective for tonifying the Kidney and strengthening the lower back. However, it is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist or practitioner of Traditional Chinese Medicine before attempting to use acupressure or moxibustion on this or any other acupoint.
Qi Xue | Qi Cleft | Kidney 13 | KI-13
Known as Qi Xue or the Qi Cleft point, is an acupuncture point located on the abdomen. It is found on the midline of the body, 3 cun (or about 4 finger widths) below the belly button, on the upper border of the pubic symphysis. Stimulation of KI-13 is believed to help regulate the flow of qi and blood in the lower abdomen and can be used to treat a variety of conditions related to the reproductive, digestive, and urinary systems. It is commonly used to treat gynecological issues such as irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, and infertility. It may also be used to treat urinary issues like painful urination, bladder incontinence, and nocturnal enuresis. Additionally, KI-13 can be used to treat digestive issues such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation.
Si Man | Fourfold Fullness | Kidney 14 | KI-14
Known as the Si Man or Fourfold Fullness point, is located on the abdomen. Specifically, it is located on the lower abdomen, 2 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the center of the umbilicus. KI-14 is considered an important point in traditional Chinese medicine for treating disorders of the urinary system and the lower abdomen. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as frequent or painful urination, incontinence, nocturnal emissions, impotence, infertility, irregular menstruation, and other disorders of the reproductive system. It is also believed to be effective in treating digestive disorders such as abdominal distension, constipation, and diarrhea. Additionally, KI-14 is believed to help regulate the body's energy and promote overall health and well-being. As with all acupuncture points, KI-14 should be used under the guidance of a qualified and licensed practitioner.
Zhong Zhu | Central Flow | Kidney 15 | KI-15
This is an acupuncture point located on the abdomen. Specifically, it is located on the lower abdomen, 2 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the center of the umbilicus and 2 cun superior to the pubic symphysis. This point is traditionally used in Chinese medicine to treat conditions related to the kidneys, including kidney deficiency, low back pain, urinary problems, and impotence. It is also used to treat conditions related to the lower back, including sciatica and lumbago. Additionally, it is used for digestive issues, such as constipation and diarrhea. As with all acupuncture points, KI-15 should only be stimulated by a licensed acupuncturist or trained medical professional. It should not be self-administered.
Huang Shu | Vitals Shu | Kidney 16 | KI-16
This is an acupuncture point that is located on the abdomen. Specifically, it is located on the lower abdomen, 2 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the center of the umbilicus and 4 cun superior to the pubic symphysis. KI-16, known as Huangshu or Vitals Shu, is traditionally used in Chinese medicine to treat a variety of conditions related to the kidneys, such as kidney pain, nephritis, enuresis (bed-wetting), and frequent urination. It is also thought to regulate and strengthen the qi of the entire body, and to promote the health of the spleen and stomach. In addition, KI-16 is sometimes used to treat digestive disorders such as stomach pain, constipation, and diarrhea. As with any acupuncture point, KI-16 should only be stimulated by a qualified practitioner and in accordance with proper acupuncture techniques. It is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using acupuncture as a treatment for any condition.
Shang Qu | Upper Spring | Kidney 17 | KI-17
This one is located in the supraclavicular fossa, approximately 1 cun lateral to the anterior midline, in the hollow between the clavicle and the sternocleidomastoid muscle. In traditional Chinese medicine, KI-17 is considered to be a point that harmonizes the qi of the chest, benefits the lung, and clears phlegm. It is commonly used to treat respiratory disorders, such as cough, asthma, and chest congestion. Additionally, KI-17 is believed to help regulate the qi and blood, and can be used to treat disorders related to the chest, throat, and neck. Stimulating KI-17 can be done through acupressure, acupuncture, or moxibustion. It is recommended to consult a licensed acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment.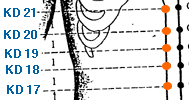
Shi Guan | Vital Diaphragm | Kidney 18 | KI-18
This is an acupuncture point that belongs to the kidney meridian. This acupoint is located on the abdomen. Specifically, it is located on the lower abdomen, 2 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the center of the umbilicus and level with the tip of the 11th rib. KI-18 is commonly used to treat respiratory and digestive disorders, such as asthma, cough, shortness of breath, hiccups, nausea, vomiting, and indigestion. This acupoint is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind, making it useful for treating anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia. Stimulation of KI-18 is thought to regulate the flow of qi and blood in the chest, diaphragm, and stomach areas, which can help to harmonize the functions of the respiratory and digestive systems. This acupoint is often used in combination with other acupoints to enhance its therapeutic effects. It is important to note that before using acupuncture to treat any medical condition, it is advisable to consult a licensed acupuncturist.
Yin Du | Yin Metropoli | Kidney 19 | KI-19
This is an acupuncture point in the Kidney meridian. It is located on the chest. Specifically, it is located on the chest, 4 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the anterior midline, in the 2nd intercostal space. KI-19 is believed to regulate the Kidney and treat various conditions associated with the Kidney system. It is commonly used to address symptoms such as lower back pain, urinary problems, impotence, infertility, menstrual disorders, and night sweats. It may also help improve digestion and alleviate abdominal pain. Additionally, KI-19 is thought to help boost the immune system and promote overall health and wellness. As with all acupuncture treatments, KI-19 should only be administered by a licensed acupuncturist after a thorough assessment of the patient's overall health and individual needs.
Tong Gu | Contemplation Palace | Kidney 20 | KI-20
This is an acupuncture point on the Kidney meridian. It is located on the chest. Specifically, it is located on the chest, 4 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the anterior midline, in the 1st intercostal space. Stimulation of this point is thought to help with conditions such as cough, asthma, chest pain, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and help with emotional disorders such as anxiety, depression, and fear. In traditional Chinese medicine, KI-20 is considered to be an important point for nourishing the Kidney Qi and balancing the body's Yin and Yang energies.
You Men | Dark Gate | Kidney 21 | KI-21
This is one of the vital points in the Kidney Meridian. It is located on the chest. Specifically, it is located on the chest, 6 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the anterior midline, in the 2nd intercostal space. Stimulating the KI-21 acupoint can have a positive impact on a range of physical and mental health conditions. Some of the common disorders and symptoms that are treated using KI-21 include chest pain, breathing difficulties, cough, asthma, anxiety, and depression. The acupoint is known to improve circulation, alleviate pain and stiffness, and promote relaxation and sleep. As with all acupoints, it's essential to consult a qualified acupuncturist or a medical professional before using KI-21 to treat any health condition. Proper evaluation and diagnosis are necessary to determine the most effective treatment plan, including the number of sessions required and the specific techniques to be employed.
Bu Lang | Corridor Walk | Kidney 22 | KI-22
This is an acupuncture point in the Kidney meridian, known as the Qi mansion. It is located on the chest. Specifically, it is located on the chest, 4 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the anterior midline, in the 4th intercostal space. KI-22 is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat disorders related to the chest and abdomen. It is particularly effective in treating conditions such as coughing, asthma, chest tightness, pain or fullness in the chest, and pain in the ribs. It is also used to treat digestive disorders such as abdominal distention, diarrhea, and dysentery. In addition, KI-22 can be used to help regulate the function of the Kidney, which is believed to help boost the immune system and promote overall health and wellbeing.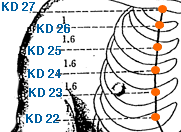
Shen Feng | Kidney Peak | Kidney 23 | KI-23
This is an acupuncture point in the kidney meridian, known as Shen Feng, which means Kidney peak. It is located on the chest, on the midclavicular line, in the 5th intercostal space, about 2 cun lateral to the nipple. KI-23 is used to treat a variety of conditions, including respiratory and chest disorders such as cough, asthma, and chest pain. It is also believed to be effective in treating anxiety, depression, and other emotional disorders, as well as menstrual problems and infertility. In traditional Chinese medicine, KI-23 is thought to tonify the Kidney Qi, strengthen the Lungs, and promote the circulation of Qi and blood. Acupressure or acupuncture at KI-23 may also be used to treat conditions related to the heart and the spirit, as well as other issues related to the Kidney meridian.
Ling Xu | Spirit Ruins | Kidney 24 | KI-24
Known as Ling Xu in Chinese, is an acupuncture point located in the supraclavicular fossa, approximately 2 cun lateral to the midline. It is at the level of the first intercostal space, and inferior to the lateral end of the clavicle. KI-24 is believed to be a useful point for treating respiratory disorders such as cough, asthma, and shortness of breath. It is also used to treat disorders of the throat, including sore throat, hoarseness, and difficulty speaking. Additionally, KI-24 is thought to be effective for the treatment of chest pain, chest congestion, and pain or stiffness in the neck and shoulder. It is said to have a calming and soothing effect on the mind and can be used to treat anxiety and insomnia. As with all acupuncture points, KI-24 should be used with caution and under the guidance of a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare practitioner.
Shier Zhong | Twelve Points | Kidney 25 | KI-25
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the abdomen. Specifically, it is located on the lower abdomen, 2 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the center of the umbilicus and level with the upper border of the pubic symphysis. It is known as Shier Zhong, which means Twelve Points. This point is primarily used to treat abdominal pain and distension, and can also be effective for digestive disorders such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It can also be used to treat disorders of the reproductive system, such as menstrual pain or irregular periods, as well as urinary problems, including difficult or painful urination. KI-25 is believed to help regulate the flow of Qi throughout the body, particularly in the lower abdomen and pelvic region, and is thought to have a calming effect on the mind and emotions. As with all acupoints, it is important to seek the advice of a qualified practitioner before using KI-25, as it may not be appropriate for everyone and could potentially have adverse effects if used improperly.
Yu Zhong | Lively Center | Kidney 26 | KI-26
Known as Yu Zhong, is located on the abdomen. Specifically, it is located on the lower abdomen, 2 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the center of the umbilicus and level with the lower border of the pubic symphysis. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), KI-26 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi (vital energy) and blood in the chest, improve respiration, and alleviate pain in the chest, abdomen, and head. It is also used for the treatment of facial paralysis, trigeminal neuralgia, and rhinitis. This point is commonly used in acupuncture and acupressure for the treatment of respiratory disorders such as asthma, shortness of breath, and coughing. It is also used to relieve toothache, facial pain, and headache. However, it is important to note that any medical conditions should be evaluated by a licensed healthcare professional and that acupuncture and acupressure should only be performed by a trained practitioner.
Shu Fu | Collection of Fluids | Kidney 27 | KI-27
This is an acupuncture point located on the front of the body, at the level of the lower border of the clavicle and in the depression about 2 inches lateral to the midline. It is known as Shu Fu, which means Collection of Fluids. It is located in the chest region, just below the collarbone, and is considered to be the last point of the Kidney meridian. KI-27 is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat respiratory disorders, such as asthma, cough, and shortness of breath. It is also thought to be effective in treating chest pain, chest congestion, and palpitations. Additionally, KI-27 is believed to help regulate and strengthen the immune system, and is often used as a point for immune support. Acupuncturists may also use KI-27 in conjunction with other points to address digestive issues, emotional imbalances, and menstrual disorders. The point is generally considered safe for most individuals, although as with any acupuncture point, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner to determine if it is appropriate for your specific needs.
Urinary Bladder Meridian
This meridian is commonly under the Element Water.
Jing Ming | Bright Eyes | Urinary Bladder 1 | UB-1
This is an acupuncture point located in the inner corner of the eye, at the level of the eyebrow, in the depression at the medial end of the supraorbital ridge. It is known as Jing Ming or Bright Eyes. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), UB-1 is considered a local point for eye disorders, such as redness, itching, and swelling of the eyes, as well as tearing and blurred vision. It is also used to treat other conditions related to the eye, such as conjunctivitis, myopia, and cataracts. In addition, UB-1 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and is often used to treat emotional and psychological disorders, such as anxiety and insomnia. It is also used to relieve frontal headaches, dizziness, and nasal congestion.
Zan Zhu | Bamboo Gathering | Urinary Bladder 2 | UB-2
Known as Zanzhu, is an acupuncture point that is located on the eyebrow, in the depression at the medial end of the eyebrow. Specifically, it is located 0.5 cun (finger widths) within the eyebrow towards the bridge of the nose. This acupoint is traditionally used in Chinese medicine to treat disorders related to the eyes, such as redness, swelling, itching, and pain, as well as other conditions that affect the face, head, and neck, including sinusitis, facial paralysis, and headaches. It is believed that needling this point can clear heat and wind, and regulate the qi and blood circulation in the eye area. In addition to its traditional use, UB-2 is also commonly used in modern acupuncture treatments for eye strain, eye fatigue, and eye diseases such as myopia (nearsightedness) and cataracts. It is often combined with other acupoints to form a comprehensive treatment plan, based on the individual needs of the patient
Mei Chong | Beautiful Rushing | Urinary Bladder 3 | UB-3
This is an acupuncture point on the urinary bladder meridian of the body. It is known as Mei Chong, meaning 'Beautiful Rushing'. UB-3 is located on the medial end of the eyebrow, in a depression at the supraorbital notch. In traditional Chinese medicine, UB-3 is believed to regulate the functions of the bladder and the eyes. It is commonly used to treat eye disorders such as conjunctivitis, redness, swelling, and pain of the eyes, as well as migraines and frontal headaches. It may also be used to treat nasal congestion, sinusitis, and other upper respiratory tract infections. Acupuncturists may stimulate this point using acupuncture needles, moxibustion (a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves burning mugwort to promote healing), or acupressure (applying pressure to the point with fingers or a tool). However, it is important to note that acupuncture should be used as a complementary therapy and not as a replacement for medical treatment.
Qu Cha | Deviating Turn | Urinary Bladder 4 | UB-4
This is a point located in the depression directly above the anterior hairline of the forehead, between the eyebrows. It is considered a meeting point of the Bladder, Gallbladder, and Stomach meridians. This point is traditionally used to treat disorders of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat, including conjunctivitis, myopia, night blindness, tinnitus, sinusitis, and nasal congestion. It is also thought to be effective in treating headaches, dizziness, and facial paralysis. Additionally, UB-4 is believed to regulate the functions of the upper and lower extremities, and to help balance the emotions, especially anger and frustration. As with all acupressure and acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner before seeking treatment and to receive a proper diagnosis before using this point for specific conditions.
Pi Shu | Fifth Place | Urinary Bladder 5 | UB-5
This is a point on the urinary bladder meridian. It is located 1.5 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 2nd lumbar vertebra. Stimulating this acupoint is thought to help with a variety of conditions including back pain, sciatica, diarrhea, constipation, and urinary tract disorders. It is also used to treat emotional issues such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. In traditional Chinese medicine, the urinary bladder meridian is associated with the water element and is believed to be responsible for the body's capacity to adapt and respond to external stimuli. Activating UB-5 is thought to help regulate the flow of qi and blood in the urinary bladder meridian, leading to a restoration of balance and improved physical and emotional well-being.
Cheng Guang | Light Guard | Urinary Bladder 6 | UB-6
This is located in the depression anterior to the suprascapular spine, at the midpoint of the line connecting Tian Zong (SI-11) and Jian Zhen (SI-9) acupoints. It is at the same level as the fourth thoracic vertebra. UB-6 is believed to regulate and strengthen the immune system and improve the overall health of the body. It is also used to treat various respiratory disorders, such as cough, asthma, and bronchitis. In addition, this point is said to be effective in treating shoulder and neck pain, stiff neck, and headache. Some traditional Chinese medicine practitioners also use this point to treat disorders related to the eyes, such as blurred vision and conjunctivitis.
Tong Tian | Celestial Connection | Urinary Bladder 7 | UB-7
Known as Tong Tian, is located in the depression between the spinous processes of the first and second cervical vertebrae. It is about 1.5 cun (approximately 1 inch) above the midpoint of the posterior hairline. Stimulation of this acupoint is believed to help with a variety of conditions related to the head, neck, and upper back, such as headaches, dizziness, neck pain and stiffness, and upper back pain. It may also help with respiratory conditions like asthma and cough, as well as eye and ear problems. UB-7 is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind, and it may be used to treat emotional and psychological conditions like anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Additionally, it is sometimes used to alleviate symptoms of the common cold or flu. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or other healthcare professional to determine if acupuncture and acupoint UB-7 are appropriate for your specific condition.
Jiao Sun | Head Vertex | Urinary Bladder 8 | UB-8
Known as Jiao Sun or Head Vertex, is an acupoint located at the midpoint of the line connecting the apex of the ear and the top of the head, on the midline of the scalp. It is situated about 3 cun (fingerbreadths) posterior to the anterior hairline and about 1.5 cun above the midpoint of the eyebrow. Stimulation of UB-8 is said to be useful in treating various disorders related to the head and neck region. It is often used to alleviate headaches, migraines, dizziness, and vertigo. Additionally, it is thought to help improve vision and relieve eye strain. In traditional Chinese medicine, UB-8 is also considered to be helpful in treating mental and emotional conditions, including anxiety, depression, and insomnia. However, it is important to note that acupuncture and acupressure should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment. If you are experiencing any concerning symptoms, you should always consult with a licensed healthcare professional.
Yu Zhen | Jade Pillow | Urinary Bladder 9 | UB-9
This is an acupuncture point on the bladder meridian, which is also called Yu Zhen in Chinese. It is located in the occipital region, in a depression 1.5 cun lateral to the superior aspect of the external occipital protuberance. Stimulating this point is believed to be beneficial for a range of conditions including neck pain, stiffness and immobility, headache, dizziness, tinnitus, sore throat, nasal congestion, cough, asthma, hypertension, and insomnia. Additionally, UB-9 can help to release stress and tension, promote relaxation and improve overall physical and mental well-being. It is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan based on individual needs.
Tian Zhu | Celestial Pillar | Urinary Bladder 10 | UB-10
This is an acupoint used in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located In the nuchal region, on the lateral border of the trapezius muscle, 1.3 cun lateral to GV 15 at the level between cervical vertebrae C1 and C2. In traditional Chinese medicine, UB-10 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi and blood in the body, and can be used to treat a variety of conditions related to the head, neck, and back. This acupoint is commonly used for the treatment of headaches, neck pain, and upper back pain. It may also be used for other conditions, such as asthma, cough, and depression. As with all acupoints, it is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist before using UB-10 or any other acupoint for therapeutic purposes. Acupressure or acupuncture applied to UB-10 should only be done by a licensed and qualified practitioner.
Da Zhu | Great Shuttle | Urinary Bladder 11 | UB-11
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine, located on the back, on the line connecting the lower edge of the scapula and the spinous process of the first thoracic vertebra. Specifically, it is located 1.5 cun (approximately 3 cm) lateral to the spinous process of the first thoracic vertebra. This acupoint is believed to be useful for treating disorders of the respiratory and digestive systems, such as asthma, bronchitis, cough, diarrhea, and constipation. It is also believed to be effective for treating back pain, as well as other musculoskeletal disorders. Stimulating this point is believed to promote the smooth flow of Qi (vital energy) and blood throughout the body, which can help to resolve blockages and restore balance to the body's systems. It is typically stimulated by acupuncture needles, acupressure, or other forms of TCM treatment. However, it is important to consult a licensed TCM practitioner before attempting to use UB-11 or any other acupoint for therapeutic purposes.
Feng Men | Wind Gate | Urinary Bladder 12 | UB-12
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that is located on the back of the body. It is known as the 'Wind Gate' and is believed to be closely related to the lung meridian. The UB-12 acupoint is located on the back, 1.5 cun (finger widths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 2nd thoracic vertebra. In TCM, UB-12 is used to treat respiratory problems, such as coughing, wheezing, and asthma. It is also believed to be effective for treating neck pain, fever, and chills, and can help to strengthen the immune system. Additionally, UB-12 is used to regulate the flow of Qi and blood, helping to bring the body into balance and promote overall health and wellbeing.
Fei Shu | Lung Shu | Urinary Bladder 13 | UB-13
Known as Feishu in Chinese, is an acupoint in the Urinary Bladder Meridian of Traditional Chinese Medicine. It is located on the back, on the same level as the third thoracic vertebra, at the level of the lower border of the scapular spine, about 1.5 cun (the width of the patient's thumb at the base of the joint) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the third thoracic vertebra. Stimulation of this point is believed to have a number of therapeutic benefits. In TCM, UB-13 is associated with the lungs and is believed to be useful for treating lung-related conditions such as asthma, coughing, and wheezing. It is also believed to help regulate the body's defensive Qi, making it useful for enhancing the immune system and fighting off infections. Other conditions that UB-13 is thought to benefit include back pain, shoulder pain, and emotional disorders such as grief and sadness. Additionally, it is believed to be useful for treating conditions that affect the skin, such as eczema and hives.
Jue Yin Shu | The Great Hammer | Urinary Bladder 14 | UB-14
This is located on the back of the body, at the level of the fourth thoracic vertebra. Specifically, it is located at the midpoint of the line connecting the spinous processes of the third and fourth thoracic vertebrae, about 3 centimeters lateral to the spine. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, UB-14 is considered to be an important point for the treatment of lung and heart disorders, including asthma, bronchitis, and palpitations. It is believed that stimulating this point can help to clear lung heat and phlegm, tonify lung Qi, and regulate the flow of Qi and blood throughout the body. It may also be used to treat emotional disorders such as anxiety, fear, and sadness. As with all acupoints, it is important to consult a qualified practitioner before using UB-14 for any specific condition.
Xin Shu | Heart Shu | Urinary Bladder 15 | UB-15
This is one of the points in the bladder meridian of traditional Chinese medicine, located on the back, at the level of the 4th thoracic vertebra, about 1.5 cun (about 3 centimeters) from the spine on either side. Stimulation of UB-15 is believed to help regulate the function of the heart, calm the mind, and improve sleep. It is also used to treat conditions such as palpitations, anxiety, depression, insomnia, and poor memory. In traditional Chinese medicine, UB-15 is considered an important point for treating the shen (spirit) and regulating the flow of qi and blood through the heart and lungs. Acupressure, acupuncture, or moxibustion may be used to stimulate UB-15, and it is often used in conjunction with other points in the bladder meridian or other meridians, depending on the specific condition being treated. However, it is important to note that acupuncture and acupressure should not be used as a replacement for medical treatment, and a licensed healthcare professional should be consulted before beginning any new treatment.
Du Shu | Governing Vessel Shu | Urinary Bladder 16 | UB-16
Known as the Du Shu or Governing Vessel Shu, is located on the back of the body, at the level of the fifth thoracic vertebrae. It is located approximately 1.5 cun (about 2.5 centimeters) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of T5. Stimulation of UB-16 is believed to be helpful in treating respiratory and cardiac disorders, as well as emotional imbalances such as anxiety and depression. It is also thought to be useful in treating conditions such as back pain, fever, and hypertension. Additionally, UB-16 is often used in acupuncture treatments to help improve the overall energy flow in the body, and to help reduce stress and promote relaxation. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a qualified acupuncturist or healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for any specific health condition.
Ge Shu | Diaphragm Shu | Urinary Bladder 17 | UB-17
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the back, specifically in the middle of the third thoracic vertebrae, at the same level as the lower border of the scapular spine. It is known as the Diaphragm Shu and is believed to regulate the functions of the diaphragm, lungs, and heart. Stimulating UB-17 is believed to be useful in the treatment of various respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and cough, as well as chest pain, palpitations, and anxiety. It is also believed to help regulate blood circulation and is sometimes used to treat conditions such as high blood pressure and anemia. It is important to note that while acupuncture and acupressure can be beneficial for many people, they should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment from a qualified healthcare professional. If you are experiencing any symptoms or health concerns, it is important to seek advice from a licensed healthcare provider.
Gan Shu | Liver Shu | Urinary Bladder 18 | UB-18
Known as Gan Shu, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the back, below the spinous process of the ninth thoracic vertebra, about 1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process. UB-18 is associated with the liver and is believed to regulate its function. According to traditional Chinese medicine theory, the liver is responsible for storing blood and ensuring its smooth flow throughout the body. It is also responsible for regulating the emotions and maintaining the body's overall health and vitality. By stimulating UB-18, practitioners believe they can help to alleviate conditions related to liver qi stagnation, such as hypochondriac pain, jaundice, and hepatitis. UB-18 is also said to be effective in treating menstrual disorders, vision problems, and digestive issues, as well as promoting overall relaxation and reducing stress. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Dan Shu | Gallbladder Shu | Urinary Bladder 19 | UB-19
This is an acupoint in the Bladder Meridian of Traditional Chinese Medicine. It is known as Dan Shu in Chinese. UB-19 is located on the back, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the ninth thoracic vertebra. It is about 1.5 cun (one body inch) lateral to the posterior midline. This acupoint is believed to be related to the liver, and stimulating it is thought to be helpful in treating conditions related to the liver and gallbladder. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, the liver is believed to play a vital role in the body's overall health and well-being, including regulating the smooth flow of qi, or energy, throughout the body. Stimulation of UB-19 is believed to help regulate the liver, alleviate liver congestion and stagnation, and promote the smooth flow of qi. It is used to treat various conditions such as liver and gallbladder disorders, hypochondriac pain, chest pain, menstrual disorders, and emotional disorders like depression and anger. It may also be used for other conditions, such as skin conditions, allergies, and digestive problems. However, as with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a qualified acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Pi Shu | Spleen Shu | Urinary Bladder 20 | UB-20
This is an acupuncture point located on the bladder meridian. It is known as Pishu in traditional Chinese medicine. The point is located on the back, 1.5 cun (the width of the patient's thumb at the distal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the eleventh thoracic vertebra. UB-20 is used to treat digestive disorders, such as stomach pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. It is also thought to benefit the spleen and pancreas. In traditional Chinese medicine, it is believed that stimulating this point can help regulate the body's Qi and promote healthy digestion.
Wei Shu | Stomach's Back Shu | Urinary Bladder 21 | UB-21
This is an acupuncture point on the Urinary Bladder meridian. It is known as the Stomach's Back Shu point. Location: UB-21 is located on the back, at the level of the lower border of the spinous process of the 2nd lumbar vertebra, approximately 1.5 inches (4 cm) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process. Illnesses and conditions treated: UB-21 is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat a variety of digestive disorders, such as abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and poor digestion. It is also used to tonify the Qi of the Stomach and Spleen, which are important organs in the digestive system. In addition, UB-21 is thought to strengthen the immune system and regulate the functions of the Liver and Gallbladder.
San Jiao Shu | Triple Burner Shu | Urinary Bladder 22 | UB-22
This is an acupuncture point located on the back of the body, along the Urinary Bladder meridian. It is known as Sanjiaoshu. This acupoint is found in the lower back, at the level of the lower border of the spinous process of the 2nd lumbar vertebra. Stimulating UB-22 is believed to benefit the Kidney and Bladder systems, tonifying Kidney Qi and promoting urination. It can be used to treat lower back pain, sciatica, and other disorders related to the Kidney and Bladder, such as urinary incontinence, frequent urination, and edema. UB-22 is also said to have a regulatory effect on the reproductive system, and can be used to treat infertility, impotence, and menstrual disorders. It is believed to nourish the Blood and tonify Qi, making it useful for chronic fatigue, anemia, and weakness. Overall, UB-22 is a useful acupoint for promoting vitality and overall health.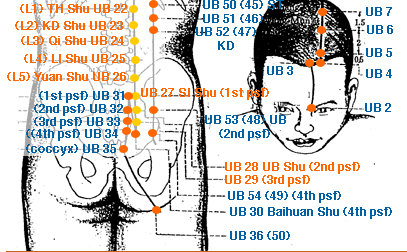
Shen Shu | Kidney Shu | Urinary Bladder 23 | UB-23
Known as Shen Shu in Chinese, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. This acupoint is located on the back, on the level of the lower border of the spinous process of the second lumbar vertebra, 1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the fourth lumbar vertebra. Stimulating this point is believed to tonify the Kidney Qi and nourish the Kidney Yin and Yang, which is why it is commonly used to treat various Kidney related conditions such as low back pain, weak or sore knees, frequent urination, nocturnal emission, impotence, infertility, irregular menstruation, menopausal symptoms, and other urinary and reproductive disorders. It is also believed to strengthen the bones and nourish the marrow, making it useful for bone and joint problems such as arthritis and osteoporosis. In addition, UB-23 is believed to help with the digestive system, including constipation and diarrhea, as well as improving overall energy and vitality.
Qi Hai Shu | Sea of Qi Shu | Urinary Bladder 24 | UB-24
Known as Qi Hai Shu, is located on the back, at the level of the lower border of the spinous process of the 2nd lumbar vertebra, on either side of the spine. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, UB-24 is believed to regulate the function of the kidney and bladder, tonify the kidney qi, and promote the transformation and transportation of fluids in the body. Stimulating this acupoint is thought to help with various urinary and reproductive disorders, such as incontinence, frequent urination, impotence, and infertility. It may also be useful in treating lower back pain, lumbar strain, and weakness in the lower extremities. In addition, UB-24 is often used as part of a broader treatment plan for conditions such as chronic fatigue syndrome, insomnia, and anxiety, as it is thought to nourish and regulate the kidney yin and yang. However, it is important to note that acupuncture and acupressure should always be used in conjunction with standard medical care, and not as a substitute for professional diagnosis and treatment.
Da Chang Shu | Large Intestine Shu | Urinary Bladder 25 | UB-25
Known as Da Chang Shu, is a vital acupoint in the Urinary Bladder Meridian. It is located at the lower back, 1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the fourth lumbar vertebra. UB-25 is traditionally used in Chinese medicine to treat conditions related to the large intestine, such as constipation, diarrhea, and other digestive issues. It can also be helpful in treating lower back pain, sciatica, and other musculoskeletal disorders. By stimulating this point, it is believed to regulate the flow of Qi in the lower back and pelvic region, tonify the function of the large intestine, and promote healthy bowel movements. However, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or medical professional to determine if this acupoint is appropriate for an individual's specific health concerns.
Guan Yuan Shu | Gate of the Original Qi | Urinary Bladder 26 | UB-26
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that is believed to be connected to the Urinary Bladder Meridian. It is also called Guan Yuan Shu, which means Gate of the Original Qi. UB-26 is located in the lower back, approximately at the level of the sacrum and 1.5 cun (or 1.5 body inches) lateral to the midline. In TCM, UB-26 is believed to be a vital point for regulating Qi and blood flow in the lower back area. It is also believed to have an effect on the Kidneys, Bladder, and reproductive system. The acupoint is often used to treat lower back pain, stiffness, and weakness, as well as problems with the urinary and reproductive systems, such as frequent urination, incontinence, impotence, and menstrual disorders. UB-26 is also thought to be beneficial for those with digestive issues, such as abdominal distension, constipation, and diarrhea. Additionally, some practitioners use UB-26 to address emotional imbalances, including anxiety and depression. It's important to note that, while UB-26 may be helpful for some conditions, it should not be used as a substitute for medical care. It's always best to consult with a qualified healthcare practitioner before trying any new treatment, including acupuncture or acupressure.
Xiao Chang Shu | Small Intestine Shu | Urinary Bladder 27 | UB-27
This is an acupuncture point that is known as Xiao Chang Shu. It is located on the lower back, at the level of the fourth sacral foramen, 1.5 cun (finger widths) lateral to the midline. UB-27 is often used to treat conditions related to the lower back, hips, and buttocks. It is also believed to be helpful for a variety of digestive issues, such as constipation, diarrhea, and irritable bowel syndrome. In addition, UB-27 is sometimes used to address urinary and reproductive system problems, including urinary tract infections, menstrual cramps, and impotence. As with any acupuncture point, the specific conditions that UB-27 is used to treat may vary depending on the practitioner and the individual needs of the patient.
Pang Guang Shu | Bladder Shu | Urinary Bladder 28 | UB-28
Known as the Bladder Shu point, is a vital acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. This point is located on the back, on the sacrum, about 1.5 cun (approximately the width of the patient's thumb) lateral to the midline at the level of the second posterior sacral foramen. This acupoint is used to treat various conditions related to the bladder and reproductive system, including urinary tract infections, incontinence, cystitis, dysmenorrhea, impotence, and infertility. Additionally, UB-28 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi and blood, promote circulation, and strengthen the lower back. It is commonly used in acupuncture and acupressure therapy, and its stimulation can also provide relief for lower back pain and sciatica. As with all acupuncture points, the use of UB-28 should be carried out by a licensed and experienced practitioner.
Zhong Lu Shu | Central Backbone Shu | Urinary Bladder 29 | UB-29
This is an acupuncture point on the urinary bladder meridian. It is known as Zhong Lu Shu or Central Backbone Shu. This point is located in the lower back, at the level of the second posterior sacral foramen, 1.5 cun lateral to the midline. UB-29 is commonly used to treat conditions of the lower back, such as low back pain, sciatica, and stiffness. It is also used to treat urological disorders such as incontinence, painful urination, and urinary retention. Additionally, it may be used to treat disorders of the reproductive system, such as impotence, irregular menstruation, and dysmenorrhea. Stimulation of this point is thought to help regulate and strengthen the function of the bladder, kidney, and reproductive organs, and to relieve pain and discomfort in the lower back. This point is often used in combination with other points along the urinary bladder meridian for a comprehensive treatment approach. It is important to note that acupuncture should only be performed by a qualified practitioner.
Bai Huan Shu | White Ring Shu | Urinary Bladder 30 | UB-30
This is an acupuncture point located in the lower back region. It is known as Baihuan Shu and is translated to mean Hundred Meetings. Specifically, it is located at the level of the second sacral foramen, 1.5 cun lateral to the midline, on the level of the lower border of the posterior superior iliac spine. This point is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat a variety of conditions related to the lower back and pelvic area. Some of the conditions that may benefit from UB-30 stimulation include lower back pain, sciatica, hip pain, pelvic inflammation, and irregular menstruation. Additionally, it is believed that stimulating this point can help to regulate the flow of Qi in the body and promote overall balance and well-being.
Shang Liao | Upper Bone Hole | Urinary Bladder 31 | UB-31
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine, known as the Midway between the greater trochanter and the sacral hiatus. It is located in the sacral region, at the level of the 2nd sacral foramen. UB-31 is believed to be effective in treating a variety of conditions, particularly those affecting the lower back and legs. It is often used to relieve pain and stiffness in the lower back, hips, and legs, as well as sciatica, hemorrhoids, and other conditions that affect the lower part of the body. Additionally, UB-31 is sometimes used to treat urinary and genital disorders, as well as menstrual cramps and irregular periods. In TCM theory, this point is located on the Urinary Bladder Meridian, which runs along the back of the body, and is considered to be a hui-meeting point of the tendons, which refers to a point where the meridian is particularly susceptible to therapeutic intervention.
Ci Liao | Second Bone Hole | Urinary Bladder 32 | UB-32
Known as the Ci Liao point, is an acupuncture point that is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located in the lower back, in the center of the sacrum, just below the fourth lumbar vertebrae. In traditional Chinese medicine, UB-32 is believed to regulate the function of the bladder and kidneys, and to promote the circulation of blood and energy in the lower back and legs. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as lower back pain, sciatica, and urinary incontinence. It is also believed to be helpful for menstrual cramps and irregular periods. To stimulate the UB-32 acupoint, an acupuncturist may use thin, sterile needles or apply pressure with their fingers or other tools. Other techniques such as moxibustion (the burning of herbs near the skin) may also be used in conjunction with the acupoint to enhance its effects. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to seek the services of a qualified and licensed practitioner.
Zhong Liao | Central Bone Hole | Urinary Bladder 33 | UB-33
This is an acupuncture point that is used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) to treat a variety of conditions. The point is located on the lower back, in the depression that is directly below the spinous process of the fourth sacral vertebra. Stimulation of the UB-33 point is believed to help regulate the function of the lower bowel and rectum, making it useful for treating conditions such as constipation, diarrhea, and hemorrhoids. It is also believed to help alleviate pain in the lower back and hips, making it useful for treating conditions such as sciatica and lower back pain. In TCM, UB-33 is also considered to be a point that helps to nourish the kidneys and tonify the Yang, or warming, energy in the body. This makes it useful for treating conditions related to the kidneys and bladder, such as frequent urination, urinary incontinence, and urinary tract infections. It is also thought to help regulate the menstrual cycle and alleviate menstrual pain in women. Overall, UB-33 is a versatile point that can be used to treat a variety of conditions related to the lower back, bowel and rectum, kidneys, and bladder. It is typically stimulated through acupuncture needles or acupressure, and should be used under the guidance of a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare provider.
Xia Liao | Lower Bone Hole | Urinary Bladder 34 | UB-34
Known as the Xia Liao point in Traditional Chinese Medicine, is an acupoint located on the sacral region, in the fourth posterior sacral foramen B-34 is commonly used to treat disorders of the lower back and sacrum, such as lumbago, sciatica, and lower limb paralysis. It can also be used to treat digestive disorders, such as constipation, as well as menstrual cramps, genital pain, and hemorrhoids. In traditional Chinese medicine, UB-34 is believed to be an important point for promoting the circulation of qi and blood in the lower limbs, as well as for tonifying the kidneys and strengthening the lumbar region. It is often used in combination with other acupoints to treat a variety of conditions. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a qualified acupuncturist to determine if this point is appropriate for your individual needs.
Hui Yang | Meeting of Yang | Urinary Bladder 35 | UB-35
Known as Hui Yang, is located in the lower back region. Specifically, it is located in the depression below the spinous process of the fourth sacral vertebra. UB-35 is believed to be useful in treating a wide range of conditions related to the lower back and pelvis. It is commonly used to treat lower back pain, sciatica, and pain and stiffness in the hips and legs. It is also used for menstrual disorders such as irregular periods, painful periods, and premenstrual syndrome (PMS). In traditional Chinese medicine, this acupoint is thought to be important for nourishing the kidney and regulating qi and blood flow in the lower back region. Stimulating this point is believed to improve the functioning of the kidneys, promote circulation of blood and energy, and help to alleviate pain and discomfort. UB-35 is often used in conjunction with other acupoints to provide a more comprehensive treatment for lower back and pelvic pain.
Cheng Fu | Support | Urinary Bladder 36 | UB-36
Known as Cheng Fu, is located on the back of the leg, 7 cun (finger widths) below the midpoint of the popliteal crease, between the medial and lateral heads of the biceps femoris muscle. UB-36 is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat various conditions related to the lower back and legs, including lower back pain, sciatica, leg cramps, and knee pain. It is also believed to have a regulating effect on the digestive system, and can be used to treat conditions such as constipation, diarrhea, and bloating. Additionally, UB-36 is often used to tonify the Qi and blood, promote circulation, and support overall health and well-being. It is considered a powerful point for strengthening the body's immune system, and can be used to treat conditions related to immune deficiency or weakness.
Yin Men | Gate of Abundance | Urinary Bladder 37 | UB-37
This is an acupuncture point in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the back of the leg, approximately 6 cun (Chinese inches) below UB-36, and one finger breadth (or cun) lateral to the midline of the leg. Stimulating this point is believed to have therapeutic effects on a range of conditions related to the lower body, including lower back pain, leg pain, knee pain, and sciatica. It may also be used to treat conditions related to the bladder, such as urinary incontinence or frequent urination. UB-37 is often used in conjunction with other acupuncture points and techniques, as part of a larger treatment plan tailored to the individual patient's needs. It is typically stimulated with acupuncture needles, although other techniques such as moxibustion (the burning of mugwort near the skin) may also be used. As with any medical treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner before attempting acupuncture.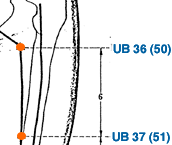
Fu Xi | Superficial Cleft | Urinary Bladder 38 | UB-38
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine that is used to treat a variety of conditions. It is known as the Fu Xi point and is located on the back of the thigh, 7 cun (finger-width) below the lower border of the gluteus maximus muscle and 2 cun (finger-width) lateral to the midline of the body. UB-38 is said to be effective for treating lower back pain, sciatica, hip pain, and pain in the legs. It is also believed to be useful in treating disorders of the urinary and reproductive systems, such as impotence, infertility, and irregular menstruation. Stimulating UB-38 is said to help improve the flow of Qi and blood through the affected area, reducing pain and promoting healing. It is often used in combination with other acupoints and TCM therapies, such as acupuncture, moxibustion, and herbal medicine, to achieve optimal results.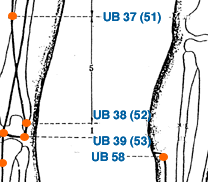
Wei Yang | Bend Yang | Urinary Bladder 39 | UB-39
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine that is located on the back of the lower leg, three cun (or fingerbreadths) below the popliteal crease and one fingerbreadth lateral to the posterior midline of the leg. It is known as Wei Yang in Chinese. Stimulating UB-39 is believed to have a number of therapeutic effects, including improving the health of the lower back and lumbar region, regulating qi and blood circulation, and treating conditions like lower back pain, sciatica, and leg pain. In addition, UB-39 is also thought to be effective in treating menstrual disorders and abdominal pain. As with all acupuncture treatments, it's important to consult with a qualified acupuncturist or healthcare provider before receiving treatment with UB-39 or any other acupoint.
Wei Zhong | Bend Middle | Urinary Bladder 40 | UB-40
Known as Wei Zhong, is an acupoint located in the back of the knee, in the center of the popliteal crease, where the knee joint bends. To locate this point, flex your knee joint, and UB-40 is found at the midpoint of the crease behind your knee. UB-40 is believed to be one of the most essential acupoints in the body. It is used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat various ailments and is associated with the Bladder Meridian. It is thought to stimulate the flow of Qi (vital energy) in the bladder channel, which helps regulate the body's water metabolism, strengthen the immune system, and promote healing. Some of the common conditions treated with UB-40 include knee pain, lower back pain, sciatica, constipation, diarrhea, urinary problems, menstrual cramps, and respiratory problems. This acupoint is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind, making it useful for treating insomnia and anxiety. Additionally, stimulating this acupoint is believed to help reduce swelling, stimulate blood circulation, and boost energy levels in the body.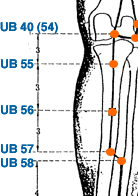
Fu Fen | Attached Branch | Urinary Bladder 41 | UB-41
This is an acupoint in the Urinary Bladder Meridian of the body. It is located on the upper back, 3 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the second thoracic vertebra (T2), at the level of BL 12. UB-41 is believed to have therapeutic effects on various conditions such as lower back pain, leg pain, knee pain, ankle pain, and heel pain. It is also believed to help with conditions related to the genitourinary system, such as cystitis, urethritis, impotence, and menstrual problems. In traditional Chinese medicine, UB-41 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi in the body and to remove any blockages or imbalances in the Bladder Meridian. It is often used in combination with other acupoints to treat various ailments. However, it's important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare professional before trying acupuncture or acupressure on your own.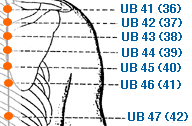
Po Hu | Po Door | Urinary Bladder 42 | UB-42
This is an acupuncture point that is known as Po Hu or the Po Door. This point is located on the back, 3 cun (finger widths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 7th thoracic vertebra. Stimulating UB-42 is said to be helpful in treating disorders that affect the back, spine, and lower limbs. It is believed to regulate and harmonize the flow of Qi and blood in the area, thereby providing relief from pain and inflammation. It is also believed to be helpful in treating conditions such as sciatica, knee pain, leg cramps, and heel pain. This point is usually stimulated by applying pressure or acupuncture needles, and it should be done under the guidance of a qualified and experienced acupuncturist.
Gao Huang Shu | Above The Diaphragm Shu | Urinary Bladder 43 | UB-43
Known as Gao Huang Shu, is an acupuncture point on the urinary bladder meridian. It is located on the back, at the level of the third thoracic vertebra, about 1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of T3. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), UB-43 is believed to regulate the function of the lungs, kidneys, and bladder. It is commonly used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma and bronchitis, as well as urinary and genital disorders, such as urinary retention, impotence, and irregular menstruation. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind, making it useful in the treatment of anxiety and depression. UB-43 can be stimulated with acupuncture needles, acupressure, or moxibustion. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to seek the advice of a qualified and licensed acupuncturist before undergoing treatment.
Shen Tang | Spirit Hall | Urinary Bladder 44 | UB-44
Known as the Shen Tang acupoint, is located on the back, 3 cun (finger widths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 4th thoracic vertebra. UB-44 is believed to be connected to the Liver meridian and is traditionally used to treat various conditions related to the Liver, such as liver qi stagnation, liver heat, and liver blood deficiency. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can be used to treat anxiety, depression, and insomnia. In addition, UB-44 is sometimes used to alleviate pain and stiffness in the lower back, hips, and legs. As with any acupuncture treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine if UB-44 is an appropriate treatment option for your specific needs.
Zhong Xing | Middle Star | Urinary Bladder 45 | UB-45
Known as the Middle Star or Zhong Xing in Chinese, is an acupoint located on the back, 3 cun (finger widths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 3rd thoracic vertebra. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, UB-45 is believed to regulate the circulation of qi and blood, harmonize the triple burner (a concept in Chinese medicine referring to the upper, middle, and lower parts of the body), and benefit the neck and spine. It is often used to treat conditions such as neck pain, stiffness, and tension, as well as headache, dizziness, and visual and auditory disorders. This point is also thought to have a calming effect on the mind and spirit, and may be used in the treatment of anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Additionally, UB-45 is sometimes used in the treatment of digestive disorders, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Ge Guan | Diaphragm Pass | Urinary Bladder 46 | UB-46
Known as the Diaphragm Pass, is an acupuncture point located on the back, 3 cun (finger widths) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the 2nd thoracic vertebra. This acupoint is believed to be effective for treating conditions such as low back pain, sciatica, leg pain, swelling and pain of the ankle, and general weakness and numbness of the lower limbs. Stimulating this point is also believed to help relieve stress and anxiety, as well as to promote better circulation throughout the body. However, it is important to note that acupuncture and acupressure should be used as complementary therapies, and individuals should seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional before using these therapies to treat any health conditions.
Hun Men | Hun Gate | Urinary Bladder 47 | UB-47
Known as Hun Men, is an important point in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the back, 3 cun (4 fingers) lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the eleventh thoracic vertebra (T11). Stimulating this point is believed to promote the circulation of qi and blood in the body, which can help to tonify the liver and kidneys and regulate the digestive system. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as lower back pain, sciatica, and digestive disorders. In addition, UB-47 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and emotions, making it a useful point for treating anxiety, stress, and other emotional imbalances. It is also believed to have a regulatory effect on the menstrual cycle and is commonly used in the treatment of gynecological disorders. As with all acupuncture points, UB-47 should only be stimulated by a trained acupuncturist using sterile needles to avoid infection or other adverse effects.
Yang Gang | Yang Headrope | Urinary Bladder 48 | UB-48
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the bladder meridian. It is known as the Yang Gang point and is believed to have therapeutic benefits for certain ailments. The location of UB-48 is on the back, midway between the spinous processes of the second and third lumbar vertebrae, approximately 3 cun (about 4 cm) lateral to the spine. In traditional Chinese medicine, UB-48 is believed to be effective in treating lower back pain, sciatica, and other disorders of the lumbar region. It is also believed to be beneficial for digestive disorders, such as constipation and diarrhea, as well as for conditions such as asthma and coughing. Additionally, UB-48 is thought to have a calming effect on the mind and may be used to treat anxiety and insomnia. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine whether UB-48 is an appropriate treatment option for your individual needs.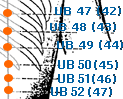
Yi She | Reflection Abode | Urinary Bladder 49 | UB-49
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the bladder meridian. It is known as Yi She, and it is translated as Yang Headrope in English. UB-49 is located on the back, below the spinous process of the eleventh thoracic vertebra. It is one and a half cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the eleventh thoracic vertebra. UB-49 is believed to be effective in treating conditions related to the lower back and spine. It is also used for conditions such as lower limb paralysis, pain and numbness in the legs, and constipation. Stimulating UB-49 is also thought to be useful in treating coughs, asthma, and other respiratory issues. Additionally, it is used for issues related to the spleen and the stomach, such as indigestion, bloating, and diarrhea. It is important to note that before undergoing any acupuncture treatment, it is essential to consult with a qualified practitioner to determine if it is appropriate and safe for you.
Wei Cang | Stomach Granary | Urinary Bladder 50 | UB-50
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine 3 cun lateral to the GV line, level with T12. In traditional Chinese medicine, this acupoint is believed to be associated with the Bladder meridian and is said to be effective in treating various conditions, including lower back pain, sciatica, and hip pain. It is also believed to have a regulatory effect on the bladder, making it potentially useful for the treatment of urinary incontinence or retention. In addition, it is thought to be beneficial for reproductive issues, such as impotence or menstrual disorders. As with all acupuncture points, it is recommended to consult a licensed acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Huang Men | Huang Gate | Urinary Bladder 51 | UB-51
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the small of the back, halfway between the top of the hip bone and the lower border of the ribcage. In TCM, UB-51 is believed to be the point where the kidney channel connects with the bladder channel. Stimulating this point is thought to benefit the kidneys, bladder, and lower back. UB-51 is also said to regulate Qi and blood, and help to relieve pain and stiffness in the lower back and legs. UB-51 is often used to treat conditions such as lower back pain, sciatica, urinary problems, and impotence. It may also be used to address digestive issues such as abdominal pain and diarrhea, as well as emotional problems such as anxiety and depression. As with all acupoints, it's important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare provider before using UB-51 or any other acupoint for self-treatment.
Zhi Shi | Will Chamber | Urinary Bladder 52 | UB-52
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is known as the Zhi Shi point and is located on the back, below the spinous process of the second lumbar vertebrae, approximately 3 cun lateral to the midline. This acupoint is commonly used to treat lower back pain, sciatica, and leg pain. It is believed that stimulation of this point can help to strengthen the lower back and relieve pain and stiffness in the surrounding area. Additionally, it may be used to treat urinary disorders, such as frequent urination or incontinence. As with any medical treatment, it is important to consult a licensed healthcare professional before seeking treatment with acupuncture or other forms of traditional Chinese medicine.
Bao Huang | Bladder Huang | Urinary Bladder 53 | UB-53
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine, known as the Urinary Bladder Meridian 53. This point is located in the lower back, at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra, and approximately three finger-widths lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the fourth lumbar vertebra. UB-53 is primarily used for treating disorders related to the bladder and the reproductive system, including urinary incontinence, enuresis, impotence, irregular menstruation, and dysmenorrhea. It is also sometimes used to treat lower back pain and sciatica. The stimulation of this acupoint can help to promote the flow of Qi and blood in the lower back, as well as improve the functioning of the bladder and reproductive system. It can be stimulated through acupuncture, acupressure, or moxibustion. As with all acupuncture points, it should be used only under the guidance of a qualified practitioner.
Zhi Bian | Sequential Limit | Urinary Bladder 54 | UB-54
Known as Zhi Bian, is located on the back of the body in the gluteal region, approximately 3 cun (approximately 4 fingers) lateral to the midline and at the level of the lower border of the sacrum. This acupoint is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine for treating conditions such as sciatica, lower back pain, hip pain, muscle cramps, and numbness or weakness in the legs. It is also believed to help regulate the function of the urinary bladder and alleviate disorders such as urinary incontinence, retention, and painful urination. Stimulation of UB-54 is typically performed using acupuncture needles, moxibustion, or acupressure. Moxibustion involves burning a small amount of dried mugwort on or near the skin at the acupoint to warm and stimulate the area, while acupressure involves applying pressure to the point with the fingers or a massage tool.
He Yang | Yang Union | Urinary Bladder 55 | UB-55
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that is believed to have therapeutic effects on various health conditions. This acupoint is located on the back of the leg, 2 cun (finger widths) directly below UB40 (Wei Zhong), in the depression between the medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius muscle. In TCM, UB-55 is believed to have a regulatory effect on the lower part of the body, especially the urinary and reproductive systems. This acupoint is traditionally used to treat conditions such as lower back pain, sciatica, hemorrhoids, constipation, diarrhea, and other disorders related to the lower abdomen and pelvis. UB-55 is also used to treat gynecological conditions such as irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, and uterine bleeding. Stimulation of UB-55 is typically achieved using acupuncture needles, moxibustion, or acupressure. However, it is important to note that while UB-55 has been used for centuries in TCM, further research is needed to determine its efficacy in treating specific health conditions. Therefore, it is recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare provider before using UB-55 for therapeutic purposes.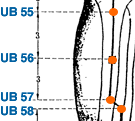
Cheng Jin | Sinew Support | Urinary Bladder 56 | UB-56
Known as Cheng Jin, is a point on the bladder meridian in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located in the center of the belly of the gastrocnemius muscle, about 7 cun or handbreadths above the tip of the inner ankle bone. UB-56 is often used to treat pain and stiffness in the lower back and leg, as well as cramps and other muscular issues in the leg. It is also believed to be useful in treating menstrual cramps and irregularities, as well as digestive problems and constipation. Additionally, UB-56 is believed to have a calming and grounding effect on the mind, and can be used to treat anxiety and insomnia. As with all acupoints, it is important to seek the guidance of a qualified practitioner before using UB-56 to treat any health condition.
Cheng Shan | Mountain Support | Urinary Bladder 57 | UB-57
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that is located on the posterior aspect of the lower leg, 8 cun (about 4 inches) above the prominence of the lateral malleolus, on the line connecting UB-60 and UB-40. This point is known as Cheng Shan, and it is believed to be effective in treating various ailments related to the lower body, especially those related to the bladder and lower back. It is said to help with conditions such as lower back pain, sciatica, leg pain, numbness, and muscular atrophy in the lower limbs. Stimulation of UB-57 is believed to help improve circulation in the lower body and promote the smooth flow of Qi and blood in the lower back and legs, helping to alleviate pain and discomfort. It is often used in combination with other acupoints to treat these types of conditions.
Fei Yang | Taking Flight | Urinary Bladder 58 | UB-58
Known as Fei Yang, is an acupuncture point located 7 cun directly above UB 60 on the posterior border of the fibula about 1 cun lateral and inferior to UB 57. This point is commonly used in acupuncture to treat conditions such as lower back pain, sciatica, leg pain, knee pain, ankle pain, and heel pain. It is also believed to help regulate the body's energy, promote circulation, and relieve stress and anxiety. Additionally, UB-58 may be used to treat conditions related to the ears, such as tinnitus and deafness. It is important to note that acupuncture points are often used in conjunction with other treatments, and any use of acupuncture should be supervised by a licensed and experienced acupuncturist.
Fu Yang | Instep Yang | Urinary Bladder 59 | UB-59
This is an acupuncture point located on the posterior aspect of the leg, in the depression between the tip of the external malleolus and tendo calcaneus. It is also called the Instep Yang. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, UB-59 is believed to regulate and nourish the liver and gallbladder channels. It is commonly used to treat a range of conditions, such as pain and stiffness in the lower back and legs, sprains, strains, and cramps in the calf and ankle, and foot drop (a condition that causes difficulty lifting the front part of the foot). UB-59 is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and is sometimes used to treat anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia. Additionally, it is sometimes used to treat menstrual cramps and irregular periods, as well as digestive disorders such as diarrhea and constipation. As with any acupuncture point, it's important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine whether UB-59 is appropriate for your specific condition and overall health status.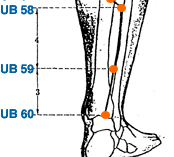
Kun Lun | Source of the Water | Urinary Bladder 60 | UB-60
This is an acupuncture point located on the ankle joint of the foot. It is known as Kunlun, which means the 'Source of the Water'. UB-60 is located in the depression between the prominence of the outer ankle bone and the Achilles tendon. This acupoint is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat disorders of the lower limbs, such as pain, numbness, and swelling in the foot, ankle, and heel. It is also used to treat headaches, neck pain, and dizziness. In addition, UB-60 is thought to be effective in treating insomnia, anxiety, and depression. Stimulation of UB-60 is often performed with acupuncture needles, but other techniques such as acupressure, moxibustion, and electroacupuncture may also be used. However, it is important to consult a qualified practitioner before attempting to use any of these techniques.
Pu Can | Subservient Visitor | Urinary Bladder 61 | UB-61
Known as Pu Can, is a point on the Urinary Bladder Meridian that is often used in acupuncture and acupressure treatments. It is located on the back of the ankle joint, in the depression between the tip of the lateral malleolus and the Achilles tendon. This acupoint is commonly used to treat conditions related to the bladder, such as urinary retention, frequent urination, and incontinence. It is also believed to be effective in treating pain and stiffness in the ankle and heel, as well as certain conditions affecting the reproductive and endocrine systems, such as menstrual cramps and infertility. Stimulating UB-61 is thought to help promote the free flow of Qi and blood throughout the body, which can help to alleviate pain and promote healing. It is often used in conjunction with other acupoints on the Bladder Meridian to treat a wide range of conditions, and is considered to be particularly effective when used in combination with the acupoint UB-60.
Shen Mai | Extending Vessel | Urinary Bladder 62 | UB-62
Known as Shen Mai, is located on the lateral side of the foot, in the depression distal to the fourth and fifth metatarsophalangeal joints, just below the head of the fifth metatarsal bone. This acupoint is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat a variety of conditions, such as headache, neck pain, dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus, deafness, sore throat, cough, asthma, insomnia, and anxiety. It is also believed to stimulate the body's immune system and improve overall energy and vitality. In addition, UB-62 is often used in conjunction with other acupoints to treat disorders of the lower limbs, such as ankle and foot pain, plantar fasciitis, and heel spurs. It is said to promote the free flow of Qi and blood in the meridians, helping to alleviate pain and stiffness. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to seek guidance from a qualified practitioner to determine if UB-62 is appropriate for your individual needs and health concerns.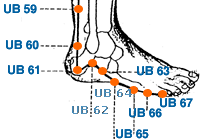
Jin Men | Metal Gate | Urinary Bladder 63 | UB-63
Known as Jin Men, is located on the lateral side of the foot, in the depression distal and inferior to the external malleolus. This acupoint is often used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat conditions related to the lower limbs, including pain and swelling in the ankle, heel, and foot. It is also believed to have a therapeutic effect on conditions that affect the head and neck, such as migraines, stiff neck, and sore throat. Additionally, UB-63 is said to be effective in treating emotional disorders, such as anxiety and depression, by helping to regulate the flow of Qi in the body. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to seek guidance from a qualified practitioner to determine if UB-63 is appropriate for your specific condition and medical history. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Urinary Bladder Meridian.
Jing Gu | Capital Bone | Urinary Bladder 64 | UB-64
This is an acupoint in the Urinary Bladder Meridian. It is located on the lateral side of the foot, in the depression between the fourth and fifth metatarsal bones, just distal to the base of the fifth metatarsal bone. UB-64 is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat conditions related to the lower back, legs, and feet. It is believed to be effective in relieving pain, numbness, and swelling in these areas. It is also believed to be useful in treating headaches and dizziness. In addition, UB-64 is often used to regulate the flow of Qi and blood, and to balance Yin and Yang in the body. This acupoint is often stimulated through acupuncture, acupressure, or moxibustion.
Shu Gu | Bundle Bone | Urinary Bladder 65 | UB-65
This is a point on the urinary bladder meridian. It is located on the lateral side of the foot, in a depression between the prominence of the lateral malleolus and the calcaneal tendon. Stimulating this point is thought to benefit conditions such as headache, neck pain, back pain, menstrual cramps, and digestive issues. It is also believed to be helpful in relieving symptoms of anxiety and insomnia. Additionally, UB-65 is commonly used to help turn a breech baby during pregnancy. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine if UB-65 is an appropriate treatment option for a specific condition.
Tong Gu | Valley Passage | Urinary Bladder 66 | UB-66
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the lateral side of the foot. It is known as the 'Valley Passage' because of its strong influence on the neck region. Specifically, UB-66 is found in the depression between the tip of the lateral malleolus (outer ankle bone) and the calcaneal tendon, at the level of the tip of the lateral malleolus. This acupoint is commonly used to treat conditions related to the neck, such as neck pain, stiffness, and tension. It is also believed to help with headaches, migraines, and other upper body discomforts. Additionally, UB-66 is thought to help with the symptoms of insomnia, anxiety, and depression. Some practitioners also use this point for gynecological disorders, such as menstrual cramps and irregular periods. As with all acupuncture points, it's important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare professional before using UB-66 or any other acupoint to address specific health concerns.
Zhi Yin | Reaching Yin | Urinary Bladder 67 | UB-67
This is an acupuncture point located on the small toe of the foot, at the lateral side of the tip of the toenail. It is known as the Zhiyin or Reaching Yin point in Traditional Chinese Medicine. In TCM, UB-67 is considered to be the starting point of the Yang Qiao Meridian, which runs from the foot up to the head. It is also believed to be connected to the uterus and can be used to promote labor, as well as for turning a breech baby in late-term pregnancy. In addition to its use in obstetrics, UB-67 is also believed to have a variety of other therapeutic benefits, such as promoting the descending of Qi (energy) and alleviating headache, neck pain, and other conditions related to the upper body. It is also used to clear heat and calm the mind. It is important to note that the use of UB-67 for inducing labor should only be performed by a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare professional who is trained in obstetric acupuncture, and should only be used under certain circumstances and with proper caution.
Liver Meridian
This meridian is commonly under the Element Wood.
Da Dun | Large Pile | Liver 1 | LR-1
This is an acupoint located on the big toe, just below the nail bed on the lateral side of the big toe. It is also known as Da Dun in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and is the first point of the Liver meridian. In TCM, LR-1 is believed to regulate the functions of the liver and improve the circulation of Qi and blood in the body. It is commonly used to treat conditions related to the liver, such as jaundice, hepatitis, and liver qi stagnation. It is also believed to have a regulating effect on the female reproductive system and can be used to treat menstrual disorders, PMS, and infertility. Additionally, LR-1 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the body, helping to improve energy levels and promote overall health and vitality. It can also be used to treat conditions related to the lower body, such as lower back pain, sciatica, and knee pain.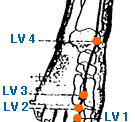
Xing Jian | Moving Between | Liver 2 | LR-2
Known as Xing Jian, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine that is located on the top of the foot, in the webbing between the big toe and the second toe. Specifically, it is found approximately 0.5 cun (or finger widths) proximal to the margin of the webbing between the two toes, in the depression that is created when the toes are dorsiflexed. In traditional Chinese medicine, LR-2 is believed to be associated with the liver meridian, and it is commonly used to treat a variety of conditions related to liver Qi stagnation, including menstrual disorders, digestive issues, emotional imbalances, and eye problems. It is also used to promote the smooth flow of Qi and blood throughout the body, and to regulate the emotions. LR-2 is often used in combination with other acupoints, depending on the specific condition being treated. It is typically stimulated with acupuncture needles, but can also be massaged or treated with moxibustion, a technique in which dried mugwort is burned near the skin to warm and stimulate the acupoint. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed and qualified practitioner before using LR-2 or any other acupoint for medicinal purposes.
Tai Chong | Great Rushing | Liver 3 | LR-3
Known as Tai Chong, which means Great Rushing. Location: LR-3 is located on the dorsum of the foot, in the depression anterior and inferior to the head of the first metatarsal bone. Function: In TCM, LR-3 is believed to regulate the Liver Qi, which is responsible for the smooth flow of Qi and blood throughout the body. By regulating the Liver Qi, LR-3 can help to alleviate a wide range of conditions, including headaches, menstrual cramps, anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Illnesses and Conditions: LR-3 is commonly used to treat a variety of illnesses and conditions such as: It is important to note that while acupuncture can be a helpful adjunct therapy for a variety of conditions, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. It is important to consult with a qualified healthcare provider before beginning any acupuncture treatment.
Zhong Feng | Mound Center | Liver 4 | LR-4
This is an acupuncture point located on the foot, in the depression anterior and inferior to the medial malleolus. Specifically, it is found in the depression distal and inferior to the junction of the first and second metatarsal bones. LR-4 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi throughout the liver meridian, which is associated with the liver and gallbladder organs in traditional Chinese medicine. Stimulating this acupoint is thought to help alleviate various conditions related to the liver and gallbladder, including jaundice, hepatitis, cholecystitis, and liver cirrhosis. Additionally, it may be used to address menstrual disorders, emotional imbalances, and headaches. It is important to note that while acupuncture can be beneficial for many conditions, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. It is always best to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before using acupuncture or any other complementary therapy.
Li Gou | Insect Ditch | Liver 5 | LR-5
This is an acupuncture point located on the medial aspect of the foot, in the depression distal and inferior to the medial malleolus. It is also called Insect Ditch in traditional Chinese medicine. Stimulating LR-5 is believed to have various therapeutic effects on the body, including regulating liver Qi, calming the mind, and resolving dampness. It is often used to treat gynecological disorders such as irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, and leukorrhea. Additionally, LR-5 can help to alleviate digestive issues such as abdominal bloating and diarrhea, as well as lower back pain and stiffness. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LR-5 for treatment.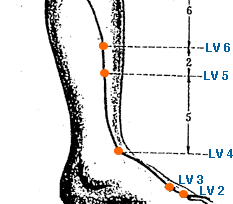
Zhong Du | Central Metropolis | Liver 6 | LR-6
Known as Zhong Du, is a point on the Liver Meridian in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the medial side of the leg, posterior to the tibial medial margin, 7 cun superior to the medial malleolus. Stimulating this point is believed to regulate the Qi (vital energy) and blood of the liver and promote the smooth flow of Qi and blood throughout the body. It is commonly used to treat gynecological and digestive issues, including menstrual irregularities, dysmenorrhea (painful periods), urinary incontinence, and constipation. Additionally, it may be used to relieve lower abdominal pain and promote fertility. As with any acupuncture point, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare practitioner before using LR-6 for any specific condition. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Gallbladder Meridian.
Xi Guan | Knee Joint | Liver 7 | LR-7
Known as Xi Guan or Knee Joint, is located on the medial side of the leg, inferior to the medial condyle of the tibia, in the upper
portion of the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle, 1 cun posterior to SP 9. This acupoint is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) to treat various conditions related to the liver, including menstrual disorders, hepatitis, depression, and anxiety. It is also used to relieve knee pain, lower back pain, and foot and ankle pain. In TCM, the liver meridian runs through the knee joint, and stimulating LR-7 is believed to help regulate liver qi and relieve stagnation. It is also said to promote the smooth flow of qi and blood throughout the body. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine if LR-7 is appropriate for an individual's specific condition and medical history.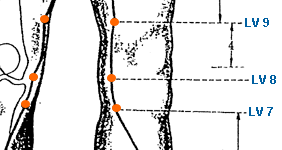
Qu Quan | Spring at the Bend | Liver 8 | LR-8
Known as Qu Quan, is located on the medial side of the knee, 3 cun (about 4 fingers) above the prominence of the medial malleolus, in the depression between the tendons of the semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles. Stimulation of LR-8 is thought to benefit conditions such as pain, swelling, and stiffness of the knee, leg cramps, and weakness or paralysis of the lower limb. It may also be useful for gynecological disorders such as irregular menstruation and uterine prolapse. Additionally, LR-8 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can help to relieve anxiety and insomnia. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using LR-8 for any specific condition.
Yin Bao | Yin Bladder | Liver 9 | LR-9
Known as Yin Bao, is an acupuncture point located on the medial thigh, 4 cun superior to the medial epicondyle of the femur, between sartorius muscle anteriorly and vastus medialis posteriorly. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, LR-9 is believed to regulate and harmonize the liver and spleen, and to nourish the yin and blood of the body. It is commonly used to treat gynecological disorders such as irregular periods, menstrual cramps, and menopausal symptoms. It is also believed to be effective in treating digestive disorders, including diarrhea, constipation, and bloating. Additionally, LR-9 is used to address emotional imbalances, including anger, irritability, and depression. LR-9 is often used in combination with other acupuncture points to enhance its therapeutic effects. It is usually needled bilaterally for a duration of 15 to 30 minutes. As with all acupuncture points, LR-9 should only be stimulated by a licensed acupuncturist using sterile needles.
Zu Wu Li | Foot Five Li | Liver 10 | LR-10
Known as Zu Wu Li, is located on the medial side of the thigh, 2 cun (finger widths) above the transverse popliteal crease and 3 cun (finger widths) lateral to the anterior midline. This point is used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) to treat a variety of conditions related to the liver and gallbladder meridians, including liver and gallbladder disorders such as hepatitis, cholecystitis, and gallstones. It is also used to treat menstrual disorders, genital pain, hernia, and leg pain. Acupressure or acupuncture stimulation of LR-10 can help regulate the liver and gallbladder qi, promote circulation of blood and qi in the lower body, and alleviate symptoms related to the above-mentioned conditions. As with all acupuncture points, it should only be stimulated by a qualified practitioner.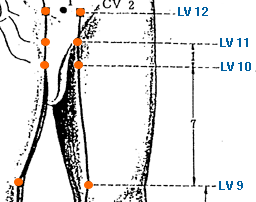
Yin Lian | Yin Corner | Liver 11 | LR-11
Known as Yin Lian, is located in the inguinal region, on the medial side of the thigh, midway between the symphysis pubis and the anterior superior iliac spine. This point is located on the Liver Meridian of the body. Stimulation of LR-11 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the liver and can help to regulate its function. This acupoint is commonly used to treat conditions such as menstrual disorders, genital pain, and inguinal hernias. It is also thought to be effective in treating digestive issues, such as constipation and diarrhea, as well as hip and groin pain. Acupuncturists may also use LR-11 as part of a treatment plan for emotional disorders such as anxiety and depression, as the liver is associated with emotions in traditional Chinese medicine. However, it is important to note that acupuncture should not be used as a sole treatment for any medical condition, and that individuals should seek the advice of a qualified healthcare practitioner before beginning any new treatment.
Ji Mai | Urgent Pulse | Liver 12 | LR-12
Known as Ji Mai or Urgent Pulse, is located on the lower abdomen, about 3 cun below the navel and 2 cun lateral to the anterior midline of the body. It lies on the same level as CV-3 and UB-25. This acupoint is mainly used to treat disorders related to the lower abdomen and reproductive organs, such as irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, leukorrhea, impotence, and infertility. It is also thought to be effective in treating digestive disorders, including abdominal pain, constipation, and diarrhea. Stimulating this acupoint is believed to regulate the Qi and Blood of the lower abdomen, promote the smooth flow of Qi and Blood in the Ren and Chong channels, and regulate the function of the uterus and ovaries. It is commonly used in combination with other acupoints to enhance its therapeutic effect.
Zhang Men | Camphorwood Gate | Liver 13 | LR-13
Known as Zhang Men, is an acupuncture point located on the lateral aspect of the abdomen, at the lower border of the 11th rib. It is approximately four finger-widths lateral to the anterior midline of the body. In traditional Chinese medicine, this point is believed to regulate the Liver Qi and soothe Liver Qi stagnation. It is commonly used to treat disorders of the Liver and Gallbladder, including abdominal pain, distension, and bloating, jaundice, hepatitis, cholecystitis, and gallstones. It is also thought to be effective in treating emotional and mental disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and irritability, which are believed to be related to Liver Qi stagnation. Additionally, LR-13 is believed to aid in the regulation of digestion, helping to alleviate symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare professional before seeking treatment.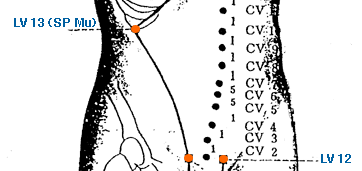
Qi Men | Cycle Gate | Liver 14 | LR-14
Known as Qi Men, is an acupuncture point located on the lateral aspect of the chest, in the sixth intercostal space, approximately 4 cm lateral to the nipple. In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), this point is considered to be the front Mu point of the liver meridian. Stimulation of this point is believed to benefit the liver and gallbladder and to promote the free flow of qi (energy) throughout the body. LR-14 is commonly used to treat conditions such as liver and gallbladder disorders, including jaundice, hepatitis, and cholecystitis. It is also used to alleviate pain in the chest and ribs, regulate menstruation, and treat emotional disorders such as depression, anger, and frustration. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare professional before attempting to use LR-14 for any health condition.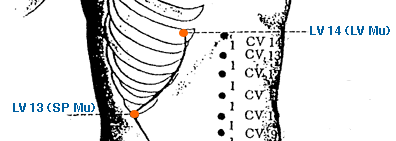
Gallbladder Meridian
This meridian is commonly under the Element Wood.
Tongzi Liao | Pupil Crevice | Gallbladder 1 | GB-1
This is an acupuncture point that is known as Tongziliao or Pupil Crevice. It is located at the lateral end of the eyebrow, in the depression directly above the outer canthus of the eye. GB-1 is traditionally used to treat eye disorders such as redness, itching, and tearing, as well as migraines, temporal headaches, and facial paralysis. It is also believed to be helpful for disorders of the ears, such as tinnitus and vertigo, as well as nasal congestion and sinusitis. Additionally, GB-1 is sometimes used to treat insomnia, anxiety, and depression. Stimulating this point can be done through acupressure, acupuncture, or with the use of moxibustion. However, it is important to seek the guidance of a qualified practitioner before attempting to use this point to treat any health condition.
Ting Hui | Auditory Convergence | Gallbladder 2 | GB-2
Known as Ting Hui, is located at the highest point of the ear, in the depression anterior to the intertragic notch. It is approximately at the same level as the corner of the eyebrow when the ear is folded forward. GB-2 is indicated for various conditions including headache, neck pain, ear problems, dizziness, facial paralysis, tinnitus, and blurred vision. It is also commonly used for calming the mind, reducing stress, and treating insomnia. GB-2 is believed to stimulate the flow of Qi (vital energy) in the Gallbladder meridian and regulate the function of the Gallbladder and Sanjiao (Triple Heater) organs. Additionally, it is often used in combination with other acupoints to enhance the effectiveness of treatment.
Shang Guan | Upper Gate | Gallbladder 3 | GB-3
Known as Shang Guan, is located in the temporal region of the head. Specifically, it is located in a depression at the midpoint of the eyebrow, directly above the pupil of the eye. GB-3 is the crossing point of the Gallbladder and Triple Heater meridians. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, GB-3 is believed to be connected to the gallbladder and the brain. This acupoint is commonly used to treat headaches, dizziness, migraines, and eye pain. It can also be used to treat emotional conditions such as depression and anxiety. Additionally, GB-3 may be helpful in reducing symptoms associated with allergies and sinusitis. GB-3 can be stimulated through various techniques, including acupressure, acupuncture, and moxibustion. It is recommended that you consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare provider before attempting to use GB-3 for any condition.
Han Yan | Forehead Fullness | Gallbladder 4 | GB-4
Known as the Han Yan acupoint, is located at the temple area, in a small depression anterior and superior to the center of the ear. This point is considered to be the meeting point of the Gallbladder meridian and the Yang Wei vessel. GB-4 is primarily used to treat headaches, migraines, and other disorders of the head and face. It is also commonly used to treat dizziness, vertigo, and tinnitus. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), GB-4 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi in the head and face, and to expel wind and clear heat from the body. It is also thought to nourish the eyes and improve vision. Additionally, GB-4 can be used to relieve stress and anxiety, as well as to treat insomnia. It is sometimes used in combination with other acupoints to treat hypertension, sinusitis, and trigeminal neuralgia. However, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using GB-4 or any other acupoint for medical purposes.
Xuan Lu | Suspended Head | Gallbladder 5 | GB-5
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) located in the temporal region, posterior to the hairline, midway between ST 8 and GB 7 GB-5 is commonly used to treat conditions such as migraines, headaches, and neck stiffness. It is also believed to improve eye disorders, tinnitus, and vertigo. Additionally, it is thought to have a calming effect on the mind and promote mental clarity. GB-5 is often combined with other acupoints in treatment protocols to enhance its effectiveness.
Xuan Li | Suspended Tuft | Gallbladder 6 | GB-6
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine that is located in the temporal region, posterior to the hairline, 2 cun inferior to GB4 on the curved line connecting ST 8 and GB 7. In traditional Chinese medicine, GB-6 is believed to be a key point for treating disorders of the gallbladder and liver, as well as related conditions such as jaundice, nausea, vomiting, and migraines. It is also commonly used for pain and stiffness in the neck and shoulder region, as well as for the treatment of hypertension and insomnia. In addition, some practitioners use GB-6 as a point for promoting digestion, stimulating the appetite, and regulating the menstrual cycle. As with any medical treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner of traditional Chinese medicine before using acupressure or acupuncture for any specific condition.
Qu Bin | Hill-Wind | Gallbladder 7 | GB-7
This is an acupoint in the Gallbladder meridian, known as Qu Bin, meaning Hill-Wind. It is located in the depression anterior to the ear and posterior to the condyloid process of the mandible. GB-7 is known to have a calming effect on the mind and helps in treating conditions like anxiety, depression, and insomnia. It is also helpful in treating migraines, vertigo, and ear disorders such as tinnitus and deafness. GB-7 is also considered to be beneficial in treating throat problems like sore throat and hoarseness of voice. It is often used in combination with other acupoints to treat these conditions. GB-7 should be used with caution in patients with a history of ear surgery or trauma in the area around the point.
Shuai Gu | Valley Lead | Gallbladder 8 | GB-8
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the head, on the scalp, just above the ear, between the Gallbladder meridian and the Triple Heater meridian. Specifically, it is located in the depression between the temple and the eyebrow, at the midpoint of a line connecting ST-8 and GB-7. GB-8 is traditionally used to treat various conditions related to the head and sensory organs, including headache, dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus, and blurry vision. It is also believed to be effective in treating conditions such as epilepsy, convulsions, and other nervous system disorders. In addition, GB-8 is sometimes used to treat emotional disorders such as anxiety and depression. However, it is important to note that acupuncture treatment should always be tailored to the individual's specific condition and should be carried out by a licensed and experienced practitioner.
Huang Men | Celestial Hub | Gallbladder 9 | GB-9
Known as Tian Chong, is an acupuncture point located on the head, in the depression on the scalp approximately 1.5 cm directly above the apex of the auricle (highest point of the ear). GB-9 is used to treat a variety of conditions related to the head and neck area. It is often used to treat headaches, especially migraines, as well as vertigo, dizziness, and tinnitus. Additionally, GB-9 can be used to address stiffness and pain in the neck and shoulder areas. According to traditional Chinese medicine theory, stimulating GB-9 can clear heat and wind from the body, improve circulation in the head and neck, and relieve pain and tension in the surrounding muscles and tissues. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind, making it useful for treating anxiety and other emotional conditions. However, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the effects of acupuncture and acupressure on the body and mind.
Fu Bai | Floating White | Gallbladder 10 | GB-10
This is an acupuncture point located on the head and is known as the Gallbladder Meridian 10 . It is located approximately 1.5 cun (fingerbreadth) behind the earlobe, within the hairline. GB-10 is primarily used to treat headaches, migraines, and vertigo, and is believed to help regulate the flow of Qi (energy) in the body. It can also be used to alleviate symptoms of hypertension, tinnitus, and earache. As with all acupuncture points, GB-10 should only be used by a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare professional who has been trained in the proper techniques and safety precautions. It is important to discuss any health concerns with a qualified practitioner before beginning acupuncture treatment.
Tou Qiao Yin | Head Portal Yin | Gallbladder 11 | GB-11
Known as Touqiaoyin, is located in the depression above the posterior border of the mastoid process, between the sternocleidomastoid muscle and trapezius muscle. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, GB-11 is believed to have a cooling and calming effect on the mind and is commonly used to treat headaches, migraines, vertigo, neck pain, and stiffness. It is also thought to have a beneficial effect on the ears, eyes, and throat, and can be used to treat tinnitus, deafness, sore throat, and difficulty swallowing. Additionally, GB-11 is believed to be helpful in treating emotional imbalances, anxiety, and depression. As with all acupoints, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner before using GB-11 for any specific condition, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or are pregnant.
Wan Gu | Completion Bone | Gallbladder 12 | GB-12
This is an acupuncture point located on the head, at the midpoint of the line connecting the lateral end of the eyebrow and the hairline, approximately 0.5 cm within the anterior hairline. GB-12 is known for its ability to alleviate pain, especially in the neck and shoulders, as well as in the face and head. It is often used to treat migraines, headaches, and facial pain. This point is also said to be effective in treating ear disorders such as tinnitus, deafness, and earaches. Additionally, it may be used to treat hypertension, anxiety, and depression. Stimulating this point can be done with acupuncture needles or acupressure, which involves applying pressure with the fingers or a massage tool. It is important to note that GB-12 should only be stimulated by a trained acupuncturist or healthcare professional, as improper stimulation can cause adverse effects.
Ben Shen | Root Spirit | Gallbladder 13 | GB-13
Known as Ben Shen, is located on the head, at the midpoint of the line connecting the lateral end of the eyebrow and the hairline. In traditional Chinese medicine, GB-13 is believed to help treat various conditions related to the head and mind, including headaches, migraines, vertigo, dizziness, tinnitus, and blurry vision. It is also believed to help calm the mind and improve mental clarity, making it useful for treating anxiety, depression, and insomnia. GB-13 can be stimulated by applying pressure or massage with the fingers, or by using acupuncture needles. It is typically used in combination with other acupoints to create a comprehensive treatment plan for the individual. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare practitioner before attempting to use GB-13 for any specific condition.
Yang Bai | Yang White | Gallbladder 14 | GB-14
Known as Yang Bai, is an acupuncture point located on the forehead, approximately 1 cm above the midpoint of the eyebrow. GB-14 is traditionally used to treat various conditions related to the head and face, including headaches, migraines, dizziness, and eye disorders. It is also believed to be effective in treating emotional disorders such as anxiety and depression. In traditional Chinese medicine, GB-14 is believed to be located at the crossing point of the gallbladder meridian and the triple burner meridian. It is thought to regulate the flow of energy and blood in the head and face region, as well as promote the movement of qi throughout the body. GB-14 should be stimulated with firm pressure or acupuncture needles for 1-2 minutes, and can be used in combination with other acupuncture points to treat various conditions. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Tou Lin Qi | Head Overlooking Tears | Gallbladder 15 | GB-15
Known as Tou Lin Qi in Chinese, is an acupoint located on the head, at the midpoint between the occipital protuberance (the highest point of the occipital bone) and the mastoid process (the bony prominence behind the ear), within the hairline. Stimulation of GB-15 is believed to benefit the brain and the eyes, and is used to treat a variety of conditions related to these organs, such as headaches, migraines, dizziness, vertigo, blurry vision, glaucoma, and cataracts. It is also thought to help with emotional disorders such as anxiety, depression, and irritability. In traditional Chinese medicine, GB-15 is often used in conjunction with other acupoints to address the root cause of the patient's symptoms. It is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare practitioner before attempting to use acupressure or acupuncture for any medical conditions.
Mu Chuang | Wind Screen | Gallbladder 16 | GB-16
This is an acupuncture point located on the Gallbladder meridian. It is known as the Wind Screen point, and is traditionally used for the treatment of headaches, dizziness, vertigo, and other disorders related to the head and neck. The location of GB-16 is on the head, approximately 1.5 cun (finger widths) posterior to the midpoint between the hairline and the top of the head, in the depression of the temporal region. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, GB-16 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi and Blood in the head, and to expel Wind and alleviate pain. It is often used in combination with other points to treat various conditions related to the head, including migraines, tension headaches, and trigeminal neuralgia. GB-16 is contraindicated for needling in patients who have had recent cranial surgery or trauma, as well as those with severe hypertension. It should also be needled with caution in patients with a history of stroke or other neurological disorders. It is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before receiving treatment.
Zheng Ying | Upright Construction | Gallbladder 17 | GB-17
Known as Zheng Ying, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the head, in the depression on the back of the head, just below the external occipital protuberance (the bony prominence at the base of the skull). This acupoint is commonly used to treat conditions related to the head and neck, including headaches, migraines, dizziness, and vertigo. It is also believed to be effective for treating disorders related to the eyes and ears, such as tinnitus and blurred vision. Additionally, GB-17 is thought to be helpful in the treatment of depression and anxiety. GB-17 is often used in conjunction with other acupoints to create a comprehensive treatment plan for the conditions mentioned above. As with all acupoints, it should only be used under the guidance of a trained and licensed acupuncturist.
Cheng Ling | Spirit Support | Gallbladder 18 | GB-18
Known as Cheng Ling, is an acupuncture point located on the head, at the midpoint between the external occipital protuberance (the bony bump at the base of the skull) and the mastoid process (the bony prominence behind the ear), on the same horizontal level as GB17. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), GB-18 is considered to be a vital point for treating various conditions such as headache, vertigo, dizziness, and visual disturbance. It is also believed to be beneficial for treating hypertension, stress, and emotional imbalances such as irritability, anger, and depression. GB-18 is an important point in TCM because it is located on the Gallbladder meridian, which is associated with decision making and action. The point is believed to help clear the mind, strengthen decision-making abilities, and promote action and initiative. It is also considered to be a point for tonifying the Qi (energy) and blood in the body, which can help to alleviate fatigue, weakness, and other symptoms of deficiency.
Nao Kong | Window of the Sky | Gallbladder 19 | GB-19
Known as the Window of the Sky, is an acupoint that is located on the head and is used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat various disorders related to the head and neck region. Location: GB-19 is located in the occipital region, 2.25 cun lateral to the posterior midline, at the level of the upper border of the external occipital protuberance. Indications: In traditional Chinese medicine, GB-19 is believed to be useful in treating disorders related to the head and neck region, including headaches, migraines, neck stiffness, dizziness, vertigo, and blurred vision. It is also used to alleviate emotional disturbances such as depression, anxiety, and insomnia. According to traditional Chinese medicine theory, GB-19 is considered to be a window of the sky point, meaning it has a strong effect on the flow of Qi (life force energy) between the head and the rest of the body. It is believed that by stimulating GB-19, practitioners can regulate the flow of Qi in the body and promote a healthy balance of energy throughout the entire system. As with any medical treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed and qualified healthcare practitioner before using acupuncture or any other form of traditional Chinese medicine.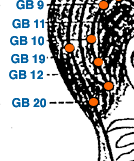
Feng Chi | Wind Pool | Gallbladder 20 | GB-20
Known as Feng Chi, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the posterior aspect of the neck, in the depression between the upper portion of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the trapezius muscle. To locate the point, first, locate the mastoid bone behind the ear, then follow the groove back to the neck. GB-20 is commonly used to treat a wide range of conditions related to the head and neck, including headache, neck pain, dizziness, tinnitus, vertigo, and insomnia. It is also thought to help with hypertension, depression, anxiety, and eye problems such as blurred vision and optic nerve atrophy. The point is believed to regulate the flow of Qi and blood to the head, soothe the liver, and calm the mind. It is often used in combination with other acupoints to enhance its therapeutic effects. GB-20 can be stimulated with acupuncture needles or acupressure.
Jian Jing | Shoulder Well | Gallbladder 21 | GB-21
Known as Jian Jing or Shoulder Well, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the shoulder. It is located in the depression between the upper part of the shoulder blade and the spine, approximately halfway between the base of the neck and the tip of the shoulder. This acupoint is believed to help relieve tension and pain in the neck and shoulders, as well as alleviate headaches and migraines. It is also thought to help regulate the flow of qi (vital energy) in the body and promote relaxation. GB-21 is often used in combination with other acupoints to treat conditions such as neck and shoulder pain, stiffness and tension, headaches, migraines, and stress. It is also sometimes used to help relieve the symptoms of respiratory disorders such as asthma and bronchitis. However, it is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare provider before attempting to use acupuncture for any health condition.
Yuan Ye | Armpit Abyss | Gallbladder 22 | GB-22
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the gallbladder meridian. It is known as Yuan Ye or Armpit Abyss. The location of GB-22 is in the hollow below the axilla (armpit), halfway between the acromion and the fifth rib. GB-22 is believed to have a regulating effect on the gallbladder and can help to relieve gallbladder disorders such as gallstones, gallbladder inflammation, and biliary colic. It may also be used to alleviate chest pain, difficulty breathing, and arm pain. Additionally, GB-22 is thought to have a calming effect on the mind, making it useful for anxiety and stress-related disorders. GB-22 is often used in combination with other acupoints as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Zhe Jin | Sinew Seat | Gallbladder 23 | GB-23
Known as Zhe Jin, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine that is located on the lateral aspect of the chest, on the midclavicular line, in the sixth intercostal space. Stimulation of this acupoint is believed to help with various conditions such as chest pain, cough, asthma, and breast disorders. GB-23 is also thought to be effective in treating emotional disorders such as depression, anxiety, and irritability. GB-23 is commonly used in combination with other acupoints to treat conditions such as angina pectoris, intercostal neuralgia, pleurisy, and bronchitis. It is also believed to help regulate the Liver and Gallbladder meridians, as well as improving Qi circulation in the chest and breast areas. As with any medical treatment, it's important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare provider before using GB-23 or any other acupoint for therapeutic purposes.
Ri Yue | Sun and Moon | Gallbladder 24 | GB-24
Known as Ri Yue, is an acupoint located on the body, approximately 2 cun (finger widths) lateral to the lower border of the free end of the 11th rib, and approximately 4 cun (finger widths) lateral to the navel. GB-24 is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) to treat digestive and liver-related disorders. It is believed that stimulating this acupoint can help to regulate the flow of Qi and blood, strengthen the liver and gallbladder, promote bile secretion, and relieve symptoms such as bloating, abdominal distension, and jaundice. GB-24 is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can be used to treat anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Additionally, GB-24 is sometimes used to relieve pain in the chest and upper abdomen. As with all medical treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed healthcare provider before using acupuncture or acupressure to treat any condition.
Jing Men | Capital Gate | Gallbladder 25 | GB-25
Known as Jing Men, is an acupuncture point located on the lateral aspect of the abdomen, approximately 2 cun (finger widths) anterior and inferior to the free end of the 12th rib. In traditional Chinese medicine, GB-25 is believed to regulate the gallbladder, the liver, and the spleen. It is also used to alleviate pain, especially in the lower abdomen and back. GB-25 is commonly used to treat conditions such as liver and gallbladder disorders, digestive disorders, lower back pain, and menstrual disorders. It is also used to alleviate symptoms associated with urinary disorders, hernia, and emotional stress. Acupressure or acupuncture at this point is generally considered safe and can be effective in combination with other treatments for the above conditions. However, it is always recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare professional before attempting any kind of treatment.
Dai Mai | Girdling Vessel | Gallbladder 26 | GB-26
Known as Dai Mai, is an acupuncture point that is located on the lower abdomen, 4 cun (finger widths) lateral to the midline, and 3 cun (finger widths) inferior to the umbilicus, at the level of the upper border of the pubic symphysis. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, GB-26 is believed to regulate the Dai meridian and benefit the lower abdomen, hips, and lower back. It is commonly used to treat gynecological disorders such as irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, and amenorrhea. It may also be used to relieve lower back pain, sciatica, and digestive disorders such as constipation and diarrhea. In addition, GB-26 is thought to have a regulating effect on emotions and is sometimes used to treat emotional disorders such as anxiety, stress, and depression. It may also be used to promote urination and improve overall body circulation. However, it is important to note that acupuncture should not be used as a replacement for conventional medical treatment and should always be done under the guidance of a qualified practitioner.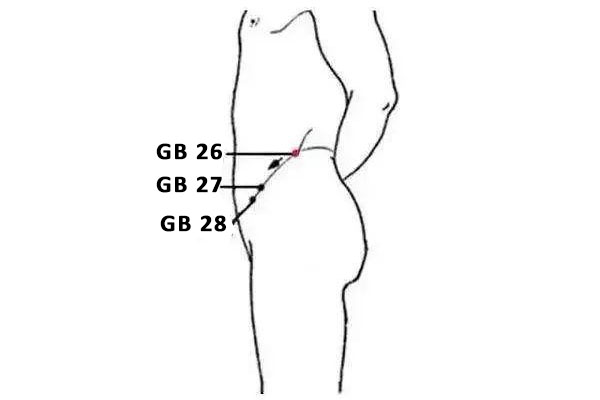
Wu Shu | Fifth Pivot | Gallbladder 27 | GB-27
Known as Wu Shu, is an acupoint located in the lower abdomen. Specifically, it is located four cun (a unit of measurement) lateral to the midline of the lower abdomen, on the level of the upper border of the pubic symphysis. GB-27 is believed to have several benefits for the body, both physical and mental. It is commonly used to treat issues with the lower abdomen and reproductive system, such as menstrual cramps, urinary tract infections, and impotence. Additionally, GB-27 is thought to have an impact on emotional well-being and can be used to treat anxiety, depression, and stress. In traditional Chinese medicine, GB-27 is considered to be a meeting point of the kidney, bladder, and large intestine meridians. Stimulating this point is thought to help regulate the qi (energy) flow between these meridians and promote overall health and balance in the body. It is often used in conjunction with other acupoints and treatments to address specific health concerns.
Wei Dao | Linking Path | Gallbladder 28 | GB-28
Known as Wei Dao, is an acupuncture point that belongs to the Gallbladder meridian. It is located in the lower abdomen, 3 cun below the umbilicus and 2 cun lateral to the midline. In traditional Chinese medicine, GB-28 is believed to regulate the Qi flow in the Gallbladder and Liver meridians, as well as promote the circulation of Blood and Qi in the lower abdomen. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as lower abdominal pain, hernia, and irregular menstruation. In addition, GB-28 is known for its ability to promote the smooth flow of urine and alleviate urinary dysfunction, making it a useful point for treating conditions such as urinary tract infections and bladder problems. It may also be used to treat digestive disorders such as constipation, diarrhea, and indigestion. As with any acupuncture point, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using GB-28 to treat any health condition.
Ju Liao | Squatting Bone Hole | Gallbladder 29 | GB-29
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine, known as Ju Liao. It is located on the lateral aspect of the thigh, 5 cun (finger widths) directly above the popliteal crease, in the depression between the femur and the tensor fasciae latae muscle. GB-29 is traditionally used to treat disorders of the lower back and legs, such as sciatica, hip pain, and leg weakness. It is also believed to be effective in treating disorders of the genitourinary system, including urinary incontinence and difficulty with urination. Stimulating this point is thought to promote the smooth flow of Qi and blood in the lower body, as well as tonify the Kidney and Liver channels. It is commonly used in combination with other acupoints to provide relief from pain and improve overall mobility. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner before seeking treatment.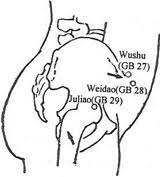
Huan Tiao | Jumping Round | Gallbladder 30 | GB-30
Known as Huan Tiao, is an important point in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the lateral side of the buttock, at the junction of the sacrum and the femur bone. Specifically, it is found in the depression below the anterior superior iliac spine, at the midpoint of a line connecting the tip of the coccyx and the greater trochanter. This acupoint is commonly used for treating a wide range of conditions, including low back pain, hip pain, sciatica, numbness or weakness in the lower limbs, and muscle tension or spasm in the hip and thigh. It is also used to promote the circulation of qi and blood throughout the body. To activate this point, acupuncturists may use needles or moxibustion, a technique in which a small amount of an herb called mugwort is burned near the skin to warm the area and stimulate circulation. Self-massage or pressure on this point may also be effective for those who prefer non-invasive techniques. However, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner before attempting any acupressure or acupuncture techniques.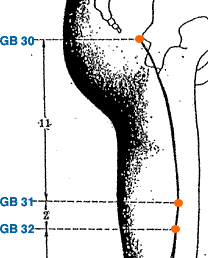
Feng Shi | Wind Market | Gallbladder 31 | GB-31
Known as Feng Shi, is an acupuncture point on the Gallbladder meridian. It is located on the lateral side of the thigh, in the depression anterior and inferior to the head of the greater trochanter of the femur. GB-31 is commonly used to treat conditions related to the lower limbs, including hip pain, thigh pain, knee pain, and leg paralysis. It is also believed to have a regulatory effect on the Gallbladder meridian and may be used to treat disorders associated with this meridian, such as migraines, hypertension, and emotional disorders like anger and irritability. In addition, GB-31 may be used to treat disorders of the genitourinary system, such as urinary retention and impotence. However, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine the appropriate use of this point for specific conditions.
Zhong Duon | Knee Yang Joint | Gallbladder 32 | GB-32
Located on the lateral aspect of the thigh. Specifically, it is located 6 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) superior to the popliteal crease, between the tendons of the biceps femoris and the vastus lateralis muscles. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), GB-32 is believed to regulate the Liver and Gallbladder meridians. It is commonly used to treat lower limb issues, such as pain, swelling, and numbness in the knee, leg, and foot. It can also help with sciatica, lower back pain, and muscular atrophy. Additionally, GB-32 is considered a meeting point of the tendons and muscles, making it useful in treating sprains, strains, and other injuries affecting the lower limbs. In TCM, it is also thought to help with emotional imbalances related to the Liver and Gallbladder, such as irritability, depression, and anger.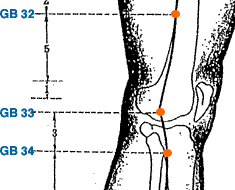
Xi Yang Guan | Knee Yang Joint | Gallbladder 33 | GB-33
Known as the Yang Ling Quan or Yang Mound Spring, is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine. It is located on the lateral aspect of the lower leg, 3 cun (approximately 4 fingers) superior to the prominence of the lateral malleolus, in the depression anterior and inferior to the head of the fibula. Stimulation of GB-33 is believed to have various therapeutic effects, including treating disorders of the lower limbs, such as knee pain, lower leg pain, and ankle pain. It is also believed to benefit the lower back and lumbar region, and can be used to treat sciatica, lower back pain, and other related conditions. Additionally, GB-33 is believed to be helpful in regulating the qi and blood flow, improving circulation, and strengthening the immune system. GB-33 can be stimulated through acupuncture, acupressure, or moxibustion. However, as with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare practitioner before attempting any treatment.
Yang Ling Quan | Yang Mound Spring | Gallbladder 34 | GB-34
Known as the Yang Ling Quan or Yang Mound Spring, is an acupoint located on the lateral aspect of the lower leg. It is located in the depression anterior and inferior to the head of the fibula, about one finger-breadth from the crest of the tibia. GB-34 is a widely used acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine and is believed to have a variety of therapeutic effects. It is primarily used to treat disorders of the liver and gallbladder, such as jaundice, hepatitis, and cholecystitis. It is also commonly used to treat knee pain, muscle cramps, and numbness or paralysis of the lower limbs. In addition, GB-34 is believed to have a regulating effect on the flow of qi and blood throughout the body, making it a useful point for treating a wide range of conditions, including digestive disorders, menstrual cramps, and emotional imbalances such as depression and anxiety. Acupuncture practitioners typically stimulate GB-34 with acupuncture needles or by applying pressure with their fingers or other instruments. The point is generally considered safe, although as with any acupuncture treatment, it is important to seek treatment from a qualified practitioner to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Yang Jiao | Yang Intersection | Gallbladder 35 | GB-35
Known as Yang Jiao, is an acupuncture point that is located in the lateral aspect of the lower leg. It is found on the line joining the head of the fibula and the prominence of the lateral malleolus, 7 cun above the latter. In traditional Chinese medicine, GB-35 is used to treat conditions related to the lower limbs, such as pain and stiffness in the knee, ankle and foot. It is also believed to help relieve lower back pain, sciatica, and hip joint pain. GB-35 is also considered to be useful in treating gynecological disorders, such as irregular periods, menstrual cramps, and uterine bleeding. Additionally, it is thought to be effective in treating digestive issues, such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. GB-35 can be stimulated by applying firm pressure to the point or by using acupuncture needles. It is recommended that individuals seek the advice of a licensed acupuncturist for proper diagnosis and treatment.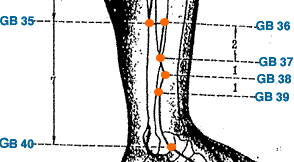
Wai Qiu | Outer Hill | Gallbladder 36 | GB-36
Known as Wai Qiu, is an acupoint located on the lower leg. It is found 7 cun above the prominence of the lateral malleolus, in the depression anterior and inferior to the head of the fibula. GB-36 is often used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat various illnesses and conditions. It is believed to be effective in treating disorders of the digestive system, such as diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. It is also thought to help regulate the menstrual cycle and alleviate menstrual pain. Additionally, GB-36 is believed to be beneficial in treating conditions such as ankle pain, knee pain, and lower back pain. GB-36 can be stimulated through various techniques, including acupuncture, acupressure, and moxibustion. However, it is important to seek the guidance of a qualified and licensed practitioner before attempting any form of treatment. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Gallbladder Meridian.
Guang Ming | Bright Light | Gallbladder 37 | GB-37
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine that is located on the lower leg. Specifically, it is found on the lateral side of the leg, 5 cun (about four fingers) above the tip of the external malleolus, in a depression anterior and inferior to the fibular head. This acupoint is known as Guang Ming, which means Bright Light in Chinese, and it is believed to be a point that can bring brightness to the eyes. GB-37 is often used to treat conditions related to the eyes and vision, such as blurred vision, cataracts, and night blindness. It can also be used to alleviate pain and inflammation in the knee and lower leg, and to treat disorders of the genitourinary system, such as painful urination, impotence, and irregular menstruation. GB-37 is also thought to be helpful in relieving stress and anxiety, and promoting relaxation. It is typically stimulated by needling, acupressure, or moxibustion.
Guang Ming | Yang Assistance | Gallbladder 38 | GB-38
Known as Yang Fu, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the lateral side of the lower leg, 4 cun above the prominence of the lateral malleolus, in the depression anterior and inferior to the head of the fibula. In TCM, GB-38 is believed to be associated with the Gallbladder meridian and is often used to treat disorders related to this organ, such as jaundice, cholecystitis, and gallstones. It is also believed to have a regulating effect on the liver and to be useful in treating conditions such as depression, anxiety, and menstrual disorders. Additionally, it may be used to treat pain and swelling in the lower leg, ankle, and foot, as well as sciatica and hip pain. Acupressure or acupuncture stimulation of this point is thought to promote the flow of Qi and blood in the meridians and help to balance the body's energy. However, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare provider before trying to stimulate GB-38 or any other acupoint on your own.
Xuan Zhong | Suspended Bell | Gallbladder 39 | GB-39
Known as Xuan Zhong, is an acupuncture point located on the lateral side of the lower leg, 3 cun superior to the prominence of the lateral malleolus, and one finger-breadth (1 cun) posterior to the anterior border of the fibula. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, GB-39 is believed to have a regulatory effect on the Gallbladder channel, as well as the Liver channel. It is also believed to have a tonifying effect on the Qi and Blood of the whole body, and is commonly used to treat conditions related to these channels and substances. Some of the conditions that GB-39 may be used to treat include: As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult a qualified acupuncturist before using GB-39 or any other acupuncture point to treat a specific condition.
Qiu Xu | Hill Ruins | Gallbladder 40 | GB-40
Known as Qiu Xu, is an acupuncture point located on the foot. Specifically, it is located in the depression distal and inferior to the lateral malleolus, between the tendons of the peroneus longus and brevis muscles. GB-40 is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat various conditions. It is believed to regulate the flow of qi and blood, relieve pain, and clear dampness. GB-40 is commonly used to treat disorders of the lower limbs, including ankle pain, cramps, and stiffness. It is also used to treat conditions such as migraines, dizziness, and menstrual disorders. Additionally, GB-40 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and is sometimes used to treat anxiety and insomnia. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using GB-40 or any other acupuncture point to treat a specific condition.
Zu Lin Qi | The Fall of Tears | Gallbladder 41 | GB-41
Known as Zu Lin Qi or The Fall of Tears, is an acupuncture point located on the foot. Specifically, it is located on the lateral aspect of the foot, in the depression distal to the junction of the fourth and fifth metatarsal bones. This point is often used to treat various disorders related to the ankle and foot, such as sprains, pain, and numbness. It is also used for menstrual disorders, anxiety, and depression. Stimulation of GB-41 can help to clear heat from the body, promote the smooth flow of qi, and relieve pain. Additionally, it is believed to help regulate the liver and gallbladder meridians, which can help to improve digestion and promote overall well-being.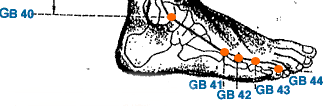
Di Wu Hui | Earth Fivefold Convergence | Gallbladder 42 | GB-42
Known as Di Wu Hui, is located on the dorsal side of the foot, between the fourth and fifth toes, in the depression proximal to the margin of the web at the junction of the red and white skin. This acupoint can be located by sliding the finger towards the margin of the web from the fourth toe. GB-42 is believed to be associated with various conditions such as headaches, neck and shoulder pain, vision problems, and anxiety. It is also commonly used for foot-related disorders such as plantar fasciitis, heel pain, and ankle sprains. Stimulating GB-42 can help to promote the smooth flow of qi and blood, reduce pain and inflammation, and regulate the function of the liver and gallbladder. This point is often used in acupuncture and acupressure treatments for these conditions. It is important to note that GB-42 should not be stimulated during pregnancy as it is believed to have an effect on the uterus.
Xia Xi | Pinched Ravine | Gallbladder 43 | GB-43
Known as Xia Xi, is an acupoint located on the dorsum (upper part) of the foot. Specifically, it is located at the junction of the fourth and fifth metatarsal bones, approximately 0.5 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) proximal to the margin of the web between the fourth and fifth toes. GB-43 is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat disorders related to the Gallbladder meridian, including gallstones, cholecystitis, jaundice, and biliary tract disorders. It is also used for treating headaches, migraines, neck and shoulder pain, and earaches. GB-43 is believed to help clear heat and dampness, as well as promote the smooth flow of Qi and Blood throughout the body. To stimulate this acupoint, a practitioner may use acupuncture needles, acupressure, or moxibustion. Moxibustion involves the burning of an herb called mugwort near the skin at the acupoint to stimulate the flow of Qi and blood. Acupuncture and acupressure both involve applying pressure or needles to the acupoint to stimulate the flow of Qi and promote healing. It is important to consult with a licensed practitioner before attempting any acupoint stimulation on your own.
Zu Qiao Yin | Foot Portal Yin | Gallbladder 44 | GB-44
Known as Zu Qiao Yin, is located on the fourth toe, on the dorsum of the foot, at the junction of the proximal one third and the distal two thirds of the nail bed. GB-44 is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat a variety of conditions, including headaches, migraines, eye pain, fever, sore throat, toothache, and anxiety. It is also used to promote labor and relieve postpartum bleeding. This point is believed to be effective in regulating the energy flow of the liver and gallbladder meridians, which may be the reason for its effectiveness in treating these conditions. However, it is important to note that acupuncture should be used as a complementary therapy and not a replacement for conventional medical treatment. Patients should always consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare professional before seeking treatment.
Heart Meridian
This meridian is commonly under the Element Fire.
Ji Quan | Highest Spring | Heart 1 | HT-1
This one is located In the center of the axilla on the radial side of the axillary artery. HT-1 is commonly used for treating cardiac disorders, such as palpitations, angina pectoris, and irregular heartbeat. It is also used to treat mental and emotional issues, such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia, as it is believed to calm the spirit and regulate the Heart. In addition, HT-1 is thought to improve circulation, relieve pain, and strengthen the immune system. HT-1 is often combined with other acupuncture points, such as PC-8 and HT-7, to enhance its therapeutic effects. However, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before receiving treatment, as the use of HT-1 may not be appropriate for everyone.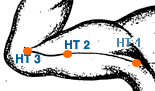
Xing Jian | Middle of the Heart | Heart 2 | HT-2
This one is located on the medial arm when the elbow is flexed, 3 cun proximal to the transverse cubital
crease. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, HT-2 is believed to be a very important acupoint for regulating the heart and mind. It is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and emotions, and is often used to treat conditions such as anxiety, insomnia, palpitations, and other emotional imbalances. It may also be used to regulate the heart's rhythm and treat heart-related conditions such as angina, hypertension, and arrhythmias. HT-2 is often used in combination with other acupoints to enhance its therapeutic effect. It can be stimulated using various techniques such as acupuncture, acupressure, or moxibustion. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner to determine if HT-2 is appropriate for individual needs and concerns.
Shao Hai | Lesser Sea | Heart 3 | HT-3
This is a point located With the elbow flexed, between the ulnar end of the cubital crease and the medial epicondyle of the humerus. HT-3 is a commonly used acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine for treating various conditions, particularly those related to the heart and chest. It is believed to regulate the heart qi and blood, and to have a calming effect on the mind and emotions. It is commonly used to treat heart palpitations, chest pain, insomnia, and anxiety, as well as other conditions such as hypertension, mania, and epilepsy. Acupuncturists may stimulate HT-3 using acupuncture needles, moxibustion, or acupressure. However, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare practitioner before using acupuncture or other alternative therapies.
Ling Dao | Spirit Pathway | Heart 4 | HT-4
This one is located on the radial aspect of the forearm, approximately three finger-widths proximal to the wrist crease, in a depression between the tendons of the palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis muscles. It is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat a variety of conditions related to the heart and the chest. Stimulation of HT-4 is believed to be beneficial for heart conditions such as palpitations, angina, and hypertension. It is also used to alleviate chest pain, tightness or discomfort, as well as emotional disturbances such as anxiety, insomnia, and depression. In addition, HT-4 is thought to help with wrist and arm pain, as well as to regulate menstrual cycles and alleviate menstrual cramps. HT-4 is commonly used in conjunction with other acupoints for a more comprehensive treatment approach.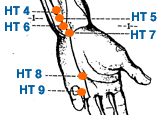
Tong Li | Connecting Li | Heart 5 | HT-5
This one is located on the radial aspect of the forearm, two cun proximal to the transverse crease of the wrist, between the tendons of the brachioradialis and the abductor pollicis longus muscles. This point is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat a variety of conditions, including heart palpitations, chest pain, anxiety, insomnia, mania, and depression. It is also thought to help improve circulation and relieve pain in the arm and hand. Additionally, HT-5 is believed to have a regulating effect on the heart, and is often used in conjunction with other acupoints to balance the body's energy and promote overall health and well-being.
Yin Xi | Yin Cleft | Heart 6 | HT-6
This one is located on the inside of the forearm, about 2 cun (approximately the width of the person's thumb at the middle joint) above the wrist crease. More specifically, it is located on the transverse cubital crease, midway between the radial border of the styloid process of the ulna and the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. HT-6 is believed to have a number of therapeutic effects, including the ability to calm the mind, regulate the heart, and balance the yin and yang energies in the body. It is commonly used in the treatment of conditions such as insomnia, anxiety, depression, and palpitations. HT-6 is also believed to be beneficial for menstrual disorders, especially irregular periods, and for the treatment of some digestive disorders, including diarrhea and abdominal pain. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Heart Meridian.
Shen Men | Spirit Gate | Heart 7 | HT-7
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) located at the wrist crease, on the radial side of the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon, between the ulna and the pisiform bones. HT-7 is considered a powerful point in TCM as it is said to connect with the Heart meridian, and it is thought to help balance the emotions and calm the mind. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as anxiety, insomnia, palpitations, and other emotional disorders. HT-7 is also believed to have a sedative effect on the nervous system, making it a helpful point for reducing stress and tension. In addition, HT-7 is said to have a regulating effect on the heart and blood vessels, which can help improve blood circulation and lower blood pressure. It is also believed to have an effect on the immune system and can be used to strengthen the body's natural defenses. HT-7 is often used in combination with other points to treat a variety of conditions related to the heart, mind, and immune system.
Shao Fu | Lesser Mansion | Heart 8 | HT-8
This is an acupoint that is used in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the palm side of the hand, in the depression between the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones, when a fist is made. In TCM, HT-8 is believed to regulate the heart and help calm the spirit. It is often used to treat conditions related to the heart, such as palpitations, chest pain, and insomnia. It may also be used to relieve anxiety and depression. To stimulate this acupoint, acupressure or acupuncture may be used. This can involve applying pressure to the point or inserting small needles into the skin to achieve therapeutic effects. HT-8 is generally considered a safe and effective acupoint, but as with all medical treatments, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner before beginning any new therapy.
Shao Chong | Lesser Surge | Heart 9 | HT-9
This is an acupuncture point 1 cun posterior to the corner of the nail on the radial side of the little finger. HT-9 is a commonly used acupoint in the treatment of heart and mental disorders. It is believed to have a calming and regulating effect on the mind, and is often used to treat symptoms of anxiety, depression, insomnia, and other emotional imbalances. In traditional Chinese medicine, the heart is associated with the 'shen' or spirit, and HT-9 is believed to regulate the flow of energy through the heart meridian, which can help to balance the emotions and promote overall wellbeing. HT-9 is also believed to help regulate heart rate and blood pressure, making it a useful point in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders. As with all acupuncture points, HT-9 should only be used by a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare professional trained in acupuncture. Treatment should always be tailored to the individual patient's needs and underlying health conditions.
Small Intestine Meridian
This meridian is commonly under the Element Fire.
Shao Ze | Lesser Marsh | Small Intestine 1 | SI-1
This is an acupuncture point located on the ulnar side of the little finger, at the corner of the nail bed. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), this point is called Shao Ze and is believed to have a strong influence on the flow of Qi in the upper extremities. SI-1 is commonly used to treat disorders related to the shoulder, arm, and hand, such as pain, numbness, and weakness. It is also believed to be effective in treating headache, neck pain, and toothache. Additionally, some TCM practitioners use SI-1 to address emotional issues, such as anxiety and irritability, which are believed to be related to imbalances in the energy flow through the upper extremities. Stimulation of SI-1 is typically done using acupuncture needles or acupressure techniques. It is important to note that acupuncture should only be performed by a licensed and trained practitioner.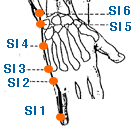
Qian Gu | Front Valley | Small Intestine 2 | SI-2
This is an important point in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) that is located on the small finger, on the ulnar side of the hand. More specifically, it is located at the distal border of the metacarpal-phalangeal joint, just proximal to the margin of the red and white skin. In TCM, SI-2 is believed to be associated with the Small Intestine meridian, which is responsible for sorting and absorbing nutrients from food and fluids, and maintaining fluid balance in the body. The Small Intestine meridian also has a role in separating pure from impure substances, which is important in TCM's view of the digestive process. Stimulating SI-2 is believed to be helpful for a range of health conditions, including digestive disorders, toothache, headache, neck pain, and pain and stiffness in the wrist and hand. It is also used in TCM to treat emotional disorders such as anxiety and depression. SI-2 is commonly stimulated by acupressure or acupuncture. During acupuncture, a fine needle is inserted into the point to stimulate and balance the body's energy flow. During acupressure, the point can be pressed and massaged using the fingers or a massage tool. However, it's important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or TCM practitioner before using SI-2 or any other acupuncture point for therapeutic purposes.
Hou Xi | Back Ravine | Small Intestine 3 | SI-3
This is an acupoint located on the hand, between the bases of the fifth metacarpal bone and the ulna. To locate it, make a fist and observe the depression at the base of the fifth metacarpal bone on the radial side. SI-4 is located in this depression, in the ulnar corner. In traditional Chinese medicine, SI-4 is believed to have therapeutic effects on several conditions. It is commonly used to alleviate pain in the neck, shoulder, arm, and wrist. SI-4 is also used to treat headaches, toothache, and eye diseases. Additionally, it is believed to help regulate the flow of energy, or Qi, in the body, making it useful for treating conditions such as anxiety and insomnia. SI-4 is often used in conjunction with other acupoints to achieve the best results.
Wan Gu | Wrist Bone | Small Intestine 4 | SI-4
This is an acupuncture point that is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat a variety of conditions. It is located on the back of the hand, in the depression just behind the metacarpal bone of the little finger, between the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones. This point is believed to help regulate the flow of Qi and blood in the body, and it is often used to treat a range of conditions, including wrist and arm pain, headaches, toothaches, and sore throat. It is also thought to be helpful in treating emotional disorders, such as anxiety and depression, as well as menstrual problems. In acupuncture, the point is stimulated by inserting a needle into the skin and manipulating it to produce a therapeutic effect. Moxibustion, the burning of an herb called moxa near the point, may also be used to stimulate the point and promote healing. SI-3 is considered a very important acupuncture point in the treatment of many conditions, and it is often used in conjunction with other points for maximum therapeutic effect.
Yang Gu | Yang Valley | Small Intestine 5 | SI-5
This is located on the ulnar side of the wrist, in the depression between the styloid process of the ulna and the triquetral bone. In traditional Chinese medicine, SI-5 is believed to regulate the flow of qi and blood in the Small Intestine meridian, and is often used to treat a variety of conditions related to the small intestine, wrist, and arm. Some of the common illnesses and conditions treated by stimulating SI-5 include wrist pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, tennis elbow, frozen shoulder, sore throat, and neck pain. Additionally, SI-5 is thought to promote mental clarity and help alleviate anxiety and stress. SI-5 can be stimulated using a variety of methods including acupuncture, acupressure, and moxibustion. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare provider before attempting to use SI-5 or any other acupuncture point for self-treatment.
Yang Lao | Nursing the Aged | Small Intestine 6 | SI-6
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine located on the ulnar side of the wrist, in the depression between the ulnar styloid process and the triquetrum and pisiform bones. SI 6 can be located when patient’s wrist is in flexion with the index finger pointing to the sternum. Stimulation of this acupoint is believed to help relieve pain in the arm and shoulder, as well as neck and back pain, and is commonly used for the treatment of conditions such as tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome, and frozen shoulder. Additionally, it is said to be effective in treating headaches and other symptoms related to stress and tension. SI-6 is also thought to benefit the eyes and ears, and is used in the treatment of tinnitus, blurred vision, and other disorders related to these sensory organs. It is often combined with other acupoints to form a comprehensive treatment plan for a variety of conditions. As with any medical treatment, it is important to consult a qualified practitioner before attempting to use this acupoint. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Small Intestine Meridian.
Zhi Zheng | Branch of the Upright | Small Intestine 7 | SI-7
This one is located on the posterior aspect of the forearm, approximately 1.5 fingerbreadths proximal to the wrist crease and on the ulnar (pinky finger) side of the forearm, in the depression between the ulna and the radius bones. SI-7 is an important acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine and is believed to have a number of therapeutic benefits. It is often used to treat pain and discomfort in the arm, wrist, and hand, and is particularly useful for treating conditions such as tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome, and wrist sprains. It is also thought to be helpful for treating a range of conditions related to the ears, nose, and throat, including tinnitus, earache, and sore throat. In addition, SI-7 is believed to be helpful for treating a range of emotional and psychological issues, including anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Some practitioners also use this point to address issues related to the lower back and hips, such as lower back pain and sciatica. Overall, SI-7 is considered to be a versatile acupoint that can be used to treat a wide range of conditions.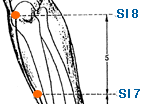
Xiao Hai | Small Sea | Small Intestine 8 | SI-8
This one is located between the olecranon process of the ulna and the medial epicondyle of the humerus, found with the elbow flexed. Stimulation of this point is believed to be effective for treating conditions related to the shoulder, arm, and hand. Specifically, it is used to treat pain and stiffness in the wrist and elbow, tennis elbow, and other conditions affecting the upper limbs. It is also believed to help with disorders of the ears, such as tinnitus, and other conditions such as sore throat and neck pain. SI-8 is often used in combination with other acupoints to provide relief for conditions involving the upper extremities. As with all acupoints, it should only be stimulated by a qualified practitioner, as self-treatment can potentially be harmful.
Jian Zhen | True Shoulder | Small Intestine 9 | SI-9
This one is known as the Small Intestine Meridian 9. It is also called the Jianzhen point and is located on the posterior aspect of the shoulder. Specifically, SI-9 is found in the depression inferior to the scapular spine, between the inferior angle of the scapula and the seventh cervical vertebra. In TCM, SI-9 is believed to be a point that regulates the function of the small intestine and can treat conditions related to it. It is also thought to have a beneficial effect on the shoulder and neck. Some of the illnesses and conditions that SI-9 can be used to treat include: Shoulder pain: SI-9 can be used to relieve shoulder pain and stiffness caused by conditions such as frozen shoulder or rotator cuff injury. Neck pain: SI-9 can be used to relieve neck pain caused by whiplash injury, cervical spondylosis, or other conditions. Digestive disorders: In TCM, SI-9 is believed to regulate the function of the small intestine and can be used to treat digestive disorders such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. Headache: SI-9 can be used to relieve headaches caused by tension in the neck and shoulder muscles. Insomnia: SI-9 can be used to improve sleep quality and relieve insomnia, as it is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and body.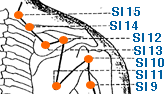
Nao Shu | Upper Arm Shu | Small Intestine 10 | SI-10
This one is located with the arm abducted, directly above SI 9 in a depression inferior to the scapular spine. In traditional Chinese medicine, SI-10 is believed to be effective in treating pain and stiffness in the arm and shoulder, as well as other conditions such as tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome, and wrist pain. It is also believed to be helpful in treating diseases such as insomnia, hypertension, and certain digestive disorders. SI-10 is often used in combination with other acupoints as part of an overall treatment plan. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner before using this point to treat any specific condition.
Tian Zong | Celestial Gathering | Small Intestine 11 | SI-11
This is an acupuncture point located in the shoulder region. It is found in the depression superior to the scapular spine and the inferior angle of the scapula. To locate this point, raise the patient's arm to expose the inferior angle of the scapula, then locate the depression between the scapular spine and the inferior angle of the scapula. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), SI-11 is considered a local point, as it is often used to treat disorders of the shoulder, neck, and upper back. It is believed to be especially effective for conditions such as frozen shoulder, rotator cuff injuries, and scapulohumeral periarthritis. In addition, SI-11 is also used to treat conditions such as headaches, neck pain, and toothache, among others. In Western medicine, the effects of acupuncture on these conditions are still being researched and understood. It is important to note that acupuncture should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment.
Bing Feng | Grasping the Wind | Small Intestine 12 | SI-12
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) located on the small intestine meridian. It is also called Bing Feng, which means 'grasping the wind.' The location of SI-12 is on the lateral aspect of the shoulder, approximately 1 cun (or thumb's width) below the highest point of the shoulder (acromion) and posterior to the shoulder joint, in the depression between the scapula and the humerus. In TCM, SI-12 is believed to be effective in treating pain and stiffness in the neck and shoulder, as well as upper back pain. It is also used to relieve numbness and weakness of the upper limb and is said to be useful in treating conditions like frozen shoulder, rotator cuff injuries, and tennis elbow. SI-12 is also believed to help with issues related to the digestive system, including indigestion, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. SI-12 can be stimulated through acupuncture, acupressure, or moxibustion. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before attempting any self-treatment.
Qu Yuan | Crooked Wall | Small Intestine 13 | SI-13
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine that is located on the lateral aspect of the shoulder, approximately 3 cun (or three thumb's width) below the highest point of the shoulder (acromion) and posterior to the shoulder joint, in the depression between the scapula and the humerus. This acupoint is also sometimes called Qu Yuan, which means 'Crooked Wall'. In traditional Chinese medicine, SI-13 is believed to be related to the Small Intestine meridian. It is thought that stimulating this point can help to regulate the flow of Qi (energy) along this meridian, which in turn may help to address various health concerns. Some of the conditions and illnesses that SI-13 is believed to be useful for treating include shoulder pain, stiffness, and immobility, as well as pain and weakness in the arms and hands. It may also be helpful for treating conditions that involve the neck, such as neck pain or stiffness, and for addressing some types of headaches. Additionally, some practitioners may use this point to help promote relaxation and relieve stress.
Jian Wai Shu | Outer Shoulder Shu | Small Intestine 14 | SI-14
This one is located in the shoulder region, specifically in the depression found on the posterior edge of the deltoid muscle, about 3 inches below the acromion process of the scapula. This acupoint is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) to treat shoulder and arm pain, as well as scapular pain, stiffness and numbness in the upper back, and motor impairment of the upper limbs. It is also believed to help with the treatment of certain respiratory conditions, including asthma, as well as skin disorders such as eczema and dermatitis. SI-14 is often stimulated through acupuncture or acupressure techniques to restore the flow of Qi (life force energy) along the corresponding meridian, which can help reduce pain and inflammation and promote overall health and wellness.
Jian Zhong Shu | Central Shoulder Shu | Small Intestine 15 | SI-15
This one is located on the back, in the depression below the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra. It is about 1.5 cun lateral to the posterior midline. This acupoint is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat conditions related to the shoulder and neck. It is believed that SI-15 helps to relieve pain, stiffness, and tension in the shoulder and neck area. It is also commonly used to treat conditions such as frozen shoulder, scapulohumeral periarthritis, and cervical spondylosis. In addition to its physical benefits, SI-15 is also believed to have emotional and spiritual benefits. According to TCM theory, it can help to soothe the mind, calm the spirit, and reduce feelings of anxiety and worry. It may also be used to treat conditions such as insomnia and palpitations.
Tian Chuang | Celestial Window | Small Intestine 16 | SI-16
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine located on the neck, at the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, midway between the transverse process of the 6th cervical vertebra and the mastoid process. This point is known as Tianchuang or Celestial Window. Stimulation of this point is thought to help with various conditions such as neck pain, shoulder pain, headache, tinnitus, vertigo, sore throat, and facial paralysis. It is believed to be particularly effective in treating stiff neck, as well as problems with the ears and eyes. Additionally, it is thought to help promote circulation of Qi and Blood in the neck and upper back region, and can be used to address problems related to these areas. As with all acupoints, it is important to seek the advice of a qualified practitioner before attempting any kind of self-treatment.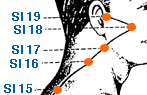
Tian Rong | Celestial Countenance | Small Intestine 17 | SI-17
This is an acupuncture point that is known as Tian Rong. It is located on the lateral aspect of the neck, level with the lower border of the earlobe, in the depression just anterior to the insertion of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. SI-17 is traditionally used in Chinese medicine to treat various disorders of the head and neck, including neck pain and stiffness, sore throat, tinnitus, and toothache. It is also believed to be effective in treating facial paralysis, hemiplegia, and trigeminal neuralgia. In acupuncture, SI-17 is often used in combination with other acupoints to help relieve pain and restore balance to the body's energy system. It is typically stimulated with acupuncture needles, moxibustion (the burning of an herb near the point), or acupressure. As with any acupuncture treatment, it is important to seek the guidance of a qualified practitioner.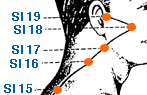
Quan Liao | Cheek Bone Hole | Small Intestine 18 | SI-18
This is an acupuncture point that is located on the lateral aspect of the face, anterior to the midpoint of the tragus of the ear and the corner of the mouth, in the depression at the lower border of the zygomatic arch. In traditional Chinese medicine, SI-18 is believed to influence the Small Intestine meridian, and is often used to treat disorders of the ear, nose, and throat. Specifically, it is thought to be effective in relieving pain and discomfort associated with facial paralysis, jaw pain, and trigeminal neuralgia. It may also be used to treat conditions such as tinnitus, deafness, and toothache. SI-18 is considered an important point for treating facial disorders, as it is believed to regulate the flow of Qi and blood in the face and head, which can help to reduce pain and inflammation. It is also thought to help stimulate the immune system and improve overall health and well-being. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare professional before attempting to use SI-18 or any other acupuncture point for self-treatment.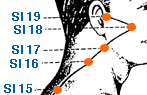
Ting Gong | Auditory Palace | Small Intestine 19 | SI-19
This is an acupuncture point located on the lateral aspect of the face, in the depression anterior and superior to the condyloid process of the mandible (the joint where the jawbone meets the skull) and posterior to the lower border of the zygomatic arch. SI-19 is primarily used for treating ear-related problems such as tinnitus, hearing loss, earache, and ear infections. It is also believed to help with throat disorders and facial paralysis. Stimulating this acupoint is said to regulate the Qi in the channels of the ear, clear heat and eliminate dampness, and calm the Shen (spirit). It is often used in combination with other acupoints, depending on the specific symptoms being treated. It is important to note that acupuncture should not be used as a replacement for conventional medical treatment for serious conditions such as hearing loss, ear infections, and facial paralysis, but rather as a complementary therapy.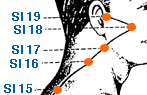
Stomach Meridian
This meridian is commonly under the Element Earth.
Cheng Qi | Tear Container | Stomach 1 | ST-1
This is an acupuncture point located on the face. Specifically, it is located in the depression below the pupil, at the infraorbital foramen. It is located near the lower edge of the orbit of the eye and in the depression on the infraorbital ridge. ST-1 is commonly used to treat eye and facial disorders. Some of the conditions it is thought to treat include blurry vision, night blindness, pain and swelling of the eyes, and tearing. ST-1 is also thought to have a calming effect on the mind and may be used to treat anxiety, stress, and insomnia. In addition, ST-1 is sometimes used for cosmetic purposes. Acupuncture at this point may help to reduce facial wrinkles, improve skin tone and texture, and promote overall facial rejuvenation. It is important to note that acupuncture treatment for cosmetic purposes is often performed in conjunction with other therapies and is not intended as a stand-alone treatment.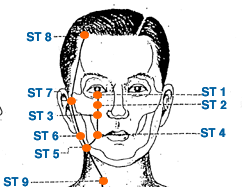
Si Bai | Four Whites | Stomach 2 | ST-2
This is an acupuncture point located on the face, near the corner of the eye. Specifically, it is located in a depression at the lower border of the zygomatic arch, directly below the pupil when looking straight ahead. ST-2 is traditionally used to treat a variety of conditions related to the face, including facial paralysis, facial spasms, and facial pain. It is also believed to help alleviate symptoms of sinusitis, nasal congestion, and allergies. In addition, some practitioners may use ST-2 to improve vision, as it is believed to stimulate the eyes and improve blood flow to the area. Stimulation of ST-2 can be achieved through a variety of acupuncture techniques, including needling, acupressure, and moxibustion. It is important to note that acupuncture should only be performed by a licensed and trained practitioner. If you are considering acupuncture treatment, be sure to speak with a qualified practitioner to determine if it is a safe and appropriate therapy for your specific condition.
Ju Liao | Great Bone-Hole | Stomach 3 | ST-3
This is an acupuncture point located on the face. It is found in the depression at the lower border of the zygomatic arch, directly below the pupil of the eye. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), this point is believed to regulate the functions of the stomach and improve digestive health. ST-3 is commonly used to treat a variety of conditions related to the digestive system, including bloating, nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain. It can also be used to alleviate facial pain, facial paralysis, and other facial disorders. Additionally, ST-3 is sometimes used in cosmetic acupuncture to improve the appearance of the face by reducing wrinkles, improving skin tone and texture, and tightening sagging skin. Like all acupuncture points, ST-3 should only be used by a qualified acupuncturist, and treatment should be tailored to the individual needs of the patient. It is important to note that acupuncture should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical care.
Di Cang | Earth Granary | Stomach 4 | ST-4
This is an acupuncture point that is located on the face. Specifically, it is located on the cheek, in the depression that lies directly below the pupil when the eye is looking straight ahead. To locate ST-4, one can feel for the depression in the cheekbone while the patient is looking straight ahead. ST-4 is often used to treat various disorders of the face, including facial paralysis, trigeminal neuralgia, facial spasms, and facial pain. It is also believed to be effective in treating toothache, sore throat, and jaw pain. In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-4 is considered to be a point where the Stomach and Large Intestine meridians intersect, and is said to regulate the functions of these organs. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine whether ST-4 is an appropriate treatment option for a particular condition.
Da Ying | Great Reception | Stomach 5 | ST-5
This is an acupuncture point located on the face. It is situated in the depression anterior and inferior to the tragus of the ear, where the condyloid process of the mandible moves when the mouth is opened. This acupoint is traditionally used in the treatment of a variety of conditions related to the face and head, including facial paralysis, toothache, trigeminal neuralgia, and facial spasms. It is also believed to be helpful in treating eye disorders such as blurred vision and twitching eyelids. In addition to its traditional uses, ST-5 has been studied for its potential therapeutic benefits in treating temporomandibular joint disorders (TMJ), a condition that causes pain and dysfunction in the jaw joint and muscles that control jaw movement. Research has shown that acupuncture, including stimulation of ST-5, may provide pain relief and improved jaw function for people with TMJ. However, more research is needed to fully understand the benefits of this treatment.
Jia Che | Jawbone | Stomach 6 | ST-6
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that is commonly used to treat various conditions related to the head and face, including facial pain, paralysis, trigeminal neuralgia, toothache, and jaw stiffness. ST-6, known as Jiache, is located on the face, approximately one finger's width anterior to the earlobe and at the level of the corner of the mouth. It lies on the Stomach meridian, which originates from the face, and extends down to the lower leg. The stimulation of ST-6 is thought to help clear energy blockages in the Stomach meridian, as well as promote the free flow of qi and blood throughout the face and head. It may also help to stimulate the facial muscles and nerves, leading to improved function and reduced pain. ST-6 is often used in conjunction with other acupoints to create a comprehensive treatment plan, tailored to each individual's specific needs. It is typically stimulated using acupuncture needles or pressure from acupressure, and may also be combined with other therapies, such as herbal medicine or moxibustion. As with any TCM treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner before seeking treatment with ST-6 or any other acupoint.
Xia Guan | Below the Joint | Stomach 7 | ST-7
This is an acupuncture point that is located on the face, specifically on the lower border of the zygomatic arch, anterior to the condyloid process of the mandible, and approximately halfway between the angle of the mouth and the anterior border of the hairline. In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-7 is believed to have a strong influence on the stomach, spleen, and other digestive organs. It is often used to treat conditions such as toothache, facial paralysis, facial swelling, and pain in the face, neck, and shoulder. ST-7 is known for its calming effect on the mind and is frequently used to treat anxiety, depression, and other emotional imbalances. It may be stimulated using acupuncture needles or pressure and can be used in combination with other acupoints for a more comprehensive treatment. However, it is important to seek the advice of a qualified practitioner before using ST-7 or any other acupuncture point for medical purposes.
Tou Wei | Head Corner | Stomach 8 | ST-8
This is an acupoint in the stomach meridian of the body. This point is located on the forehead, in the center of the hairline, midway between the eyebrows. It is in the depression that is approximately 0.5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline and 4.5 cun lateral to the midline of the head. In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-8 is believed to have a regulating effect on the qi and blood of the head and face. It is often used to treat disorders related to the head, such as headaches, dizziness, and sinus congestion. ST-8 is also thought to benefit the eyes and ears, and is sometimes used to treat visual and auditory problems. In addition, ST-8 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind, and may be used to treat anxiety, stress, and insomnia. It is sometimes used in conjunction with other acupoints to treat mental and emotional disorders. It is important to note that before using any acupoint, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare provider.
Ren Ying | Confluent Point | Stomach 9 | ST-9
This is an acupuncture point located in the neck region. More specifically, it is located at the midpoint of the lower border of the Adam's apple, known as the thyroid cartilage. This point is known as Renying and is classified as a 'confluent point' because it connects the twelve primary meridians. ST-9 is used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat a variety of conditions related to the throat, neck, and head, including sore throat, neck pain, difficulty swallowing, and toothache. It can also be used to treat emotional imbalances such as depression and anxiety, as well as digestive issues such as vomiting, nausea, and bloating. Additionally, ST-9 can be used for conditions affecting the skin, including rashes, itching, and hives. As with all acupuncture points, the specific conditions and illnesses that can be treated with ST-9 may vary depending on the individual case and should be determined by a licensed acupuncturist after a thorough examination and diagnosis.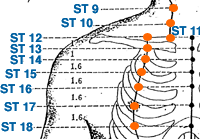
Shui Tu | Water Prominence | Stomach 10 | ST-10
This is an acupoint in the Stomach meridian. It is located about three fingerbreadths below the Adam's apple, in a depression between the hyoid bone and the lower border of the thyroid cartilage. ST-10 is traditionally used in Chinese medicine to treat throat and neck disorders, such as sore throat, hoarseness, and difficulty swallowing. It is also believed to be effective in treating chest pain, asthma, and coughing. In addition, this acupoint is sometimes used to relieve emotional stress, anxiety, and depression. As with any medical treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner of acupuncture and Chinese medicine to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your individual needs.
Qi She | Qi Abode | Stomach 11 | ST-11
This is an acupuncture point located on the stomach meridian. It is found on the lower border of the middle of the clavicle, in a depression between the sternal and clavicular heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-11 is considered an important point for regulating the flow of Qi and blood in the chest and upper abdomen. It is often used to treat various respiratory disorders such as asthma, cough, and bronchitis, as well as chest pain and tightness caused by Qi stagnation. ST-11 is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and is used to treat anxiety, depression, and other emotional imbalances. Additionally, it is used to alleviate pain and discomfort in the chest, upper back, and neck, as well as digestive disorders such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. As with any acupuncture point, it is important to seek the advice of a qualified practitioner before using ST-11 to treat any specific condition.
Que Pen | Empty Basin | Stomach 12 | ST-12
This is an acupuncture point located on the stomach meridian of the body. It is located in the area beneath the clavicle, midway between the center of the sternum and the shoulder joint. ST-12 is used to treat a variety of conditions, including chest pain, cough, asthma, bronchitis, and sore throat. It can also be used to alleviate pain and stiffness in the neck and shoulder area, as well as digestive disorders, such as nausea and vomiting. Additionally, it is believed to promote the smooth flow of qi throughout the body, which can help boost overall immunity and improve energy levels. As with all acupuncture points, ST-12 should only be stimulated by a trained and licensed acupuncturist using sterile needles. It is not recommended to attempt to self-treat or diagnose any medical condition.
Qi Hu | Qi Door | Stomach 13 | ST-13
This is an acupuncture point located on the chest, 4 cun (finger widths) lateral to the midline, in the fourth intercostal space. It is located on the same level as the nipple, in the hollow between the ribs and the pectoral muscles. ST-13 is used to treat a variety of conditions including chest and stomach pain, coughing, asthma, and other respiratory issues. It is also used to treat conditions of the digestive system such as vomiting, indigestion, and acid reflux. In addition, it is sometimes used to treat emotional imbalances such as anxiety and depression. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using ST-13 or any other acupoint to treat specific health conditions.
Ku Fang | Clavicle Center | Stomach 14 | ST-14
This acupoint is located in the center of the supraclavicular fossa, approximately 4 cun lateral to the anterior midline, at the level of the 1st intercostal space. According to TCM theory, ST-14 is believed to regulate the Qi and blood circulation of the chest and promote the function of the lung and heart meridians. It is also said to help relieve coughing, asthma, and chest pain. ST-14 is also used in the treatment of pain and stiffness in the shoulder and neck region. ST-14 is often used in conjunction with other acupoints as part of a comprehensive treatment strategy. It is commonly used in acupuncture and acupressure treatments for a variety of conditions, such as respiratory disorders, anxiety, and stress. However, as with any form of medical treatment, it is important to consult with a qualified healthcare practitioner before attempting to use acupuncture or acupressure on oneself.
Tian Tu | Celestial Chimney | Stomach 15 | ST-15
This is an acupuncture point in Traditional Chinese Medicine located on the chest, 4 cun (approximately 2 inches) lateral to the anterior midline of the body, at the level of the fourth intercostal space. It is known as Tian Tu, which translates to Celestial Chimney. ST-15 is said to regulate the flow of Qi and blood in the chest and is commonly used to treat chest and breast pain, coughing, asthma, and other respiratory problems. It is also thought to have an effect on emotional imbalances and is used to treat conditions such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. In addition, ST-15 is believed to help with digestive issues such as nausea, vomiting, and poor appetite. It may also be useful for treating shoulder and arm pain, as well as for strengthening the immune system. However, as with any medical treatment, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner before using acupuncture or any other form of alternative medicine.
Ying Chuang | Breast Window | Stomach 16 | ST-16
This is an acupuncture point located on the front of the chest, midway between the center of the chest and the shoulder. Specifically, it is located in the 5th intercostal space, 4 cun lateral to the anterior midline. This point is traditionally believed to regulate the function of the chest and stomach, and to alleviate chest pain and discomfort. It is also thought to be helpful in treating asthma, coughing, and other respiratory problems, as well as digestive disorders such as acid reflux, indigestion, and abdominal distension. Additionally, ST-16 is often used to address emotional issues related to the chest and upper abdomen, such as anxiety, depression, and grief. As with any acupuncture point, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine if ST-16 is appropriate for your specific needs and health concerns.
Ru Zhong | Breast Center | Stomach 17 | ST-17
This acupoint is located on the midline of the chest, 4th intercostal space (in the same horizontal plane as the nipple), between the two nipples. It can be found by locating the sternum and moving laterally towards the nipples. In TCM, ST-17 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi and Blood in the chest, especially in the breast and lung areas. It is often used to treat conditions related to the chest and breasts, including pain, congestion, and inflammation. ST-17 can also be used to treat respiratory problems such as cough, asthma, and chest tightness, as well as emotional issues such as anxiety and depression that affect the chest and respiratory system. As with any medical treatment, it is important to consult with a qualified healthcare provider before using acupuncture or any other form of complementary medicine.
Ru Gen | Breast Root | Stomach 18 | ST-18
This is an acupoint used in traditional Chinese medicine that is located on the abdomen, 4 cun (finger widths) lateral to the midline, at the level of the lower border of the ninth rib. In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-18 is believed to regulate the functions of the lungs and the chest, and is commonly used to treat respiratory disorders, such as coughing, asthma, and bronchitis. It is also believed to be useful for treating chest pain, chest congestion, and other disorders of the chest and upper abdomen. Additionally, ST-18 is thought to have a calming effect on the mind, and may be used to treat anxiety and depression. ST-18 can be stimulated by pressing or needling the point. It is typically used in combination with other acupoints as part of an overall treatment plan tailored to the individual patient's specific health needs. As with all medical treatments, it is important to consult with a qualified healthcare practitioner before beginning any acupuncture or traditional Chinese medicine treatment.
Bu Rong | Not Contained | Stomach 19 | ST-19
This is an acupuncture point located on the stomach meridian. The point is located in the midline of the abdomen, about 4 cun above the belly button and 2 cun below the sternocostal angle. In anatomical terms, it corresponds to the level of the xiphoid process, which is the cartilaginous extension at the lower end of the sternum. ST-19 is traditionally used to treat a variety of gastrointestinal disorders such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It is also used for the treatment of asthma, cough, and chest congestion, as well as anxiety and depression. Additionally, it is said to help regulate the function of the liver, spleen, and stomach. Stimulation of ST-19 is typically achieved through acupuncture, acupressure, or moxibustion. In these techniques, fine needles, finger pressure, or heat is applied to the point to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. As with any acupuncture treatment, it is important to consult a licensed practitioner before trying to stimulate ST-19 or any other acupuncture point.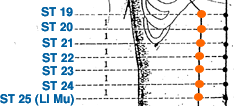
Cheng Man | Assuming Fullness | Stomach 20 | ST-20
This is an acupuncture point located on the abdomen, 4 cun (finger widths) lateral to the midline, at the level of the umbilicus. This acupoint is commonly used in the treatment of digestive disorders such as abdominal bloating, stomach pain, indigestion, nausea, and vomiting. It is also used to address emotional issues such as anxiety and depression, as well as respiratory conditions such as asthma and cough. Additionally, ST-20 is believed to have a regulating effect on the energy flow of the stomach meridian, which is associated with the digestive system, and can also be used for general stomach health. ST-20 can be stimulated with acupuncture needles, acupressure, or moxibustion. However, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare professional before attempting to use acupressure or acupuncture for any health condition.
Liang Men | Beam Gate | Stomach 21 | ST-21
This is located on the abdomen, 2 cun (finger widths) lateral to the midline, at the level of the lower border of the ninth rib. It is located on the same horizontal level as ST20 (Cheng Man). In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-21 is believed to regulate the function of the stomach and the intestines. It is often used to treat conditions related to the digestive system such as abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, and indigestion. ST-21 is also believed to be useful in treating emotional disorders such as anxiety, stress, and depression. Acupuncturists may stimulate the ST-21 acupoint using acupuncture needles or other techniques such as acupressure or moxibustion. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to seek the advice of a qualified practitioner before using ST-21 or any other acupoint for therapeutic purposes.
Guan Yuan | Gate of the Original Qi | Stomach 22 | ST-22
This is an acupuncture point located on the abdomen, 2 cun (finger widths) lateral to the midline, at the level of the upper border of the pubic symphysis. This point is traditionally used in Chinese medicine to tonify the digestive system, especially the spleen and stomach, and promote the flow of qi and blood. It is also said to regulate the lower jiao, which includes the small intestine, bladder, and reproductive organs. ST-22 is commonly used to treat digestive disorders, such as diarrhea, constipation, and indigestion. It is also used to address menstrual and gynecological issues, such as irregular periods, painful periods, and infertility. Additionally, ST-22 is believed to support the immune system, increase energy, and relieve stress and anxiety.
Tai Yi | Great Medical | Stomach 23 | ST-23
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine located on the stomach meridian. The point is located on the lower border of the orbit, in the depression at the infraorbital foramen. ST-23 is used to treat disorders related to the Stomach and Spleen, such as abdominal pain, indigestion, diarrhea, vomiting, and other gastrointestinal issues. It is also used to treat eye and facial disorders, including facial paralysis, twitching, and pain, as well as toothache, nasal congestion, and sinusitis. Additionally, it is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and is used to treat emotional and mental disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Hua Rou Men | Slippery Flesh Gate | Stomach 24 | ST-24
This is an acupoint in the stomach meridian. It is located 2 cun lateral to the center of the umbilicus, in the depression lateral to the rectus abdominis muscle. ST-24 is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat abdominal pain, distension, and diarrhea. It is also believed to be effective for the treatment of digestive disorders, such as gastroenteritis, vomiting, and indigestion. In addition, ST-24 is said to be useful for treating mental and emotional conditions, including anxiety, depression, and stress. It is believed that stimulation of this acupoint can help to regulate the qi and blood flow in the body, promoting a sense of calm and relaxation. As with all acupoints, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner before attempting to use ST-24 or any other acupoint for the treatment of a specific condition.
Tian Shu | Celestial Pivot | Stomach 25 | ST-25
This is an acupuncture point that is located on the abdomen, two finger-breadths (approximately 1.5 inches) lateral to the navel. It is located on the line connecting the navel and the anterior superior iliac spine (the bony protrusion on the front of the hip). In Traditional Chinese Medicine, ST-25 is considered an important point for regulating the intestines and treating digestive disorders. It is believed to stimulate the large intestine, improve bowel function, and alleviate symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and constipation. It is also believed to be useful in the treatment of menstrual cramps, irregular periods, and urinary problems. Additionally, ST-25 is thought to be helpful in strengthening the body's resistance to disease and boosting the immune system. ST-25 is commonly used in combination with other acupuncture points for the treatment of conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, diarrhea, dysentery, and other gastrointestinal disorders. It may also be used to relieve menstrual cramps, urinary tract infections, and other conditions related to the lower abdomen. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine the best course of treatment for each individual.
Wai Ling | Outer Mound | Stomach 26 | ST-26
This is an acupuncture point that is located on the abdomen. This point is located on the same horizontal line as the lower border of the umbilicus. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, ST-26 is believed to be effective in treating digestive and gynecological disorders. This point is thought to regulate the function of the intestines and stomach, and can be used to treat conditions such as abdominal distention, constipation, and diarrhea. ST-26 is also believed to have a regulatory effect on the uterus and can be used to treat gynecological disorders such as irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, and amenorrhea. In addition to its digestive and gynecological benefits, ST-26 is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can be used to treat anxiety and stress-related conditions. It is also believed to have an effect on the lower back and can be used to treat pain and stiffness in this area. However, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.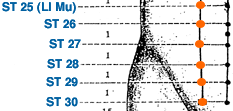
Da Ju | Great Gigantic | Stomach 27 | ST-27
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that is located on the lower abdomen, 3 cun (finger widths) below the umbilicus and 1 cun (finger width) lateral to the midline, in the lower abdominal groove. In TCM, ST-28 is believed to regulate the bladder and urinary system. It is said to be effective in treating conditions such as painful urination, frequent urination, urinary incontinence, and other urinary problems. ST-28 is also believed to be effective in regulating menstrual cycles and treating menstrual cramps, as well as aiding in digestion. To stimulate ST-28, acupuncturists typically use fine needles, moxibustion, or acupressure. It is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine if ST-28 is appropriate for your specific condition, and to receive proper treatment.
Shui Dao | Water Passage | Stomach 28 | ST-28
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) located on the lower abdomen, 3 cun (finger widths) below the umbilicus and 2 cun lateral to the midline, in the area of the lower abdominal groove. In TCM, ST-28 is used to regulate water metabolism and is often employed for issues related to the urinary and reproductive systems. It is effective for treating conditions such as edema, urinary retention, painful urination, and dysuria. Additionally, ST-28 can be beneficial for gynecological concerns like menstrual cramps, irregular menstruation, and reproductive health. Acupuncture stimulation of ST-28 typically involves fine needles, moxibustion, or acupressure. As with all acupoints, it is essential to consult a licensed acupuncturist for a proper diagnosis and treatment to ensure that ST-28 is suitable for your specific needs.
Gui Lai | Return | Stomach 29 | ST-29
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the lower abdomen, 2 cun (finger widths) below the lower border of the body of the pubic bone and 2 cun (finger widths) lateral to the midline. ST-29 is commonly used to treat urinary system disorders such as urinary retention, incontinence, and painful urination. It can also be used to alleviate abdominal pain and bloating, as well as menstrual pain and irregularities. In addition, ST-29 is sometimes used to address male sexual dysfunction, such as impotence and premature ejaculation. The acupoint can be stimulated with acupuncture needles, acupressure, or moxibustion to promote healing and balance in the body. However, it's important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare provider before seeking treatment.
Qi Chong | Surging Qi | Stomach 30 | ST-30
This is an acupuncture point located on the lower abdomen, on the lower border of the pubic symphysis, and 3 cun (about the width of 4 fingers) lateral to the midline of the body. In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-30 is believed to be associated with the stomach and spleen meridians, and is considered to be a useful point for addressing digestive issues, such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. It is also thought to be helpful for menstrual problems, including irregular periods and pain associated with menstruation. Additionally, ST-30 is believed to be useful for treating lower abdominal pain, hernias, and urinary dysfunction. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare provider before using ST-30 or any other acupoint to address specific health concerns.
Bi Guan | Thigh Joint | Stomach 31 | ST-31
This is an acupuncture point located on the thigh, on the line connecting the anterior superior iliac spine and the superior lateral border of the patella. More specifically, it is located about 2 inches below the anterior superior iliac spine and 1 inch lateral to the upper edge of the patella. ST-31 is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat disorders related to the urinary and reproductive systems. It is believed that this point can regulate the function of the bladder, uterus, and lower abdomen. ST-31 is often used to treat urinary incontinence, pain in the lower abdomen and groin, as well as menstrual problems. It can also be used to relieve pain and stiffness in the thigh and knee. Additionally, ST-31 is thought to have a calming effect on the mind and can be used to treat anxiety and stress-related disorders.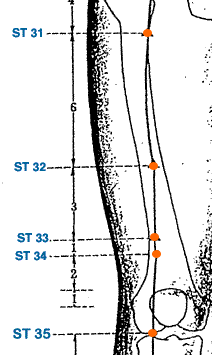
Fu Tu | Crouching Rabbit | Stomach 32 | ST-32
This is an acupuncture point located on the stomach meridian, which runs along the front of the leg. Specifically, ST-32 is located on the thigh, about four finger-widths below the top of the thigh bone (greater trochanter) and one finger-width lateral to the anterior border of the thigh bone. ST-32 is used to treat a variety of conditions related to the stomach and digestive system, including abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal disorders. It is also believed to be effective in treating genitourinary disorders, such as painful urination, impotence, and menstrual irregularities. Additionally, ST-32 is thought to be useful in treating musculoskeletal disorders, including pain and stiffness in the thigh and knee. ST-32 is often used in combination with other acupoints along the stomach meridian, as well as points on other meridians, in order to achieve a more comprehensive treatment of the patient's specific condition. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual.
Yin Shi | Yin Market | Stomach 33 | ST-33
This is an acupuncture point located on the Stomach meridian. Its location is on the anterior thigh, on a line between the anterior superior iliac spine and the superolatero patella, 3 cun superior to lateral patella. In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-33 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi (life force energy) throughout the body, as well as improve the function of the Stomach and Spleen organs. It is commonly used to treat a variety of conditions, including: Acupuncture practitioners may use ST-33 alone or in combination with other acupoints to treat these conditions. However, it is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist before using acupuncture as a treatment for any medical condition.
Liang Qiu | Beam Hill | Stomach 34 | ST-34
This is an acupuncture point located with knee flexed, 2 cun above the superior lateral border of the patella on the line connecting with the ASIS. In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-34 is believed to have a wide range of functions, including regulating the Stomach and strengthening the Spleen. It is commonly used to treat digestive disorders, such as indigestion, bloating, and diarrhea. Additionally, it is also believed to have a regulating effect on the menstrual cycle and can be used to treat irregular periods, dysmenorrhea, and other gynecological disorders. Other conditions that ST-34 may be used to treat include knee pain and stiffness, leg muscle tension, and muscle atrophy. In addition, this point is sometimes used to stimulate the immune system, and to reduce stress and anxiety. ST-34 is often combined with other acupoints for a more comprehensive treatment approach. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Stomach Meridian.
Du Bi | Calf's Nose | Stomach 35 | ST-35
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine located on the leg, located on the anterior aspect of the knee joint, just below the patella and lateral to the patellar ligament. ST-35 is believed to benefit the knee and leg, and is commonly used to treat conditions such as pain, swelling, and stiffness of the knee joint. It is also thought to improve digestion, alleviate constipation, and relieve abdominal distension. In TCM theory, ST-35 is part of the Stomach meridian, which is associated with the digestion and processing of food and fluids in the body. ST-35 is considered to be a key point for regulating the function of the Stomach, and is often used in conjunction with other acupoints to treat digestive disorders. Additionally, the Stomach meridian is believed to have a close relationship with the leg, so ST-35 is thought to be particularly effective for treating knee problems.
Zu San Li | Divine Indifference Over Earthly Matters | Stomach 36 | ST-36
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the leg. The location of ST-36 is three fingers' width below the kneecap and one finger's width to the outside of the tibia. In some areas an cultures, this point is called 'The Point of 100 Illnesses' du to its versitile use. It can heal or boost healing in just about any treatment. ST-36 is believed to be an important acupoint for regulating and strengthening the body's Qi, or vital energy. It is commonly used to treat digestive disorders, such as diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. It can also be used to boost the immune system, increase energy levels, and relieve fatigue. Additionally, ST-36 is known to have a beneficial effect on the skin, making it a popular point for treating skin disorders like eczema, acne, and psoriasis. The point can be stimulated by acupressure, acupuncture, or moxibustion, which involves burning a small amount of mugwort near the skin to warm the area and stimulate blood flow. ST-36 is a point that is commonly used by acupuncturists and is considered safe for most people. However, as with any medical treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner before trying any new therapies.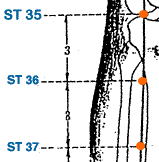
Shang Ju Xu | Upper Great Hollow | Stomach 37 | ST-37
This is an acupuncture point located on the stomach meridian. It is found on the lower leg, on the anterior border of the fibula, 6 cun (finger widths) below the lower border of the knee cap and one finger-breadth (middle finger) from the crest of the tibia. ST-37 is traditionally used to treat digestive and gastrointestinal problems, such as stomach ache, diarrhea, and constipation. It is also believed to help regulate the body's qi (energy) and blood flow, and promote general well-being. In addition, it is often used to alleviate pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen, and to boost the immune system. To stimulate ST-37, acupuncturists may use needles, pressure, or heat therapy. It is important to note that anyone considering acupuncture should seek treatment from a licensed and trained practitioner.
Tiao Kou | Ribbon Opening | Stomach 38 | ST-38
This is an acupuncture point that is located on the lower leg, 8 cun below ST 35, one finger width lateral from the anterior border of the tibia. In traditional Chinese medicine to treat various conditions related to the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems. When stimulated, ST-38 is said to be effective in treating abdominal distention, diarrhea, constipation, dysuria (difficulty urinating), and menstrual disorders. It can also help with lower back pain, stiffness in the legs, and other musculoskeletal disorders. In addition, this point is believed to have a tonifying effect on the body, improving overall vitality and promoting general health and wellness. As with any acupuncture treatment, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner before using ST-38 or any other acupoint to address specific health concerns.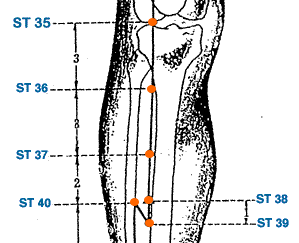
Xia Ju Xu | Lower Great Hollow | Stomach 39 | ST-39
This one is located on the lower leg, about three inches below the kneecap and one inch lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia. To locate ST-39, it is important to flex the foot so that the muscle beneath the skin protrudes, and the acupoint can be found on the lower border of the muscle. ST-39 is believed to have a range of therapeutic uses in traditional Chinese medicine. It is commonly used to treat digestive disorders such as diarrhea and constipation. It is also used to treat disorders of the urinary system, such as difficulty in urination and bladder infections. Additionally, ST-39 is used in the treatment of gynecological disorders, including menstrual cramps and irregular periods. ST-39 is often used in combination with other acupoints for a more comprehensive approach to treating these conditions. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner before attempting to stimulate ST-39 or any other acupoint.
Feng Long | Beautiful Bulge | Stomach 40 | ST-40
This one is located on the lower leg, approximately 3 finger widths superior to the prominence of the lateral malleolus, on the anterior border of the fibula bone. ST-40 is said to have a number of benefits and is used to treat a variety of conditions. Some of these include abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, ankle and foot pain, ankle sprains, asthma, coughing, and menstrual disorders. It is also thought to help strengthen the immune system, promote the flow of Qi (energy) in the body, and improve overall energy levels. Acupuncture practitioners often use ST-40 in combination with other acupoints in order to achieve the best results. The point is typically needled using a fine, sterile needle, and may be manipulated manually or with electrical stimulation. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner to determine if ST-40 is appropriate for your particular health condition.
Jie Xi | Ravine Divide | Stomach 41 | ST-41
This is an acupoint located on the dorsum of the foot, in the depression distal to the junction of the second and third metatarsal bones. Specifically, it is located at the midpoint between the web of the toes and the ankle joint. In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-41 is believed to regulate the flow of qi and blood and strengthen the spleen and stomach. It is commonly used to treat digestive disorders such as abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea. ST-41 is also said to help alleviate symptoms of some respiratory disorders, such as asthma and cough. Additionally, it may be used to treat other conditions like edema, ankle pain, and foot spasms. ST-41 can be stimulated through various methods, including acupuncture, acupressure, and moxibustion. It is recommended to consult with a qualified practitioner of traditional Chinese medicine before attempting to use this point for any health conditions.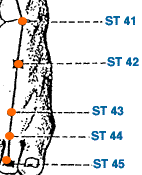
Chong Yang | Surging Yang | Stomach 42 | ST-42
This one is an acupuncture point located on the foot, in between the 2nd and 3rd metatarsals and the cuneiform bone, between the tendons of the long extensor muscles of the big toe and other toes. Stimulating ST-42 is believed to promote digestive health, as well as alleviate symptoms of headaches, vertigo, and dizziness. It can also be used to treat foot pain, ankle pain, and sprains. ST-42 is contraindicated for pregnant women, as stimulation of this point is thought to promote uterine contractions. It should also be used with caution in patients with osteoporosis or other bone disorders, as it is located near the bones of the foot. Acupuncture treatment should always be carried out by a licensed and trained practitioner.
Xian Gu | Sunken Valley | Stomach 43 | ST-43
This is an acupoint located on the top of the foot, in the depression between the second and third metatarsal bones. Specifically, it is located at the junction of the second and third metatarsal bones, approximately one finger's width distal to the web margin between the second and third toes. In traditional Chinese medicine, ST-43 is believed to be a crucial point for treating digestive and gastrointestinal issues. It is also said to be effective in treating pain and stiffness in the foot, ankle, and lower leg. More specifically, ST-43 is commonly used to treat stomach and digestive disorders such as abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea. It may also be used to address menstrual cramps and other gynecological issues. Additionally, ST-43 may help to relieve foot pain and cramps, as well as issues such as ankle sprains and arthritis. It is important to note that acupuncture and acupressure should always be performed by a trained and licensed practitioner. If you are experiencing any of the above conditions or other health concerns, it is best to consult with a healthcare provider before pursuing acupuncture treatment.
Nei Ting | Inner Court | Stomach 44 | ST-44
This is an acupuncture point on the stomach meridian located on the dorsum of the foot, between the second and third toe. The point is approximately 0.1 cun posterior to the web margin between the second and third toes, at the level of the junction of the red and white skin. ST-44 is used to treat a variety of conditions such as headaches, dizziness, vertigo, sore throat, toothache, nausea, and vomiting. It is also believed to be effective in treating digestive issues such as constipation, diarrhea, and abdominal distension. ST-44 is considered to be a 'master point' for treating disorders of the stomach and digestive system, and it is commonly used in acupuncture treatments for these conditions. Additionally, ST-44 is thought to be beneficial for emotional issues such as anxiety and depression. As with all acupuncture points, ST-44 should only be used by a qualified practitioner and after a thorough assessment of the patient's condition. Acupuncture should be used in conjunction with conventional medical treatments, and patients should consult with their doctor before beginning any course of treatment.
Liang Qiu | Severe Mouth | Stomach 45 | ST-45
This is an acupoint that is located on the lateral side of the second toe, at the corner of the nail bed. It is the last point on the Stomach meridian and is one of the most commonly used points for treating digestive disorders. ST-45 is believed to have a cooling effect on the body, and is commonly used to treat conditions related to heat, such as fever, irritability, and dry mouth. It is also used to treat sore throat, toothache, and headache. In addition, ST-45 can be used to regulate the Stomach and promote digestion, making it an effective point for treating nausea, vomiting, and other digestive disorders. ST-45 can be stimulated by pressing, massaging, or needling the point. It is important to note that acupuncture should only be performed by a qualified and licensed practitioner.
Spleen Meridian
This meridian is commonly under the Element Earth.
Yin Bai | Hidden White | Spleen 1 | SP-1
This is the first acupoint of the spleen meridian. It is located on the medial side of the big toe, in the depression at the corner of the nail bed closest to the second toe. SP-1 is commonly used in acupuncture to treat disorders related to the spleen, such as digestive problems, bloating, and diarrhea. It is also used to address menstrual disorders, genital pain, and certain emotional issues such as anxiety and depression. Additionally, this acupoint is believed to have a calming effect on the mind, making it useful for promoting relaxation and reducing stress. In traditional Chinese medicine, SP-1 is considered a powerful point for tonifying the body's Qi, or life force energy.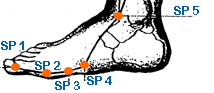
Da Du | Great Metropolis | Spleen 2 | SP-2
This is an acupoint located on the inside of the big toe, just distal to the metatarsophalangeal joint. To locate it, you can palpate the depression on the medial side of the big toe when it is in a plantar flexed position. SP-2 is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) to treat digestive disorders, especially those related to the spleen and stomach. It is believed that this acupoint can regulate the flow of Qi and blood, tonify the spleen, and resolve dampness in the body. As such, it is often used to treat conditions such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, poor digestion, and bloating. Additionally, SP-2 may also be used to address gynecological issues, such as irregular menstruation and leukorrhea. SP-2 can be stimulated by applying gentle pressure or massage to the point using the thumb or finger. It can also be stimulated using acupuncture needles. However, it is important to consult a licensed and qualified acupuncturist before attempting to use acupuncture or acupressure techniques.
Tai Bai | Supreme White | Spleen 3 | SP-3
This is located on the inside of the foot, in the depression between the first and second metatarsal bones, about one-third of the distance from the base of the first metatarsal bone towards the heel. SP-3 is believed to regulate the Spleen and Stomach meridians, and is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat digestive disorders such as abdominal bloating, diarrhea, and poor appetite. It is also used to relieve symptoms of gynecological issues such as irregular menstruation, painful periods, and infertility, as well as emotional imbalances like anxiety and insomnia. Additionally, SP-3 is thought to have a tonifying effect on the entire body and to promote overall wellness.
Gong Sun | Yellow Emperor | Spleen 4 | SP-4
This is an important acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the inner aspect of the foot, in the depression distal and inferior to the base of the first metatarsal bone. SP-4 is believed to have a wide range of benefits and is commonly used in acupuncture treatments for various illnesses and conditions. Some of the conditions that SP-4 is believed to treat include digestive disorders, menstrual problems, anxiety, insomnia, and depression. It is also believed to help regulate the immune system and improve blood circulation. In addition to its therapeutic uses, SP-4 is also used as a diagnostic point. The tenderness or sensitivity of the point can help practitioners diagnose various conditions related to the Spleen or other organs in the body.
Shang Qiu | Shang Hill | Spleen 5 | SP-5
This one is located on the medial aspect of the foot, in the depression proximal and inferior to the base of the first metatarsal bone. In TCM, SP-5 is considered to be a point that regulates the Spleen meridian and is commonly used to treat various conditions related to the digestive system, such as indigestion, diarrhea, and abdominal distention. It is also believed to be effective in treating gynecological disorders, including irregular menstruation, painful periods, and infertility. SP-5 is also used to address mental and emotional conditions, such as anxiety and depression.
San Yin Jiao | Three Yin Intersection | Spleen 6 | SP-6
This one is located on the inner lower leg, approximately three finger-widths above the medial malleolus (the bony bump on the inside of the ankle). SP-6 is believed to be a powerful point for regulating the blood, balancing the yin energy, and treating gynecological and digestive issues. Some specific conditions that SP-6 is thought to help with include menstrual cramps, irregular periods, infertility, digestive problems, urinary incontinence, and insomnia. Acupressure or acupuncture to stimulate SP-6 is commonly used in TCM practice to promote the smooth flow of Qi and blood, as well as to harmonize the balance of yin and yang in the body. It is often used in combination with other acupoints to enhance its therapeutic effects.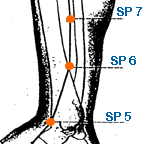
Lou Gu | Leaking Valley | Spleen 7 | SP-7
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the inner leg, approximately three finger widths above the medial malleolus (ankle bone) and just behind the tibia bone. This acupoint is believed to regulate and strengthen the spleen and stomach meridians, and is often used to treat disorders related to these organs. It is also used to address issues related to blood and qi stagnation, as well as gynecological problems. SP-7 is commonly used to alleviate digestive problems such as bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and nausea. It is also used to treat gynecological issues such as irregular menstruation, painful menstruation, and infertility. Additionally, it is believed to help relieve joint pain and reduce edema.
Di Ji | Earth's Crux | Spleen 8 | SP-8
This one is an acupuncture point on the Spleen meridian. It is located 4 cun above the tip of the medial malleolus, on the posterior border of the tibia. To locate SP-8, measure four finger-widths from the tip of the medial malleolus, and locate the point on the back border of the tibia. SP-8 is believed to be useful for the treatment of gynecological disorders, including irregular periods, menstrual cramps, and uterine bleeding. It is also thought to be effective in treating digestive disorders such as diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal distension. Additionally, SP-8 may be used for the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, including pain and weakness in the lower limbs, as well as for emotional issues such as anxiety and insomnia. As with all acupuncture points, SP-8 should only be used under the supervision of a licensed acupuncturist. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Spleen Meridian.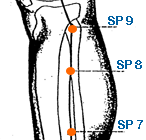
Yin Ling Quan | Yin Mound Spring | Spleen 9 | SP-9
This one is an acupuncture point located on the lower leg, on the medial aspect of the leg, about 3 cun (finger widths) below the medial condyle of the tibia, in the depression between the posterior border of the tibia and the gastrocnemius muscle. This point is traditionally used to regulate the Spleen and Kidney, nourish the Yin, promote circulation of Qi and blood, and resolve dampness in the body. SP-9 is commonly used to treat various conditions such as digestive disorders, menstrual irregularities, urinary problems, lower back pain, knee pain, ankle pain, and edema. Stimulation of SP-9 is typically achieved through acupuncture needling, moxibustion, or acupressure. As with any acupuncture point, it should only be stimulated by a licensed acupuncturist or other trained healthcare provider.
Xue Hai | Sea of Blood | Spleen 10 | SP-10
This is an acupuncture point on the spleen meridian. It is located on the medial aspect of the thigh, 3 cun above the transverse popliteal crease, and 1 cun medial to the border of the femur. SP-10 is commonly used to treat a variety of conditions, including menstrual disorders such as irregular periods, painful periods, and heavy bleeding. It is also used to treat abdominal distension and pain, as well as skin disorders such as eczema and hives. In traditional Chinese medicine, SP-10 is believed to have a strong regulating effect on the blood, making it a popular choice for conditions related to the circulatory system, including varicose veins and other blood vessel disorders. It may also be used to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.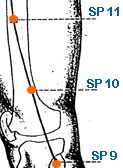
Ji Meng | Supreme Clear | Spleen 11 | SP-11
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located 6 cun above SP 10 on the line connecting SP 12 to SP 10. SP-11 is primarily used to treat gynecological and reproductive disorders. It is said to regulate the menstrual cycle, treat irregular or painful periods, and address conditions like amenorrhea, leukorrhea, and uterine bleeding. It is also used to alleviate abdominal distension and pain, promote urination, and regulate the function of the lower burner (the area below the umbilicus). In addition, SP-11 is sometimes used in the treatment of emotional disorders, such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. It is believed to help calm the mind, soothe the spirit, and promote a sense of wellbeing.
Chong Men | Rushing Door | Spleen 12 | SP-12
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the abdomen. located on the midpoint of the inguinal crease, midway between the pubic symphysis and the anterior superior iliac spine. SP-12 is commonly used to treat gynecological and urinary disorders such as irregular menstruation, uterine bleeding, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, leukorrhea, and urinary incontinence. It is also believed to regulate Qi and blood, invigorate the spleen, and regulate the stomach. It is said to be particularly effective in treating disorders that result from Qi stagnation and blood stasis. However, it is important to note that acupressure or acupuncture on this point should only be performed by a licensed practitioner.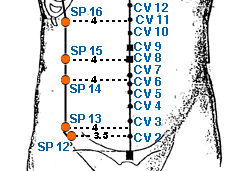
Fu She | Abode of the Fu | Spleen 13 | SP-13
This one is located on the abdomen, approximately 4 cun (finger widths) below the navel and 3 cun (finger widths) lateral to the anterior midline. It lies on the same horizontal level as the acupoint Ren-3. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, SP-13 is believed to regulate the functions of the spleen, stomach, liver, and intestines. It is used to treat a variety of digestive disorders, such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and dysentery. It is also used to address gynecological disorders, including irregular menstruation and pain during menstruation. Additionally, SP-13 is thought to help relieve lower back pain, muscle tension, and urinary disorders. SP-13 is contraindicated for pregnant women, as it is believed to induce labor. As with all acupoints, it is important to seek the guidance of a qualified practitioner before using SP-13 or any other acupoint for therapeutic purposes.
Fu Jie | Abdominal Bind | Spleen 14 | SP-14
This is an acupuncture point on the Spleen meridian of the body. It is located on the lateral side of the abdomen, 4 cun (finger widths) lateral to the navel, on the level of the fourth intercostal space. SP-14 is often used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) to treat a variety of digestive and respiratory disorders, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, and asthma. It is believed to regulate the flow of Qi (energy) in the body and to strengthen the Spleen and Stomach. In addition, SP-14 can also be used to relieve chest pain and promote lactation in breastfeeding mothers.
Da Heng | Great Horizontal | Spleen 15 | SP-15
This one is located on the abdomen, in the lower part of the stomach, 4 cun (about 2 inches) below the belly button, and 2 cun (about 1 inch) lateral to the anterior midline of the body. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, SP-15 is believed to regulate the spleen and stomach, and promote the smooth flow of qi and blood throughout the body. It is commonly used to treat digestive disorders such as abdominal pain, bloating, and constipation, as well as gynecological issues like irregular periods and menstrual pain. In addition, SP-15 is also used to address musculoskeletal problems like lower back pain and sciatica, as well as respiratory problems like coughing and asthma. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and is often used to alleviate stress and anxiety.
Fu Ai | Abdominal Lament | Spleen 16 | SP-16
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine that is located in the abdomen. More specifically, it is found approximately 4 cm lateral to the navel, along the line connecting the navel and the anterior superior iliac spine. SP-16 is often used to treat a variety of conditions related to the abdomen and reproductive system, such as abdominal distension, pain, and bloating, menstrual cramps, irregular menstruation, and infertility. It is also believed to be effective in treating other conditions such as diarrhea, constipation, and urinary tract infections. In traditional Chinese medicine, SP-16 is thought to regulate the Qi (vital energy) and blood circulation in the abdomen and help to relieve stagnation or blockages in this area.
Dan Zhong | Chest Center | Spleen 17 | SP-17
This one is located in the center of the chest, at the level of the fourth intercostal space, midway between the nipples. This acupoint is commonly used to treat respiratory and chest-related disorders, such as asthma, bronchitis, cough, and chest pain. It is also believed to be helpful in treating anxiety and emotional distress, as well as digestive disorders like indigestion, stomach pain, and diarrhea. In traditional Chinese medicine, this acupoint is thought to be an important point for regulating the flow of Qi and blood, and for calming the spirit. Stimulating SP-17 can be done with various methods such as finger pressure, acupuncture, and moxibustion. However, it is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare provider before attempting to use acupressure or acupuncture for any medical condition.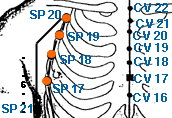
Tian Xi | Celestial Ravine | Spleen 18 | SP-18
This one is located on the lateral side of the chest, in the sixth intercostal space, four cun (about two inches) from the midline. This acupoint is known as the 'Extra Point for Blood Stasis' and is believed to help promote blood circulation, disperse blood stasis, and alleviate pain in the chest and hypochondriac region. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as chest pain, intercostal neuralgia, and pleurisy. In TCM, SP-18 is also associated with the Spleen and Stomach meridians, and it is believed that stimulating this acupoint can help regulate the digestive system and alleviate conditions such as abdominal distension, poor appetite, and diarrhea. Additionally, SP-18 is thought to have a calming effect on the mind, and can be used to treat emotional disorders such as anxiety and depression. As with all acupoints, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner before attempting to stimulate SP-18 or any other acupoint.
Xiong Man | Chest Fullness | Spleen 19 | SP-19
This one is located On the lateral chest, in the third intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the anterior midline. Stimulating SP-19 is believed to be helpful in treating disorders and discomforts related to the chest and breast area, including chest congestion, chest pain, and breast inflammation. It is also used to treat disorders of the digestive system, including indigestion, acid reflux, and abdominal bloating. SP-19 can be stimulated by applying pressure with the fingertips, or through acupuncture needles, moxibustion, or cupping. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to seek the guidance of a trained and licensed acupuncturist to ensure proper and safe treatment.
Zhou Rong | Encircling Glory | Spleen 20 | SP-20
This one is located on the lateral aspect of the chest. The SP-20 point is located on the chest, on the midaxillary line, in the 7th intercostal space. In women, it is located at the level of the nipple, while in men it is located about 4 cun (finger widths) below the nipple. In TCM, SP-20 is believed to regulate the Qi (energy) and blood of the uterus, and is used to treat various gynecological disorders, such as irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation), amenorrhea (absence of menstruation), and uterine prolapse. It is also believed to alleviate chest pain, coughing, and asthma, as well as promote lactation in nursing mothers.
Da Bao | Great Embracement | Spleen 21 | SP-21
This is an acupuncture point located in the chest, below the armpit, in the 6th intercostal space, about 6 cun lateral to the midline. It is found on the same horizontal line as the lower border of the nipple in men, and the 4th intercostal space in women. In traditional Chinese medicine, SP-21 is known to regulate the energy of the chest and the hypochondriac region. It is commonly used to treat pain in the chest and ribcage, and conditions such as asthma, cough, and difficulty breathing. It is also believed to help with conditions related to the breasts, such as mastitis and insufficient lactation, as well as menstrual problems and abdominal distension. SP-21 is often used in combination with other acupuncture points to treat various conditions. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult a qualified practitioner before trying to use SP-21 or any other acupuncture point for medical purposes.
Governing Vessel Meridian
This meridian is commonly known as an extra ordinary meridian. It is also called Tomo.
Chang Qiang | Long Strong | Governing Vessel 1 | GV-1
Known as Chang Qiang, is located at the midpoint of the sacrum, which is the triangular bone at the base of the spine. It is the starting point of the Governing Vessel Meridian and is considered to be one of the most important points in the body in traditional Chinese medicine. Stimulation of GV-1 is believed to help regulate the flow of qi (vital energy) throughout the body and strengthen the yang energy of the body. It is said to have a grounding effect on the body, promoting stability and balance. GV-1 is commonly used to treat disorders related to the lower back and sacral region, including lower back pain, sciatica, coccyx pain, and pelvic pain. It is also used to treat conditions related to the reproductive system, such as infertility and impotence, as well as digestive disorders such as constipation and diarrhea. Additionally, GV-1 is believed to be effective in treating anxiety, insomnia, and other emotional disorders.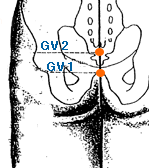
Yao Shu | Lumbar Shu | Governing Vessel 2 | GV-2
This is an acupuncture point that is also known as Yao Shu in Chinese. It is located on the midline of the back, in the depression below the spinous process of the second lumbar vertebra, approximately at the level of the umbilicus. This acupoint is commonly used to treat a variety of conditions related to the lower back and the sacral area. It is particularly effective in treating lower back pain, sciatica, and other musculoskeletal conditions that affect the lumbar spine. In addition, it is believed to have a regulatory effect on the genitourinary system, making it a useful point for conditions such as urinary incontinence, impotence, and menstrual disorders. GV-2 is also used in traditional Chinese medicine to tonify the Kidney Qi and strengthen the lumbar region, making it a useful point for individuals experiencing fatigue, weakness, and other symptoms associated with kidney deficiency. Overall, GV-2 is considered to be an important point for maintaining the health and balance of the lower back and pelvic region.
Yao Yang Guan | Lumbar Yang Pass | Governing Vessel 3 | GV-3
Known as Yao Yang Guan or Lumbar Yang Pass, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located in the midline of the back, at the level of the second lumbar vertebra, approximately three fingerbreadths below the spinous process of L2. GV-3 is said to tonify the kidneys, strengthen the lower back and relieve pain and stiffness in the lower back and legs. It is also used for conditions such as impotence, enuresis, irregular menstruation, and infertility. Additionally, it is believed to have a calming effect on the mind, aiding in the treatment of anxiety, depression, and insomnia. GV-3 can be stimulated by acupuncture or acupressure techniques to achieve its therapeutic effects. However, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner before attempting any treatment.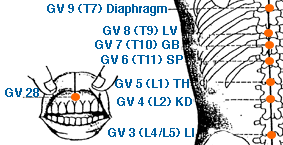
Ming Men | Life Gate | Governing Vessel 4 | GV-4
Known as Ming Men, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located in the lower back, on the spine, at the level of the second lumbar vertebra, approximately 3 finger widths below the navel. Mingmen is believed to be the gate of vitality and the source of the body's qi or vital energy. It is said to control the balance between yin and yang energies, and to be associated with the kidney and adrenal gland meridians. GV-4 is used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat a variety of conditions, including lower back pain, urinary problems, impotence, infertility, constipation, diarrhea, and general weakness or fatigue. It is also believed to improve overall vitality and boost the immune system. Acupressure or acupuncture applied to this point is thought to stimulate the flow of qi and blood in the body, helping to restore balance and promote healing. However, it is important to note that traditional Chinese medicine should not be used as a substitute for Western medicine in the treatment of serious or life-threatening conditions.
Xuan Shu | Suspended Pivot | Governing Vessel 5 | GV-5
Known as Xuan Shu (Chinese name), is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located along the Governing Vessel (GV) meridian. It is located on the midline of the body, in the lower back, about 4 cun (finger widths) below the spinous process of the 2nd lumbar vertebrae. GV-5 is believed to have a regulating effect on the lower abdomen and lower back. It is commonly used to treat conditions related to the urogenital system, such as painful or difficult urination, incontinence, impotence, and infertility. It may also be used to alleviate lower back pain and stiffness, as well as to tonify the Kidney and strengthen the body's overall energy. In acupuncture treatments, GV-5 is often combined with other acupoints in the lower back and abdomen for a more comprehensive approach to treating urogenital and reproductive disorders.
Ji Zhong | Sea of Qi | Governing Vessel 6 | GV-6
Known as the Sea of Qi point, is an important acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) located on the middle back, below the spinous process of the eleventh thoracic vertebra (T11). In TCM, GV-6 is believed to regulate the Qi (energy) and blood flow throughout the body, and to harmonize the internal organs. It is often used to treat disorders related to the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems, such as abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, bladder issues, menstrual problems, and infertility. GV-6 is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and emotions, and is often used to treat anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Additionally, it is believed to strengthen the body's immune system and promote overall health and wellbeing. GV-6 can be stimulated by applying gentle pressure with the fingers or by using acupuncture needles. It is generally considered safe, although it should be avoided during pregnancy. It is recommended to seek the guidance of a qualified TCM practitioner before using acupressure or acupuncture for any health condition.
Zhong Shu | Longitudinal Crevice | Governing Vessel 7 | GV-7
Known as the Zhong Shu or Longitudinal Crevice acupoint, is a point located on the middle back, below the spinous process of the tenth thoracic vertebra (T10). Stimulation of this acupoint is believed to benefit the lower back, the reproductive system, and the digestive system. It may also be useful for treating urinary incontinence, impotence, and menstrual cramps. GV-7 is also used to help relieve stress, anxiety, and insomnia. To stimulate GV-7, pressure can be applied using the fingertips or a blunt instrument such as a rounded tool. This can be done by pressing the point for several seconds, or by applying firm pressure and rubbing the point in a circular motion. It is important to use caution and consult a qualified acupuncturist or healthcare provider before attempting acupressure or acupuncture at this or any other acupoint.
Jin Suo | Sinew Contraction | Governing Vessel 8 | GV-8
Known as Jin Suo or Sinew Contraction, is an acupuncture point located on the midline of the body, in the sacral region, at the level of the coccyx. It is approximately 1.5 cun (finger widths) anterior to the tip of the coccyx. GV-8 is indicated for the treatment of lower back pain, sciatica, numbness or weakness in the legs, impotence, irregular menstruation, and other disorders related to the sacral and coccygeal regions. It is also commonly used for the treatment of emotional disorders such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. GV-8 is considered to be an important point for regulating and strengthening the lower back and legs, as well as for promoting the flow of Qi and blood throughout the body. It is often used in combination with other acupuncture points to treat a variety of conditions, and is typically stimulated by inserting acupuncture needles or applying pressure with acupressure techniques.
Zhi Yang | Extremity of Yang | Governing Vessel 9 | GV-9
Known as the Extremity of Yang, is a point located on the midline of the body on the lower back, in the depression below the spinous process of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4). In traditional Chinese medicine, GV-9 is believed to be the meeting point of the Governing Vessel (GV) and the Bladder Meridian, and is considered to be an important point for regulating the body's Qi and blood circulation. It is commonly used to treat disorders related to the lower back and spine, such as sciatica, lumbago, and back pain. Additionally, GV-9 is thought to have a calming effect on the mind and is often used to treat emotional imbalances such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. It is also believed to have a tonifying effect on the immune system, and may be used to treat conditions such as chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia. As with any acupuncture treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to determine if GV-9 is an appropriate point for your specific condition and overall health.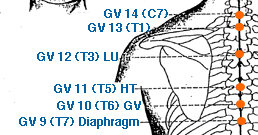
Ling Tai | Spirit Tower | Governing Vessel 10 | GV-10
Known as Shen Dao or the, is a point located on the midline of the body on the lower back, in the depression below the spinous process of the fifth lumbar vertebra. GV-10 is considered a major point in acupuncture and is believed to be connected to the brain and the nervous system. It is said to regulate the Qi (life energy) and blood circulation in the head and promote mental clarity, cognitive function, and emotional balance. GV-10 is also believed to have a beneficial effect on many conditions including headaches, vertigo, tinnitus, and insomnia. It may also be used to treat emotional disorders such as anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. Acupuncture therapy involving stimulation of GV-10 can be accomplished with needles or non-invasive techniques such as acupressure, moxibustion, and laser therapy.
Shen Dao | Spirit Path | Governing Vessel 11 | GV-11
Shen Dao, known as Spirit Path or Governing Vessel 11 (GV-11), is a significant acupuncture point located on the midline of the back, specifically below the spinous process of the eleventh thoracic vertebra. This point, found in the upper back region, is integral to the Governing Vessel meridian. GV-11 is renowned for its influence on mental and emotional health, often used in managing stress, anxiety, and mood disorders. It's believed to harmonize the heart and mind, promoting emotional stability and mental clarity. Additionally, GV-11 is thought to enhance bodily strength and vitality, making it beneficial in boosting immunity and aiding recovery from fatigue and illness. In physical health, Shen Dao is used to alleviate back pain, particularly in the upper and mid-back areas. Its strategic positioning also implies benefits for respiratory issues like asthma. Stimulation of GV-11 can be achieved through needle acupuncture, acupressure, moxibustion, or laser therapy, each technique aiming to regulate Qi flow and promote overall wellness.
Shen Zhu | Spiritual Pillar | Governing Vessel 12 | GV-12
This is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the spine in the region of the seventh thoracic vertebrae. It is known as Shen Zhu, which means Spiritual Pillar. GV-12 is located in the center of the upper back, midway between the lower border of the seventh cervical vertebra (GV-14) and the upper border of the first thoracic vertebra (GV-11). GV-12 is commonly used to treat emotional and mental disorders, including anxiety, depression, insomnia, and stress. It is believed that stimulating this point can help to calm the mind, strengthen the spirit, and improve mental clarity. Additionally, GV-12 is thought to help regulate the functions of the heart and lungs, which can help to improve overall health and vitality. GV-12 can be stimulated through acupuncture or acupressure techniques. To stimulate this point using acupressure, apply steady pressure to the point with your fingertips for several seconds, and then release the pressure. Repeat this process several times, taking deep breaths as you do so. Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into the point to stimulate it, which can be done by a trained acupuncturist.
Tao Dao | Path of the Tao | Governing Vessel 13 | GV-13
Location: The GV-13 (Tao Dao) acupoint is situated on the midline of the body, along the Governor Vessel meridian, also known as the Du Mai meridian. It is located approximately 1.5 cun (finger width) below the spinous process of the first thoracic vertebra (T1). To locate GV-13, start by finding the base of the neck and feel for the bony prominence at the top of the spine. From this point, measure 1.5 cun downward, and you will find Tao Dao. Indications and Treatments: GV-13 (Tao Dao) is a vital acupoint known to alleviate a range of illnesses and conditions, including: Mental and emotional disorders: Tao Dao is beneficial for treating anxiety, depression, and emotional instability. It helps to calm the mind and balance emotions, promoting mental well-being. Respiratory issues: GV-13 is effective in relieving asthma, cough, bronchitis, and other respiratory ailments. It helps regulate lung function, clears phlegm, and eases breathing. Neck and shoulder pain: This acupoint can relieve stiffness and pain in the neck and shoulder area, making it beneficial for those with cervical spondylosis, muscle strain, or tension headaches. Febrile diseases: Tao Dao can reduce high fever and alleviate symptoms of heatstroke. It helps to clear excess heat from the body, harmonize the internal organs, and restore balance. Immune system support: GV-13 is known to strengthen the immune system and enhance the body's ability to resist illness and disease. It helps to regulate the body's energy, known as Qi, which is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Please note that while acupuncture can be an effective treatment for various conditions, it is essential to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) practitioner for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
Da Zuhi | Great Hammer | Governing Vessel 14 | GV-14
Known as the Da Zuhi acupoint, is located on the midline of the back, below the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra (C7). It is a commonly used acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine and is believed to be an important point for regulating the energy flow throughout the body. GV-14 is used to treat a variety of conditions, including respiratory disorders such as asthma, bronchitis, and cough, as well as neck pain, shoulder pain, and stiffness. It is also commonly used to alleviate stress and anxiety, promote relaxation, and improve overall emotional well-being. GV-14 is believed to have a calming effect on the nervous system, making it useful for treating conditions such as insomnia and depression. In addition, it is sometimes used to support the immune system and promote overall vitality and energy. GV-14 is often combined with other acupoints to enhance its therapeutic effects.
Yu Men | Mute's Gate | Governing Vessel 15 | GV-15
This one is located on the midline of the neck, in the depression just below the occipital bone. It is believed to regulate the flow of Qi in the head and neck, promote circulation, and relieve pain and tension in the neck and head.
Stimulation of Yu Men is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat conditions such as headaches, neck pain, dizziness, and vertigo. It may also be beneficial for the treatment of hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions, as well as neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
As always, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if Yu Men is appropriate for your specific condition.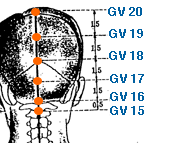
Feng Fu | Wind Mansion | Governing Vessel 16 | GV-16
This one is an acupuncture point located on the midline of the body, at the base of the skull, in the depression directly below the external occipital protuberance. This point is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat various conditions related to the head, neck, and upper body, including headache, neck pain, stiff neck, dizziness, vertigo, blurred vision, tinnitus, nasal congestion, sinusitis, and insomnia. It is also believed to help improve memory and concentration, and to promote mental clarity. GV-16 is considered to be an important point in treating conditions related to the brain and the central nervous system. It is believed that stimulating this point can help regulate the flow of qi and blood in the brain and spinal cord, promoting overall health and well-being. However, it is important to note that acupuncture should be used as a complementary therapy alongside conventional medical treatments, and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice and treatment.
Nao Hu | Brain's Door | Governing Vessel 17 | GV-17
Known as Nao Hu or Brain's Door, is located on the posterior head, 1.5 cun directly above the external occipital protuberance. GV-17 is indicated for treating various disorders of the head and neck, including headache, vertigo, tinnitus, nasal congestion, and throat soreness. It is also believed to improve memory and mental function and to treat insomnia, epilepsy, and depression. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, GV-17 is considered a crucial point for tonifying the brain, and strengthening the nervous system and the will. It is often used in combination with other points to regulate the circulation of Qi and blood and to balance the body's Yin and Yang energies. GV-17 should not be needled deeply, as there is a risk of injuring the spinal cord. It is commonly stimulated with finger pressure, moxibustion, or magnetic therapy. As with all acupuncture points, it should be used only by trained professionals and under appropriate conditions.
Qiang Jian | Unyielding Space | Governing Vessel 18 | GV-18
Known as Qiang Jian in Chinese, is an acupoint located at the top of the head, about 1.5 cun posterior to the midpoint of the anterior hairline and 0.5 cun superior to the midpoint of the line connecting the apexes of both ears. Stimulation of GV-18 is believed to have a calming and balancing effect on the mind and can be beneficial for treating mental and emotional disorders such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. It is also believed to enhance memory and cognitive function and can be used to treat conditions such as forgetfulness, dizziness, and vertigo. GV-18 is also commonly used to relieve pain in the head, neck, and upper back. It may be effective for treating conditions such as migraines, tension headaches, and neck pain. In traditional Chinese medicine, GV-18 is considered a major point for regulating the flow of Qi in the body and promoting overall wellness. It is believed to have a harmonizing effect on the body and mind, and can be used as a general tonic to enhance overall vitality. As with any acupoint or treatment, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if GV-18 is appropriate for your specific condition.
Hou Ding | Behind the Vertex | Governing Vessel 19 | GV-19
Known as Hou Ding, is an acupoint in the Governing Vessel meridian. It is located at the midpoint of the sagittal suture, which is the line of connective tissue that runs along the top of the head between the frontal and parietal bones. GV-19 is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat disorders of the brain and nervous system. It is believed that stimulating this point can help to calm the mind, improve concentration, and treat conditions such as insomnia, depression, and anxiety. In addition, GV-19 is sometimes used to treat headaches, vertigo, and dizziness. However, it is important to note that acupuncture should always be used as a complementary therapy and not as a substitute for professional medical care.
Bai Hui | Hundred Convergences | Governing Vessel 20 | GV-20
Known as Bai Hui or Hundred Convergences, is located at the top of the head, at the midpoint of a line connecting the apex of both ears. This acupoint is considered to be the meeting point of all Yang meridians, making it a powerful point in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Stimulation of GV-20 can benefit the brain and the entire body. It is believed to regulate the Qi (energy) flow throughout the body, calm the mind, and improve cognitive function. GV-20 is commonly used to treat various conditions related to the nervous system, such as headaches, vertigo, dizziness, tinnitus, and epilepsy. It is also used for psychological conditions like depression, anxiety, and stress. Moreover, it is believed to help with memory loss, insomnia, and fatigue. GV-20 can be stimulated by gentle pressure, massage, or acupuncture. It is considered to be a safe acupoint, but as with any treatment, it should be used with caution and under the guidance of a qualified practitioner.
Qian Ding | Before the Vertex | Governing Vessel 21 | GV-21
Known as Qian Ding in Chinese, is an acupoint located at the very top of the head, in the depression at the center of the vertex. Stimulation of GV-21 is believed to promote mental clarity, enhance memory, and improve cognitive function. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as forgetfulness, poor concentration, and dizziness. In traditional Chinese medicine, GV-21 is also considered a major point for regulating the flow of Qi in the body and promoting overall wellness. It is believed to have a tonifying effect on the brain, nourishing the spirit and enhancing mental and emotional well-being. GV-21 may also be beneficial for treating certain neurological and psychological conditions such as Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, and depression. It is believed to work by regulating the nervous system, improving circulation, and balancing the body's energy. As with any acupoint or treatment, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if GV-21 is appropriate for your specific condition.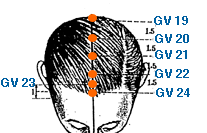
Xin Hui | Fontanel Meeting | Governing Vessel 22 | GV-22
Known as Xin Hui. It is located at the midpoint of the top of the head, at the intersection of the sagittal suture and the line drawn between the apexes of the ears. In TCM, GV-22 is believed to regulate the brain, mind, and consciousness. It is often used to treat neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, headaches, migraines, dizziness, and vertigo. It may also be used to improve mental clarity, concentration, and memory. Some practitioners also use GV-22 for spiritual purposes, such as opening the Third Eye and connecting with higher consciousness. GV-22 is typically stimulated using gentle pressure, acupuncture needles, or moxibustion (the application of heat to the point). However, it should only be performed by a licensed and experienced acupuncturist.
Shang Xing | Upper Star | Governing Vessel 23 | GV-23
Known as Shang Xing or Upper Star, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located on the midline of the forehead, approximately 0.5 cm above the midpoint of the eyebrow. It is the highest point on the forehead and is directly above the pineal gland. GV-23 is believed to treat a wide range of ailments, including headaches, dizziness, insomnia, and depression. It is also thought to improve mental clarity and concentration and enhance overall brain function. GV-23 is often used in acupuncture treatments for conditions related to the head, such as sinusitis, rhinitis, and facial paralysis. It is also used in combination with other acupoints to treat anxiety, stress, and emotional disorders. Some practitioners also use GV-23 to treat eye disorders, such as myopia, astigmatism, and night blindness.
Shen Ting | Spirit Court | Governing Vessel 24 | GV-24
Known as Shen Ting, is an acupoint located on the midline of the scalp, at the center of the anterior hairline. It is located about 1.5 cm directly above the midpoint of the forehead hairline. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), GV-24 is believed to have a regulating effect on the brain and is used to treat conditions related to the nervous system. It is also believed to help improve memory, promote mental clarity and focus, and alleviate headaches and dizziness. GV-24 is also said to have a calming effect on the mind and is used to treat insomnia, anxiety, and depression. It is often combined with other acupoints in the treatment of these conditions. In addition, GV-24 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the body's energy, or Qi, and is used to treat fatigue, weakness, and poor digestion. It may also be used to promote circulation and relieve pain in the head and face. GV-24 is also commonly used in meditation practices to help calm the mind and promote a sense of peace and relaxation.
Su Liao | White Bone-Hole | Governing Vessel 25 | GV-25
Known as Su Liao in Chinese, is located at the tip of the nose, between the two bony structures called the nasal bones. Stimulation of GV-25 at the tip of the nose is believed to have a calming effect on the mind, and can be used to treat conditions such as anxiety, stress, and depression. It is also believed to enhance the function of the sense organs, particularly the nose, and may be used to treat conditions such as sinusitis and rhinitis. In traditional Chinese medicine, GV-25 is considered a major point for regulating the flow of Qi in the body and promoting overall wellness. It is believed to have a tonifying effect on the brain and nervous system, promoting mental clarity and enhancing cognitive function. GV-25 may also be useful for treating certain neurological conditions such as epilepsy and Parkinson's disease. It is believed to work by regulating the nervous system, improving circulation, and balancing the body's energy. As always, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if GV-25 is appropriate for your specific condition.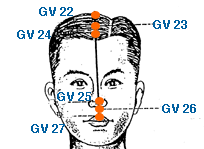
Shui Gou | Water Trough | Governing Vessel 26 | GV-26
This is an acupoint located on the philtrum, which is the vertical groove between the nose and the upper lip. It is also known as the Shui Gou or Water Trough point. This point is considered to be the meeting point of the Governing Vessel and Conception Vessel meridians. GV-26 is commonly used in first aid and emergency situations, as it is believed to have a reviving effect and can be used to restore consciousness in cases of fainting or shock. It is also used in the treatment of facial pain, nasal congestion, toothache, and other conditions related to the face and mouth. In addition to its physical benefits, GV-26 is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and is often used in the treatment of anxiety, depression, and other emotional imbalances. Some practitioners also use this point for meditation and spiritual practices. However, it is important to note that while acupuncture can be a helpful complementary therapy for certain conditions, it should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment.
Dui Duan | Extremity of the Mouth | Governing Vessel 27 | GV-27
Known as Dui Duan in Chinese, is an acupoint located at the top middle of the upper lip, just below the nasal septum. Stimulation of GV-27 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can be beneficial for treating conditions such as anxiety, stress, and depression. It is also believed to enhance the function of the sense organs, particularly the mouth, and may be used to treat conditions such as difficulty speaking or swallowing. In traditional Chinese medicine, GV-27 is considered a major point for regulating the flow of Qi in the body and promoting overall wellness. It is believed to have a tonifying effect on the brain and nervous system, promoting mental clarity and enhancing cognitive function. GV-27 may also be useful for treating certain neurological conditions such as epilepsy and Parkinson's disease. It is believed to work by regulating the nervous system, improving circulation, and balancing the body's energy. In addition, GV-27 is sometimes used for cosmetic purposes to promote facial rejuvenation and to reduce wrinkles and fine lines around the mouth and upper lip. As with any acupoint or treatment, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if GV-27 is appropriate for your specific condition.
Yin Jiao | Gum Intersection | Governing Vessel 28 | GV-28
Known as Yin Jiao in Chinese, is located in the center of the upper gum, between the two front upper teeth. Stimulation of GV-28 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can be beneficial for treating conditions such as anxiety, stress, and depression. It is also believed to enhance the function of the sense organs, particularly the tongue, and may be used to treat conditions such as speech disorders and taste disturbances. In traditional Chinese medicine, GV-28 is considered a major point for regulating the flow of Qi in the body and promoting overall wellness. It is believed to have a tonifying effect on the brain and nervous system, promoting mental clarity and enhancing cognitive function. GV-28 may also be useful for treating certain neurological conditions such as epilepsy and Parkinson's disease. It is believed to work by regulating the nervous system, improving circulation, and balancing the body's energy. In addition, GV-28 is sometimes used for cosmetic purposes to promote facial rejuvenation and to reduce wrinkles and fine lines around the mouth and chin. As with any acupoint or treatment, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if GV-28 is appropriate for your specific condition.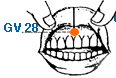
Conception Vessel Meridian
This meridian is commonly known as an extra ordinary meridian. It is also called Ren Mai.
Hui Yin | Meeting of Yin | Conception Vessel 1 | CV-1
Known as Hui Yin, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine located at the midpoint of the perineum, between the anus and the scrotum in men or between the anus and the vagina in women. It is considered the starting point of the Conception Vessel (CV), which is one of the eight extraordinary meridians in the body. CV-1 is believed to have a number of therapeutic benefits, including the treatment of genitourinary disorders, menstrual irregularities, sexual dysfunction, lower back pain, and constipation. It is also considered to have a regulating effect on the Qi (energy) flow throughout the body. Stimulating CV-1 through acupressure, acupuncture, or other forms of traditional Chinese medicine may help to alleviate a variety of physical and emotional symptoms, although it is important to consult a qualified practitioner before attempting any self-treatment.
Qu Gu | Curved Bone | Conception Vessel 2 | CV-2
This is one of the acupoints located on the conception vessel meridian. Also known as Qu Gu in traditional Chinese medicine, it is located in the lower abdomen, around 1.5 cun below the belly button and 0.5 cun above the pubic symphysis. In TCM, CV-2 is believed to regulate the lower burner, which includes the bladder, intestines, and reproductive organs. It is commonly used to treat disorders in these areas, such as painful urination, constipation, menstrual pain, and infertility. In addition, it can also be used for lower back pain, hernias, and other disorders related to the lower abdomen. CV-2 can be stimulated with manual pressure, acupuncture needles, or moxibustion. It is important to note that any kind of acupuncture or acupressure should be performed by a licensed practitioner trained in traditional Chinese medicine.
Zhong Ji | Central Pole | Conception Vessel 3 | CV-3
Known as Zhong Ji, is a point on the Conception Vessel meridian in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located four finger-widths below the navel, in the center of the body. CV-3 is used to treat a variety of conditions related to the lower abdomen, including urinary and reproductive issues. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as impotence, premature ejaculation, infertility, irregular menstruation, and menstrual pain. It can also be used to relieve lower back pain, constipation, diarrhea, and digestive issues. In addition to its physical benefits, CV-3 is believed to have emotional and mental benefits as well. It is thought to help alleviate anxiety, depression, and stress-related conditions by calming the mind and regulating the flow of qi, or energy, throughout the body.
Guan Yuan | Origin Pass | Conception Vessel 4 | CV-4
Known as Guan Yuan, is an acupoint in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the midline of the abdomen, four finger widths below the belly button and midway between the pubic bone and the navel. In traditional Chinese medicine, CV-4 is considered to be a vital point for nourishing the body's Qi, or life force energy, and is commonly used for issues related to the reproductive and digestive systems. It is believed that stimulating this point can help regulate menstrual cycles, alleviate menstrual cramps, and treat conditions such as infertility, impotence, and urinary incontinence. Additionally, it is thought to improve digestive function and relieve digestive discomforts such as constipation, diarrhea, and abdominal bloating. CV-4 is also considered to be an important point for strengthening the immune system and promoting overall vitality and wellness. It is often used in conjunction with other acupoints to treat a variety of conditions, including fatigue, anxiety, depression, and insomnia. It is important to note that while acupuncture and acupressure can be effective in treating certain conditions, they should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. It is always advisable to consult a qualified healthcare practitioner before using these therapies.
Shi Men | Lower Gate | Conception Vessel 5 | CV-5
Known as Shi Men or the Lower Gate, is an acupoint located on the front midline of the body, two finger-widths below the belly button. It is the meeting point of the Conception Vessel and the Kidney meridian. This acupoint is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat conditions related to the lower abdomen and reproductive system. It is believed to regulate the Qi (energy) flow in the lower abdomen, tonify the Kidney Qi, and nourish the Yin and Yang of the lower body. Some of the conditions that CV-5 may be used to treat include urinary incontinence, menstrual cramps, irregular periods, infertility, impotence, and lower abdominal pain. It may also be used to regulate the digestive system and relieve constipation. Additionally, CV-5 may be used for emotional imbalances such as anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders, as it is believed to calm the mind and regulate the emotions.
Qi Hai | Sea of Qi | Conception Vessel 6 | CV-6
Known as Qi Hai, is an important acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine located in the lower abdomen. It is situated approximately 1.5 inches below the belly button and midway between the two hip bones. Stimulating CV-6 is believed to strengthen the digestive system, improve blood circulation, and enhance the function of the reproductive system. It is commonly used to treat disorders of the lower abdomen, including menstrual cramps, urinary and bowel problems, and infertility. It may also be effective in treating some digestive disorders, such as bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Additionally, it is thought to have a tonifying effect on the body, promoting overall health and wellbeing. It is also commonly used in acupuncture treatments to increase energy, relieve stress, and improve mental clarity. CV-6 can be stimulated through acupuncture, acupressure, or moxibustion. As with any medical treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed healthcare practitioner before attempting to use this acupoint for therapeutic purposes.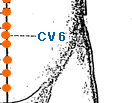
Yin Jiao | Yin Intersection | Conception Vessel 7 | CV-7
This is an acupuncture point located on the Conception Vessel meridian, also known as Ren Mai. This acupoint is located on the midline of the abdomen, approximately 1.5 cun (about 2.5 cm) directly below the navel. CV-7 is believed to have a wide range of therapeutic benefits. It is often used to regulate the function of the lower abdomen and reproductive organs, as well as to improve digestion and alleviate abdominal pain. This acupoint is also thought to be useful in treating conditions such as diarrhea, constipation, urinary tract infections, menstrual cramps, and infertility. In traditional Chinese medicine, CV-7 is considered to be a powerful point for nourishing the body's energy, or qi. It is also believed to help regulate the body's yin and yang energies, which can become imbalanced due to stress, illness, or other factors. By stimulating CV-7, practitioners aim to restore balance and harmony to the body's energy systems, leading to improved health and well-being.
Shen Que | Spirit Gate | Conception Vessel 8 | CV-8
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) located on the midline of the abdomen, two finger-widths above the belly button. This point is also known as the Shen Que or Spirit Gate. It is where the energy of the Ren Meridian is said to meet, and it is considered to be a crucial point for balancing Qi in the body. In TCM, CV-8 is believed to have a wide range of therapeutic benefits, including the treatment of digestive disorders, menstrual disorders, urinary tract infections, infertility, and low libido. This point is also believed to help regulate the energy of the Triple Burner Meridian, which is responsible for regulating the body's temperature and fluid metabolism. Additionally, CV-8 is thought to have a calming effect on the mind and emotions, making it helpful for anxiety and stress-related conditions. Practitioners of TCM may use acupuncture, acupressure, or other techniques to stimulate CV-8 and promote healing in the body. However, it's important to note that these therapies should be performed by a qualified and licensed practitioner.
Shui Fen | Water Divide | Conception Vessel 9 | CV-9
Known as the Shui Fen acupoint, is located on the midline of the abdomen, about 1.5 cun above the navel. It is the meeting point of the Conception Vessel (Ren Mai) and the Stomach Meridian (Wei Mai). Stimulating CV-9 is believed to be effective in treating conditions related to the digestive system, including bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. It is also used for conditions related to the reproductive system, such as irregular menstruation and infertility. In addition, it is thought to be helpful in reducing stress and anxiety, promoting relaxation, and improving overall energy flow in the body.
Xia Wan | Lower Venter Shu | Conception Vessel 10 | CV-10
Known as the Lower Venter Shu, is an acupuncture point located on the midline of the abdomen, 2 cun above the navel and 2 cun below the sternocostal angle. This acupoint is said to be effective in treating various gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea, constipation, abdominal bloating and pain. It is also believed to help with conditions related to the reproductive and urinary systems, such as menstrual cramps, irregular periods, impotence, and urinary incontinence. In addition, CV-10 is often used to tonify the Qi and blood, and to regulate the functions of the spleen, stomach, and intestines. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a qualified practitioner to determine if CV-10 is appropriate for your specific condition.
Jian Li | Interior Strengthening | Conception Vessel 11 | CV-11
This is an acupuncture point located on the front midline of the body, four cun (finger widths) above the navel. It is also known as the Jian Li point in traditional Chinese medicine. CV-11 is believed to have a regulating effect on the stomach and spleen, and is often used to treat digestive disorders such as indigestion, abdominal distension, and diarrhea. It is also thought to promote the movement of Qi and blood throughout the body, and can be used to address menstrual disorders, fertility issues, and urinary problems. In addition, CV-11 is thought to have a calming and grounding effect on the mind and body, and may be used to help alleviate stress, anxiety, and insomnia. It is also believed to strengthen the immune system and improve overall energy and vitality. However, it's important to note that while acupuncture can be a beneficial complementary therapy, it should not be used as a substitute for standard medical care for any serious conditions.
Zhong Wan | Central Venter | Conception Vessel 12 | CV-12
This is an acupuncture point located on the front midline of the abdomen, around the midpoint between the navel and the bottom of the breastbone (sternum). It is also known as Zhong Wan in Chinese. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), CV-12 is considered to be the convergence point of the body's Qi (life force) and is believed to regulate the functions of the digestive system, spleen, and stomach. CV-12 is commonly used to treat digestive disorders such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. It is also used to alleviate symptoms of gastric ulcers, bloating, and poor appetite. In addition, it may be used to treat emotional imbalances such as anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. Some practitioners also use it to address fertility issues, menstrual disorders, and urinary problems. Stimulation of this point can be achieved through acupressure, acupuncture, or moxibustion. As with all acupuncture points, it should be stimulated by a licensed and experienced practitioner.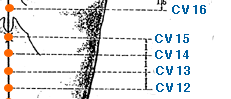
Shang Wan | Upper Venter | Conception Vessel 13 | CV-13
Known as Shang Wan, is an acupoint located on the midline of the abdomen, 4 cun above the navel. CV-13 is believed to help with various digestive issues, such as abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea. It is also used to address issues related to the respiratory and cardiac systems, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and palpitations. Additionally, it is sometimes used to help regulate menstruation and treat conditions related to the urinary system, such as frequent urination or difficulty urinating. In traditional Chinese medicine, CV-13 is thought to regulate the flow of Qi, or life force energy, in the abdomen and promote overall digestive and reproductive health. It is often used in combination with other acupoints as part of acupuncture or acupressure treatments.
Ju Que | Great Tower | Conception Vessel 14 | CV-14
Known as Ju Que or the Great Tower, is an acupoint located on the midline of the abdomen, approximately at the level of the fifth intercostal space. It is located approximately halfway between the navel and the bottom of the breastbone. CV-14 is used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat conditions related to the chest, such as cough, asthma, chest tightness, and palpitations. It is also used to treat digestive disorders, such as acid reflux, stomach pain, and nausea, as well as emotional imbalances, such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Additionally, it is believed to have a regulating effect on the immune system, making it useful in the treatment of autoimmune disorders. Stimulating this acupoint is believed to regulate the flow of Qi, or vital energy, through the chest and abdomen, helping to restore balance and alleviate symptoms of illness. It can be stimulated using acupressure, acupuncture, or moxibustion therapy.
Jiu Wei | Turtledove Tail | Conception Vessel 15 | CV-15
This is an acupoint in the Conception Vessel meridian. It is also known as Jiu Wei and is translated as Turtledove Tail. This acupoint is located in the center of the sternum, at the level of the fourth intercostal space. CV-15 is said to regulate the Qi and relieve stagnation in the chest, making it useful for treating conditions such as asthma, coughing, and chest pain. It is also believed to benefit the heart and calm the spirit, making it useful for treating anxiety, palpitations, and insomnia. Additionally, CV-15 is thought to help regulate digestion and alleviate abdominal bloating and pain. It is often used in acupuncture treatments for a wide range of conditions related to the chest and abdomen.
Zhong Ting | Center Palace | Conception Vessel 16 | CV-16
Known as the Center Palace point, is an important acupuncture point in Traditional Chinese Medicine. It is located on the midline of the sternum, at the level of the fourth intercostal space, between the nipples. CV-16 is believed to regulate and strengthen the Qi (life force energy) of the body. It is commonly used to treat disorders related to the respiratory system, such as cough, asthma, and chest congestion. It can also be used to treat emotional disorders like anxiety, depression, and stress. In addition, CV-16 is said to help with digestive disorders like indigestion and abdominal bloating, as well as menstrual irregularities and reproductive disorders. It is also thought to have a calming effect on the mind and body, making it useful in treating insomnia and other sleep disorders. To stimulate CV-16, acupuncturists may use needles or acupressure techniques. The point is considered safe for most people, but it is important to seek the advice of a qualified practitioner before attempting to use acupuncture or other forms of Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat any medical condition.
Dan Zhong | Chest Center | Conception Vessel 17 | CV-17
Known as Dan Zhong, is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine located on the front midline of the body, on the sternum, at the level of the fourth intercostal space. This point is believed to regulate and balance the Qi (vital energy) and blood circulation in the chest, lungs, and heart, promoting emotional stability and relaxation. Stimulating this point is also thought to benefit the digestive system, relieve chest congestion, and alleviate anxiety, depression, and other emotional disorders. CV-17 is commonly used in TCM to treat conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, cough, palpitations, chest pain, indigestion, and emotional stress. It is also believed to be effective in improving overall respiratory and cardiac health, strengthening the immune system, and promoting longevity. However, it is important to note that acupuncture should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice and treatment.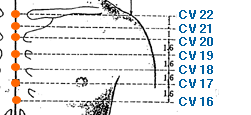
Yu Tang | Jade Hall | Conception Vessel 18 | CV-18
Known as Yu Tang in Chinese, is an acupoint located on the midline of the sternum, about four finger widths above the base of the breastbone. Stimulation of CV-18 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the body's energy, particularly on the Qi (vital energy) of the heart and lungs. It can be used to treat conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, coughing, and chest congestion. In traditional Chinese medicine, CV-18 is considered a major point for regulating the flow of Qi in the body and promoting overall wellness. It is believed to have a tonifying effect on the heart and respiratory system, promoting mental clarity and enhancing cognitive function. CV-18 may also be useful for treating certain emotional imbalances such as anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. It is believed to work by regulating the nervous system, improving circulation, and balancing the body's energy. In addition, CV-18 is sometimes used for cosmetic purposes to promote chest and breast health and to reduce wrinkles and fine lines in the chest area. As with any acupoint or treatment, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if CV-18 is appropriate for your specific condition.
Zi Gong | Purple Palace | Conception Vessel 19 | CV-19
Known as Zi Gong in Chinese, is an acupoint located on the midline of the chest, at the level of the fourth intercostal space, about four finger widths above the base of the breastbone. Stimulation of CV-19 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the body's energy, particularly on the Qi (vital energy) of the heart and lungs. It can be used to treat conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, coughing, and chest congestion. In traditional Chinese medicine, CV-19 is considered a major point for regulating the flow of Qi in the body and promoting overall wellness. It is believed to have a tonifying effect on the heart and respiratory system, promoting mental clarity and enhancing cognitive function. CV-19 may also be useful for treating certain emotional imbalances such as anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. It is believed to work by regulating the nervous system, improving circulation, and balancing the body's energy. In addition, CV-19 is sometimes used for cosmetic purposes to promote chest and breast health and to reduce wrinkles and fine lines in the chest area. As with any acupoint or treatment, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if CV-19 is appropriate for your specific condition.
Hui Gai | Florid Canopy | Conception Vessel 20 | CV-20
Known as Hui Gai in Chinese, is an acupoint located on the midline of the chest, at the level of the second intercostal space, about four finger widths above the base of the breastbone. Stimulation of CV-20 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the body's energy, particularly on the Qi (vital energy) of the heart and lungs. It can be used to treat conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, coughing, and chest congestion. In traditional Chinese medicine, CV-20 is considered a major point for regulating the flow of Qi in the body and promoting overall wellness. It is believed to have a tonifying effect on the heart and respiratory system, promoting mental clarity and enhancing cognitive function. CV-20 may also be useful for treating certain emotional imbalances such as anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. It is believed to work by regulating the nervous system, improving circulation, and balancing the body's energy. In addition, CV-20 is sometimes used for cosmetic purposes to promote chest and breast health and to reduce wrinkles and fine lines in the chest area. As with any acupoint or treatment, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if CV-20 is appropriate for your specific condition.
Xuan Ji | Jade Pivot | Conception Vessel 21 | CV-21
Known as Xuan Ji in Chinese, is an acupoint located on the manubrium midline, midway between CV 20 and CV 22. Stimulation of CV-21 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the body's energy, particularly on the Qi (vital energy) of the heart and lungs. It can be used to treat conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, coughing, and chest congestion. In traditional Chinese medicine, CV-21 is considered a major point for regulating the flow of Qi in the body and promoting overall wellness. It is believed to have a tonifying effect on the heart and respiratory system, promoting mental clarity and enhancing cognitive function. CV-21 may also be useful for treating certain emotional imbalances such as anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. It is believed to work by regulating the nervous system, improving circulation, and balancing the body's energy. In addition, CV-21 is sometimes used for cosmetic purposes to promote chest and breast health and to reduce wrinkles and fine lines in the chest area. As with any acupoint or treatment, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if CV-21 is appropriate for your specific condition.
Tian Tu | Celestial Chimney | Conception Vessel 22 | CV-22
Known as Tian Tu, is an acupoint located in the center of the suprasternal fossa, between the two heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It is at the level of the sternal angle, where the sternum and the clavicle meet. CV-22 is used to treat conditions related to the throat, chest, and upper respiratory tract, such as asthma, bronchitis, cough, and sore throat. It is also commonly used to treat emotional and mental disorders, such as anxiety, depression, and irritability. Additionally, it is believed to help with conditions related to the thyroid gland, such as goiter and hyperthyroidism. Stimulating CV-22 can help regulate the flow of qi and blood in the chest area, and promote the function of the thyroid gland. It is important to note that before using any acupoint, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or medical professional, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Lian Quan | Ridge Spring | Conception Vessel 23 | CV-23
Known as Lian Quan, is an acupuncture point located in the middle of the throat, in the depression between the two heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It is situated directly below the Adam's apple. In traditional Chinese medicine, CV-23 is believed to regulate and strengthen the voice, throat, and neck. It is commonly used to treat throat and voice disorders, such as hoarseness, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and loss of voice. It is also thought to benefit the respiratory system, treating conditions such as asthma, cough, and bronchitis. In addition, CV-23 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can help to alleviate anxiety, stress, and emotional disorders. It may also be used to treat other conditions such as neck pain and stiffness, toothache, and facial paralysis. As with any acupuncture treatment, it is recommended to consult a licensed acupuncturist to determine if CV-23 is appropriate for your individual needs and health condition.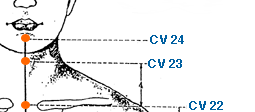
Cheng Jiang | Sauce Receptacle | Conception Vessel 24 | CV-24
Known as Cheng Jiang in Chinese, is an acupoint located on the midline of the chin, at the junction of the lower lip and the chin crease. Stimulation of CV-24 is believed to have a tonifying effect on the body's energy, particularly on the Qi (vital energy) of the mouth and throat. It can be used to treat conditions such as difficulty speaking or swallowing, sore throat, and toothache. In traditional Chinese medicine, CV-24 is considered a major point for regulating the flow of Qi in the body and promoting overall wellness. It is believed to have a tonifying effect on the mouth and throat, promoting mental clarity and enhancing cognitive function. CV-24 may also be useful for treating certain emotional imbalances such as anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. It is believed to work by regulating the nervous system, improving circulation, and balancing the body's energy. In addition, CV-24 is sometimes used for cosmetic purposes to promote facial rejuvenation and to reduce wrinkles and fine lines around the mouth and chin. As with any acupoint or treatment, it is recommended to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or qualified healthcare provider to determine if CV-24 is appropriate for your specific condition.
Pericarium Meridian
This meridian is commonly an extra ordinary meridian, though many will also place it under Fire Element.
Tian Chi | Celestial Pool | Pericardium 1 | PC-1
This is the first point of the Pericardium meridian. It is located on the chest. Specifically, it is located on the chest, 1 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) lateral to the nipple in the 4th intercostal space. PC-1 is used to treat various conditions related to the chest, heart, and lungs. It is commonly used to treat angina pectoris, palpitations, chest pain, asthma, cough, and other respiratory disorders. It is also used to treat emotional and mental disorders such as anxiety, insomnia, and depression. Additionally, PC-1 is sometimes used to treat pain and stiffness in the neck and upper back. Stimulating this acupoint is thought to regulate the flow of Qi and blood in the chest, regulate the heart rhythm, calm the mind, and improve respiration. However, it is important to note that acupressure or acupuncture should always be performed by a licensed practitioner.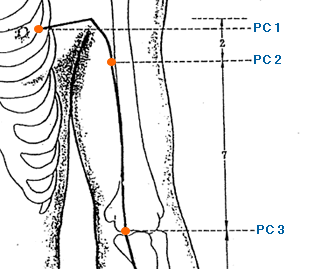
Tian Quan | Heavenly Spring | Pericardium 2 | PC-2
This is the second point on the Pericardium meridian. It is located on the upper arm, 2 cun inferior to the axillary fold, between the two heads of muscle biceps brachii.. Stimulating this point is said to be beneficial for a variety of conditions, including chest pain, heart palpitations, anxiety, depression, insomnia, and other emotional disorders. It is also thought to help regulate the function of the heart and lungs, and may be useful for conditions such as asthma and bronchitis. As with any acupuncture point, it is important to seek the guidance of a licensed acupuncturist or other qualified healthcare practitioner before attempting to use PC-2 or any other acupuncture point for therapeutic purposes.
Qu Ze | Marsh at the Bend | Pericardium 3 | PC-3
This is an acupuncture point located on the arm. Specifically, it is located on the medial aspect of the upper arm, three cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) below the axilla, on the line connecting the medial end of the transverse cubital crease and the anterior axillary fold. This point is often used to treat disorders of the heart and chest, as it is believed to have a calming and regulating effect on the heart. It is also commonly used to treat emotional disorders, such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Additionally, it can be used to alleviate wrist pain, numbness, and weakness. As with all acupuncture points, PC-3 should be used under the guidance of a licensed acupuncturist and in conjunction with appropriate medical treatment when necessary.
Xi Men | Xi Cleft Gate | Pericardium 4 | PC-4
This is an acupoint in the Pericardium Meridian. It is known as the Xi Men or Xi Cleft Gate point, which is a point along the meridian where the qi and blood are considered to converge. PC-4 is located on the anterior aspect of the forearm, about 5 cun proximal to the transverse wrist crease, between the tendons of the palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis muscles. Stimulation of PC-4 is believed to be effective in treating a wide range of conditions, including chest pain, palpitations, angina pectoris, insomnia, anxiety, depression, and irritability. In traditional Chinese medicine, the Pericardium Meridian is closely associated with the Heart Meridian, and as such, PC-4 is believed to be particularly effective in treating emotional and psychological disorders that have a strong impact on the heart, such as anxiety and depression. Additionally, PC-4 is thought to be beneficial for promoting circulation, easing tension in the chest, and balancing the body's energy systems. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Pericardium Meridian.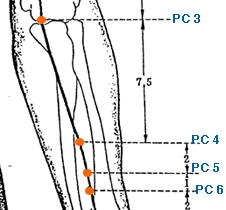
Jian Shi | Intermediary Courier | Pericardium 5 | PC-5
This is an acupoint located on the palm side of the forearm, approximately 3 cun (about 4 fingers) above the wrist crease. Stimulation of this point is believed to have a regulating effect on the Heart meridian, which can help to balance the heart rate and alleviate symptoms associated with heart problems such as chest pain, palpitations, and shortness of breath. It may also be used to address emotional issues such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. In addition to these conditions, PC-5 is also commonly used to treat pain and stiffness in the wrist and forearm, as well as conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and tennis elbow.
Nei Guan | Internal Barrier | Pericardium 6 | PC-6
This is a commonly used acupuncture point located on the Pericardium Meridian of the hand. Its Chinese name is Neiguan, which translates to Internal Barrier. Location: PC-6 is located on the palm side of the forearm, about two finger widths up from the wrist crease, between the tendons of the palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis muscles. It is a relatively easy point to locate and is often used by acupuncturists for various conditions. Illnesses and conditions: PC-6 is traditionally used for the treatment of a wide range of conditions, including nausea, vomiting, chest pain, anxiety, insomnia, palpitations, and carpal tunnel syndrome. It is also believed to help regulate the heart and improve circulation, making it useful in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, PC-6 is often used in combination with other points to relieve pain, promote relaxation, and reduce stress. PC-6 is one of the most commonly used acupuncture points and is often included in treatments for many different conditions.
Da Ling | Great Mound | Pericardium 7 | PC-7
Known as Da Ling, is an acupuncture point that is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat a variety of conditions. The point is located on the wrist. Specifically, it is located on the palmar aspect of the wrist, between the tendons of the palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis muscles, approximately 1.5 cun (a unit of measurement in acupuncture, approximately equivalent to the width of the patient's thumb at the proximal interphalangeal joint) proximal to the wrist crease. In traditional Chinese medicine, PC-7 is believed to regulate the flow of qi, or vital energy, and blood in the body, and to calm the spirit. It is commonly used to treat emotional imbalances, such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. It is also used to treat conditions that are believed to be caused by an imbalance in the heart, such as palpitations, chest pain, and poor circulation. PC-7 is also used to treat a variety of other conditions, including digestive disorders, respiratory disorders, and musculoskeletal pain. It is sometimes used in combination with other acupuncture points to treat conditions such as headaches, menstrual disorders, and carpal tunnel syndrome. As with all acupuncture treatments, it is important to consult with a licensed and qualified practitioner to determine if PC-7 is an appropriate treatment for your individual needs.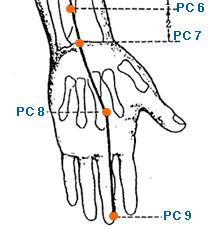
Lao Gong | Labor Palace | Pericardium 8 | PC-8
This is one of the acupuncture points in traditional Chinese medicine that is used to treat various conditions. Its Chinese name is Laogong, which means Labor Palace. Location: PC-8 is located on the palm side of the hand, in the center of the palm, in the depression that appears when the fist is clenched. Indications: PC-8 is commonly used to treat heart problems, such as palpitations, chest pain, and angina. It is also believed to be helpful for treating emotional disorders, such as anxiety, insomnia, and depression. In addition, PC-8 is sometimes used to relieve pain, particularly in the chest and throat, as well as to treat digestive disorders, such as nausea, vomiting, and indigestion. PC-8 is often used in conjunction with other acupuncture points, as part of a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual's specific needs. As with any medical treatment, it is important to consult a licensed acupuncturist before undergoing acupuncture therapy.
Zhong Chong | Central Hub | Pericardium 9 | PC-9
Known as Zhong Chong, is an acupoint on the Pericardium Meridian. It is located at the tip of the middle finger, near the nail bed. Stimulating PC-9 is said to help with a variety of conditions related to the pericardium, which is responsible for protecting the heart. This includes chest pain, palpitations, and heart palpitations. PC-9 is also said to help with mental and emotional issues such as anxiety, insomnia, and depression. In traditional Chinese medicine, PC-9 is believed to be a powerful point for restoring balance to the mind and body. It is often used in combination with other acupoints to treat a variety of conditions, and can be stimulated using acupuncture needles, acupressure, or other techniques.
Triple Heater Meridian
This meridian is commonly am extra ordinary meridian, though many place under the Fire Element.
Guan Chong | Passage Hub | Triple Heater 1 | TH-1
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) located 1 cun posterior to the corner of the nail on the ulnar side of the ring finger. Stimulation of TH-1 is said to be helpful for a variety of conditions, including pain and numbness in the arm and hand, tremors, sweating, fever, and sore throat. It is also thought to be beneficial for emotional imbalances such as anxiety, depression, and stress. TH-1 is believed to have a regulating effect on the flow of Qi in the chest and upper body, which may help to alleviate some of the physical and emotional symptoms associated with these conditions. As with all acupuncture points, TH-1 should only be stimulated by a qualified practitioner using sterile needles to reduce the risk of infection or injury.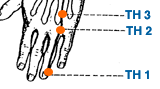
Ye Men | Humor Gate | Triple Heater 2 | TH-2
This is an acupuncture point located on the back of the hand, on the dorsal aspect, in the depression between the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones, proximal to the metacarpophalangeal joint. It is also sometimes referred to as Inner Gate. Stimulation of TH-2 is believed to have a wide range of therapeutic effects, including promoting the flow of qi, relieving pain, regulating the Triple Heater or San Jiao, calming the mind, and treating various conditions related to the upper body. It is commonly used in the treatment of pain and stiffness in the neck and shoulder, arm and elbow pain, headaches, toothaches, and sore throat. In traditional Chinese medicine, the Triple Heater refers to a functional system of the body that includes the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. It is responsible for the circulation and distribution of qi and fluids throughout the body, as well as regulating body temperature. Stimulating TH-2 is thought to help regulate this system and promote balance and harmony throughout the body.
Zhong Zhu | Central Islet | Triple Heater 3 | TH-3
This is a point located on the forearm, about 1.5 cun (finger widths) proximal to the wrist crease, on the radial side of the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle, at the midpoint of the transverse crease of the wrist. It is important to receive acupuncture treatment from a licensed and trained healthcare provider. TH-3 is commonly used in acupuncture and acupressure to treat various conditions such as shoulder pain, arm and elbow pain, neck pain, and headaches. It is known to be helpful in relieving symptoms associated with gastrointestinal disorders such as diarrhea, constipation, and indigestion. Additionally, TH-3 is believed to be useful in treating conditions like anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Stimulating TH-3 is also said to help with vision problems, tinnitus, and toothache. However, it is important to note that TH-3 should not be used during pregnancy as it may cause contractions. It is always recommended to consult a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare provider before using any acupoint.
Yang Chi | Yang Pool | Triple Heater 4 | TH-4
This is an acupuncture point located on the dorsum of the hand between the 4th and 5th metacarpal bones, in the depression that is proximal to the 5th metacarpophalangeal joint when the fingers are flexed. It is known as Yang Chi. Stimulating TH-4 is believed to be effective in treating conditions such as wrist pain, thumb pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, arm pain, and elbow pain. It can also be used to treat headaches, migraines, facial paralysis, neck stiffness, and toothache. In traditional Chinese medicine, TH-4 is considered to be a point that regulates the flow of Qi and blood in the body and promotes the smooth movement of energy in the channels.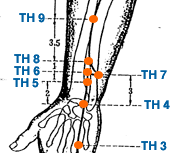
Wai Guan | Outer Barrier | Triple Heater 5 | TH-5
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine that is commonly used to treat a variety of conditions. It is known as the Waiguan point in Chinese, which translates to Outer Barrier Location: TH-5 is located on the outer side of the forearm, about 2 inches (or 3 finger-widths) above the wrist crease. It is located in the depression between the two tendons (the muscle bellies of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis). Uses: TH-5 is used to treat a variety of conditions, including wrist pain, hand and arm pain, arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and tennis elbow. It is also believed to be effective in treating headaches and migraines. Additionally, TH-5 is used to improve the function of the immune system, promote relaxation, and relieve stress and anxiety. It can be stimulated through acupuncture, acupressure, or by applying pressure with the fingers. However, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist before using this point for self-treatment.
Zhigou | Branch Ditch | Triple Heater 6 | TH-6
This is an acupuncture point in the Triple Heater or San Jiao meridian. It is known as Zhigou. The point is located on the dorsal aspect of the forearm, 3 cun above the transverse crease of the wrist, on the line joining TH-5 and the olecranon, in the depression between the radius and ulna bones. TH-6 is commonly used to treat various conditions such as wrist pain, arm pain, and elbow pain. It is also believed to help with conditions such as migraine headaches, anxiety, and depression. In traditional Chinese medicine, this point is thought to regulate the flow of Qi in the Triple Heater meridian, which governs the functions of the upper, middle, and lower parts of the body. Therefore, it is often used to treat disorders in these areas. Additionally, TH-6 is considered to be a point that harmonizes the functions of the Triple Heater and benefits the joints. It is often used in combination with other acupuncture points to enhance its therapeutic effects.
Hui Zong | Convergence and Gathering | Triple Heater 7 | TH-7
This is an acupoint in Traditional Chinese Medicine. It is located on the wrist, in the depression between the ulnar styloid process and the triquetral bone. In TCM, TH-7 is believed to be an important point for treating a variety of conditions related to the arm, shoulder, and neck, such as pain, numbness, and weakness. It is also used to treat disorders related to the head and face, such as headaches, facial paralysis, and toothache. Additionally, TH-7 is sometimes used to treat emotional issues, such as depression and anxiety. This acupoint can be stimulated by massage, acupuncture, or acupressure to improve the flow of qi (life force energy) through the meridians and bring balance to the body. As with all acupressure or acupuncture points, it is important to seek guidance from a qualified practitioner before attempting self-treatment. This specific acupoint is also the Alarm point of the Triple Heater Meridian.
San Yang Luo | Three Yang Connection | Triple Heater 8 | TH-8
This is an acupuncture point that is located on the forearm, between the radius and ulna bones. More specifically, it is found on the line connecting TH-7 and TH-9, 3 cun proximal to the wrist crease. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), TH-8 is believed to have therapeutic effects on the tendons and muscles of the forearm, wrist and hand, making it a commonly used point for conditions such as tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome, and other wrist and hand pain. TH-8 is known to be helpful in treating headaches, migraines, and eye conditions such as conjunctivitis and redness. Stimulating TH-8 with acupuncture or acupressure may help to regulate the flow of Qi, or energy, along the meridian that runs through the arm. It may also have a relaxing effect on the muscles and tendons in the area, reducing pain and inflammation. As with any acupuncture point, it should only be stimulated by a licensed acupuncturist or under their guidance.
Si Du | Four Rivers | Triple Heater 9 | TH-9
This is an acupuncture point located on the forearm, at the level of the radial styloid process (the bony protrusion at the base of the thumb) and about 1.5 cun (finger widths) proximal to the wrist crease. It is important to receive acupuncture treatment from a licensed and trained healthcare provider. TH-9 is used to treat a variety of conditions, including headache, neck pain, and shoulder pain. It is also thought to be effective in treating eye disorders, such as redness, swelling, and pain. Additionally, TH-9 is used to regulate the body's energy flow and promote relaxation, making it useful in treating anxiety, insomnia, and other stress-related conditions. In traditional Chinese medicine, TH-9 is believed to help release heat and promote the flow of energy throughout the body, making it a valuable point for maintaining overall health and wellbeing.
Tian Jing | Celestial Well | Triple Heater 10 | TH-10
This is an acupuncture point that is known as Tian Jing, and it is located on the forearm, at the midpoint of the transverse cubital crease (the crease of the elbow). It is important to receive acupuncture treatment from a licensed and trained healthcare provider. This acupoint is commonly used to treat various disorders of the upper limb, including pain, swelling, and weakness of the wrist and hand. It is also used to alleviate shoulder pain, neck pain, and headache. In addition, TH-10 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can be used to treat emotional issues such as anxiety and insomnia. Some practitioners also use TH-10 for the treatment of digestive disorders, such as nausea and vomiting, as well as respiratory disorders such as cough and asthma. However, more research is needed to fully understand the effects of TH-10 on these conditions.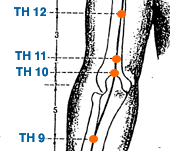
Qing Leng Yuan | Clear Cold Abyss | Triple Heater 11 | TH-11
Known as Qing Leng Yuan in Chinese, is an important point in Traditional Chinese Medicine located on the elbow. Specifically, it is located on the lateral end of the transverse cubital crease, at the midpoint of the line connecting the olecranon process of the ulna and the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. This acupoint is commonly used to treat a wide range of conditions related to the upper body, including pain, stiffness, and weakness in the elbow, forearm, wrist, and hand. It is also used to treat conditions such as tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome, and arthritis of the elbow and wrist. In addition, TH-11 can help to relieve headaches, neck pain, and shoulder pain, and is often used as a supportive treatment for respiratory conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and coughs. Stimulating TH-11 is believed to have a regulatory effect on the flow of Qi, or vital energy, throughout the body. This point is considered to be a powerful tonifying point for the Qi and blood, and is commonly used in acupuncture and acupressure to help balance and harmonize the body's energy systems. Overall, TH-11 is a versatile and effective point for addressing a wide range of physical and emotional imbalances throughout the body.
Xiao Lou | Dispersing Riverbed | Triple Heater 12 | TH-12
This one is located on the forearm. It is located on the transverse cubital crease, in the depression between the olecranon of the ulna and the medial epicondyle of the humerus. TH-12 is commonly used to treat pain and stiffness in the elbow and arm, as well as wrist pain and carpal tunnel syndrome. It is also used to treat conditions such as tennis elbow, golfer's elbow, and arthritis in the elbow and wrist. Additionally, TH-12 can be used to treat headaches, migraines, and neck pain. It is believed that stimulation of this acupoint helps to regulate the flow of Qi and blood in the arm and upper body, leading to a reduction in pain and an improvement in overall health.
Nao Hui | Upper Arm Convergence | Triple Heater 13 | TH-13
This one is located 3 cun below TH 14 on the posterior border of the deltoid muscle on line joining TH 14 and the olecranon. Stimulating TH-13 is believed to benefit conditions such as pain and stiffness in the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. It may also help relieve arm numbness, swelling, and weakness caused by neurological conditions such as stroke or peripheral neuropathy. Additionally, TH-13 may be used to alleviate symptoms associated with stress, anxiety, and depression. However, it's important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare practitioner before using TH-13 or any other acupuncture point to treat a specific condition.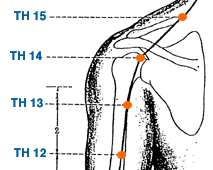
Jian Liao | Shoulder Bone Hole | Triple Heater 14 | TH-14
This is an acupuncture point located on the upper arm, on the line connecting the shoulder and the elbow, at the midpoint of the deltoid muscle. It is known as Jian Liao. TH-14 is primarily used to treat pain and stiffness in the shoulder and upper arm. It is also useful in treating conditions such as frozen shoulder, tennis elbow, and carpal tunnel syndrome. TH-14 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and can be used to treat anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Additionally, it may be used to address facial paralysis, toothache, and sore throat. As with all acupuncture points, it is important to seek treatment from a licensed acupuncturist who can evaluate your specific condition and determine if TH-14 is an appropriate treatment option.
Tian Liao | Celestial Bone Hole | Triple Heater 15 | TH-15
This is an acupoint used in traditional Chinese medicine. It is located on the upper arm, specifically on the midpoint between the acromion process (top of the shoulder blade) and the olecranon process (tip of the elbow), in a depression at the top of the humerus bone when the arm is slightly flexed. It is approximately 4 cun (finger widths) below the shoulder joint and 1 cun above TE14. TH-15 is commonly used to treat shoulder and arm pain, as well as stiffness and limited range of motion in the shoulder joint. It is also believed to help relieve headaches, neck pain, and facial paralysis. In addition, TH-15 is thought to benefit emotional disorders such as anxiety and depression by helping to regulate the flow of qi, or vital energy, throughout the body.
Tian You | Celestial Window | Triple Heater 16 | TH-16
This is an acupoint in the Triple Heater meridian. It is located on the lateral side of the neck, in the depression just posterior to the angle of the mandible, between the sternal and clavicular heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. TH-16 is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat a range of conditions related to the head, face, and neck, such as neck pain, stiff neck, headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, toothache, and facial paralysis. It is also believed to have a calming effect on the mind and emotions, and is sometimes used to treat anxiety and insomnia. To stimulate this acupoint, gentle pressure or massage can be applied with the fingers for a few minutes several times a day. It is important to note that acupressure should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment, and anyone with a serious or chronic condition should consult with a qualified healthcare practitioner.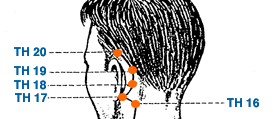
Yi Feng | Wind Screen | Triple Heater 17 | TH-17
This one is located in the depression anterior and inferior to the tragus of the ear. To locate this point, one can move the finger to feel the depression when the mouth is opened. It is the endpoint of the Triple Heater Meridian, known as the San Jiao Meridian. Acupoint TH-17 is primarily used to treat various ear disorders, including tinnitus (ringing in the ears), deafness, earache, and otorrhea (discharge from the ear). It is also believed to help with facial paralysis, facial spasms, and toothache. In traditional Chinese medicine, this point is thought to regulate the Qi and blood in the ear region and promote the smooth flow of the Triple Heater Meridian. Stimulation of TH-17 is typically done using acupuncture needles, acupressure, or moxibustion, a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves burning dried mugwort on or near the skin at the acupoint. As with any acupuncture treatment, it is important to consult with a licensed practitioner before attempting to stimulate this point.
Qi Mai | Spasm Vessel | Triple Heater 18 | TH-18
This one is a point located on the side of the neck. Specifically, it is located in the depression below the mastoid process, at the midpoint of the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. This point is traditionally used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) to treat conditions related to the throat and neck, such as sore throat, laryngitis, and stiff neck. It is also believed to help with toothache, facial paralysis, and jaw pain. In addition, TH-18 is thought to have a calming effect on the mind, making it useful in the treatment of anxiety, insomnia, and other emotional imbalances. Stimulating TH-18 can be done with gentle pressure, massage, or acupuncture needles. As with all acupuncture points, it should only be stimulated by a licensed and qualified practitioner of TCM. It is important to note that acupuncture should be used in conjunction with, not as a substitute for, conventional medical treatment when appropriate.
Lu Xi | Skull Rest | Triple Heater 19 | TH-19
This is an acupoint in the Triple Heater meridian of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). It is known as Luxi in Chinese. Location: TH-19 is located on the lateral aspect of the neck, at the midpoint of the transverse process of the second cervical vertebra (C2). Indications: TH-19 is commonly used for disorders related to the neck and throat, such as sore throat, difficulty swallowing, neck pain, and stiffness. It is also indicated for conditions like tinnitus, deafness, and ear infections. In TCM, TH-19 is believed to regulate the flow of Qi in the Triple Energizer meridian, which governs the upper, middle, and lower portions of the body, as well as the functions of the organs in these areas. Therefore, TH-19 is thought to be useful in treating conditions that involve the upper part of the body, including the head, face, neck, and throat. Note: It is important to seek advice from a qualified practitioner before using acupressure or acupuncture for any health conditions.
Jiao Sun | Angle Vertex | Triple Heater 20 | TH-20
This one is located on the head, in the depression at the midpoint of the upper border of the auricle (external part of the ear), approximately level with the superior margin of the eyebrow. It is important to receive acupuncture treatment from a licensed and trained healthcare provider. TH-20 is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat a variety of conditions related to the face and head. It is often used to alleviate symptoms of sinusitis, nasal congestion, rhinitis, and facial paralysis. This acupoint is also believed to be effective in relieving facial pain, headaches, toothaches, and eye disorders such as conjunctivitis and visual disturbances. Additionally, TH-20 is thought to have an effect on the emotions and is sometimes used to calm the mind and alleviate stress and anxiety.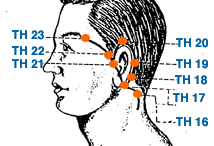
Er Men | Ear Gate | Triple Heater 21 | TH-21
This is an acupuncture point located in front of the ear, in the depression in front of the tragus of the ear (the small pointed flap of cartilage in front of the ear canal) TH-21 is primarily used for treating disorders related to the ears and eyes, such as tinnitus, deafness, vertigo, and blurred vision. It can also help alleviate pain in the temporal region, headaches, and toothache. In traditional Chinese medicine, TH-21 is believed to have a calming effect on the mind and spirit, making it useful for treating emotional and mental conditions such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. This point is contraindicated for needling in pregnant women, and should be used with caution in patients with bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulant medication. As with all acupuncture points, it should only be needled by a licensed and trained practitioner.
Er He Liao | Harmony Bone Hole | Triple Heater 22 | TH-22
This one is known as Harmony Bone Hole or Er He Liao in Chinese. TH-22 is located on the side of the face, in front of the ear and above TH21 (Er Men). TH-22 is often used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat disorders related to the ears, such as tinnitus, deafness, earache, and inflammation of the ear. It can also be used to alleviate pain and stiffness in the neck and shoulder areas. In addition, TH-22 can help relieve symptoms of temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ) and facial paralysis. To stimulate TH-22, acupuncturists typically use thin needles inserted perpendicularly to a depth of about 0.5-1 cun (approximately 1-2 cm) into the skin. Moxibustion, a technique that involves burning dried mugwort near the skin, may also be used to warm and stimulate this acupoint.
Si Zhu Kong | Four Bamboo Space | Triple Heater 23 | TH-23
This one is an acupuncture point located on the side of the face, in the depression anterior to the supratragic notch (the notch above the tragus of the ear). TH-23 is commonly used to treat headaches, migraines, facial pain, twitching eyelids, and eye pain. It is also believed to help relieve sinus congestion, nasal discharge, and other respiratory problems. Some practitioners also use this point for emotional imbalances, such as anxiety, anger, and irritability. To stimulate this point, gentle pressure can be applied with the fingertips or a rounded acupressure tool for about 1-2 minutes while taking deep breaths. It is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist or healthcare provider to determine if TH-23 is appropriate for an individual's specific condition.



